Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines repetitive manufacturing tasks by automating rule-based workflows, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical manufacturing systems, enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and predictive maintenance for optimized operations. Explore how integrating RPA and Digital Twin can transform manufacturing processes for increased productivity and innovation.
Why it is important
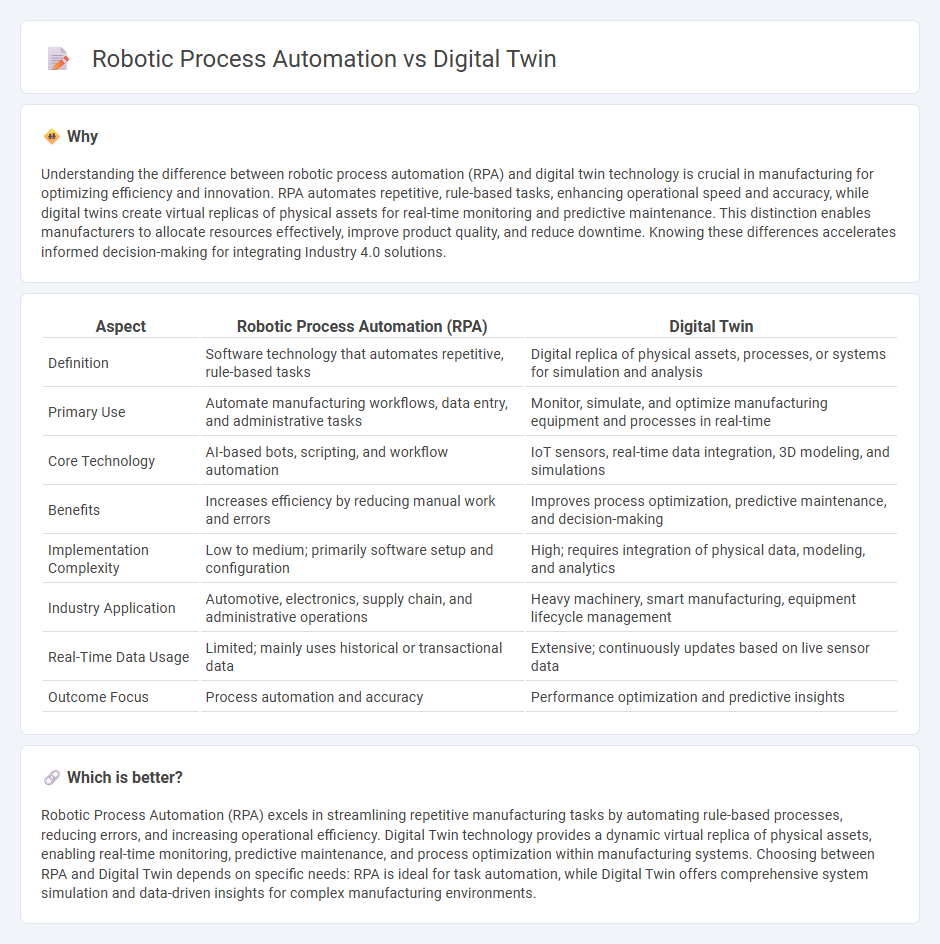
Understanding the difference between robotic process automation (RPA) and digital twin technology is crucial in manufacturing for optimizing efficiency and innovation. RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks, enhancing operational speed and accuracy, while digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This distinction enables manufacturers to allocate resources effectively, improve product quality, and reduce downtime. Knowing these differences accelerates informed decision-making for integrating Industry 4.0 solutions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software technology that automates repetitive, rule-based tasks | Digital replica of physical assets, processes, or systems for simulation and analysis |
| Primary Use | Automate manufacturing workflows, data entry, and administrative tasks | Monitor, simulate, and optimize manufacturing equipment and processes in real-time |
| Core Technology | AI-based bots, scripting, and workflow automation | IoT sensors, real-time data integration, 3D modeling, and simulations |
| Benefits | Increases efficiency by reducing manual work and errors | Improves process optimization, predictive maintenance, and decision-making |
| Implementation Complexity | Low to medium; primarily software setup and configuration | High; requires integration of physical data, modeling, and analytics |
| Industry Application | Automotive, electronics, supply chain, and administrative operations | Heavy machinery, smart manufacturing, equipment lifecycle management |
| Real-Time Data Usage | Limited; mainly uses historical or transactional data | Extensive; continuously updates based on live sensor data |
| Outcome Focus | Process automation and accuracy | Performance optimization and predictive insights |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) excels in streamlining repetitive manufacturing tasks by automating rule-based processes, reducing errors, and increasing operational efficiency. Digital Twin technology provides a dynamic virtual replica of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization within manufacturing systems. Choosing between RPA and Digital Twin depends on specific needs: RPA is ideal for task automation, while Digital Twin offers comprehensive system simulation and data-driven insights for complex manufacturing environments.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) integrates with Digital Twin technology by enabling the automated simulation of manufacturing processes, enhancing precision and efficiency in production workflows. Digital Twins provide real-time data and virtual models that RPA uses to execute tasks with minimal human intervention, reducing errors and downtime. This connection supports predictive maintenance and process optimization, driving smarter factory operations and increased productivity.
Key Terms
Virtual Simulation
Digital twin technology creates a dynamic virtual replica of physical assets or processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance through immersive virtual simulation. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive tasks by mimicking human actions in software environments but lacks the capability for detailed virtual simulation and real-time scenario analysis. Explore how digital twins enhance virtual simulation to optimize decision-making and operational efficiency.
Process Automation
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical processes to simulate and optimize operations, enhancing real-time decision-making and predictive maintenance. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks in business workflows to increase efficiency and reduce human error. Explore how integrating digital twins with RPA can revolutionize process automation by combining simulation accuracy with task automation.
Real-time Data Integration
Digital twin technology offers dynamic, real-time data integration by creating a virtual replica of physical assets, enabling continuous monitoring and simulation for improved decision-making. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) primarily automates repetitive tasks without inherently supporting real-time data synchronization or complex system updates. Explore how integrating digital twins with RPA can maximize operational efficiency by leveraging real-time insights and automation.
Source and External Links
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated data-driven virtual representation of real-world entities and processes that synchronizes with the physical counterpart in real time, enhancing understanding, improvement, decision-making, and intervention through data, physics, and domain knowledge integration.
What Is a Digital Twin? | IBM - A digital twin is a virtual model that accurately reflects a physical object's lifecycle by using real-time sensor data, machine learning, and simulations to analyze performance and improve the original physical entity.
Digital twin - Wikipedia - A digital twin is a digital counterpart of a real-world physical product, system, or process, designed to simulate, monitor, and optimize it through adaptive models updated continuously with real-time data throughout its lifecycle.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com