Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive manufacturing tasks by automating workflows, increasing efficiency and reducing human error. Predictive maintenance leverages IoT sensors and data analytics to forecast equipment failures, minimizing downtime and optimizing asset performance. Explore how integrating RPA and predictive maintenance can transform manufacturing operations and boost productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Predictive Maintenance is crucial in manufacturing because RPA streamlines repetitive tasks by automating workflows, while Predictive Maintenance uses data analytics and IoT sensors to anticipate equipment failures and minimize downtime. Properly leveraging RPA enhances operational efficiency in administrative and production processes, whereas Predictive Maintenance extends machinery life and reduces costly unplanned outages on the factory floor. Manufacturers that distinguish these technologies can allocate resources effectively, optimize productivity, and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Clear differentiation drives strategic implementation, supporting data-driven decision-making and smart factory initiatives.
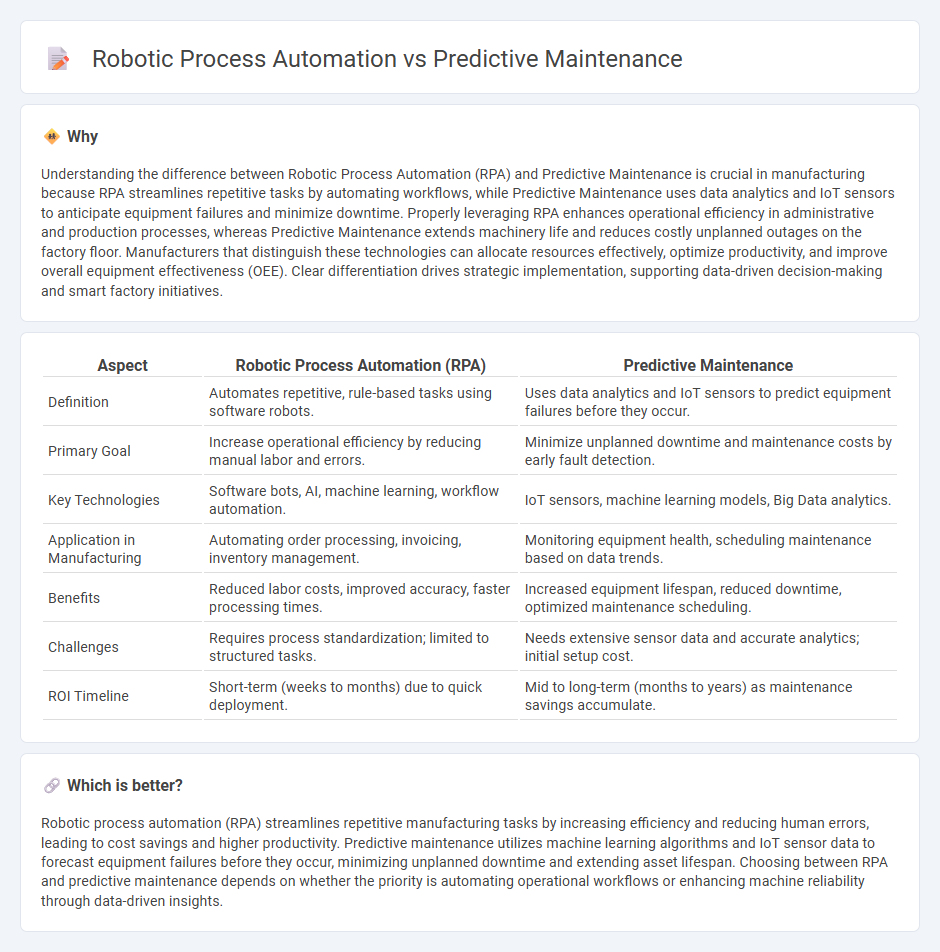
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Predictive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automates repetitive, rule-based tasks using software robots. | Uses data analytics and IoT sensors to predict equipment failures before they occur. |
| Primary Goal | Increase operational efficiency by reducing manual labor and errors. | Minimize unplanned downtime and maintenance costs by early fault detection. |
| Key Technologies | Software bots, AI, machine learning, workflow automation. | IoT sensors, machine learning models, Big Data analytics. |
| Application in Manufacturing | Automating order processing, invoicing, inventory management. | Monitoring equipment health, scheduling maintenance based on data trends. |
| Benefits | Reduced labor costs, improved accuracy, faster processing times. | Increased equipment lifespan, reduced downtime, optimized maintenance scheduling. |
| Challenges | Requires process standardization; limited to structured tasks. | Needs extensive sensor data and accurate analytics; initial setup cost. |
| ROI Timeline | Short-term (weeks to months) due to quick deployment. | Mid to long-term (months to years) as maintenance savings accumulate. |
Which is better?
Robotic process automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive manufacturing tasks by increasing efficiency and reducing human errors, leading to cost savings and higher productivity. Predictive maintenance utilizes machine learning algorithms and IoT sensor data to forecast equipment failures before they occur, minimizing unplanned downtime and extending asset lifespan. Choosing between RPA and predictive maintenance depends on whether the priority is automating operational workflows or enhancing machine reliability through data-driven insights.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) integrates with predictive maintenance by automating data collection and analysis from machinery sensors, enabling real-time monitoring of equipment health. Predictive maintenance uses this data to forecast potential failures, minimizing downtime and optimizing manufacturing productivity. The synergy between RPA and predictive analytics enhances operational efficiency by streamlining maintenance scheduling and reducing unexpected disruptions.
Key Terms
Sensors (Predictive Maintenance)
Sensors in predictive maintenance continuously monitor equipment health by collecting real-time data on temperature, vibration, and pressure to identify potential failures before they occur. These IoT-enabled sensors enable proactive maintenance scheduling, reducing downtime and increasing operational efficiency. Explore how sensor technology transforms predictive maintenance strategies for more reliable industrial operations.
Machine Learning Algorithms (Predictive Maintenance)
Predictive maintenance leverages machine learning algorithms such as regression analysis, support vector machines, and neural networks to analyze sensor data and predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive tasks across business processes without inherently utilizing machine learning models, focusing instead on rule-based task execution. Explore how integrating advanced machine learning techniques enhances predictive maintenance systems and drives operational efficiency.
Workflow Automation (Robotic Process Automation)
Workflow Automation through Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive tasks by mimicking human interactions with digital systems, enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy in business processes. Predictive maintenance leverages data analytics and IoT sensors to forecast equipment failures and schedule timely interventions, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Discover how RPA can transform your workflow automation and drive productivity growth.
Source and External Links
What is Predictive Maintenance? - Predictive maintenance uses sensor data and machine learning to anticipate equipment failures, enabling maintenance only when necessary, which reduces downtime and maintenance costs by optimizing scheduling based on the actual condition of equipment rather than fixed schedules.
Predictive maintenance - Predictive maintenance estimates when maintenance is needed based on real-time equipment condition, allowing planned maintenance that prevents unexpected failures, increases equipment life, and improves safety and resource optimization.
What is Predictive Maintenance? Benefits, Challenges & ... - Predictive maintenance analyzes real-time data from vehicles or equipment to predict potential failures weeks in advance, improving uptime, reducing maintenance costs, and enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com