Zero defect manufacturing focuses on producing flawless products by preventing defects through stringent quality control processes and error-proofing techniques, minimizing waste and rework. Continuous improvement emphasizes iterative enhancements in manufacturing processes, leveraging methodologies like Lean and Six Sigma to increase efficiency, reduce variability, and enhance product quality over time. Explore how integrating zero defect manufacturing with continuous improvement can drive operational excellence and maximize output quality.
Why it is important
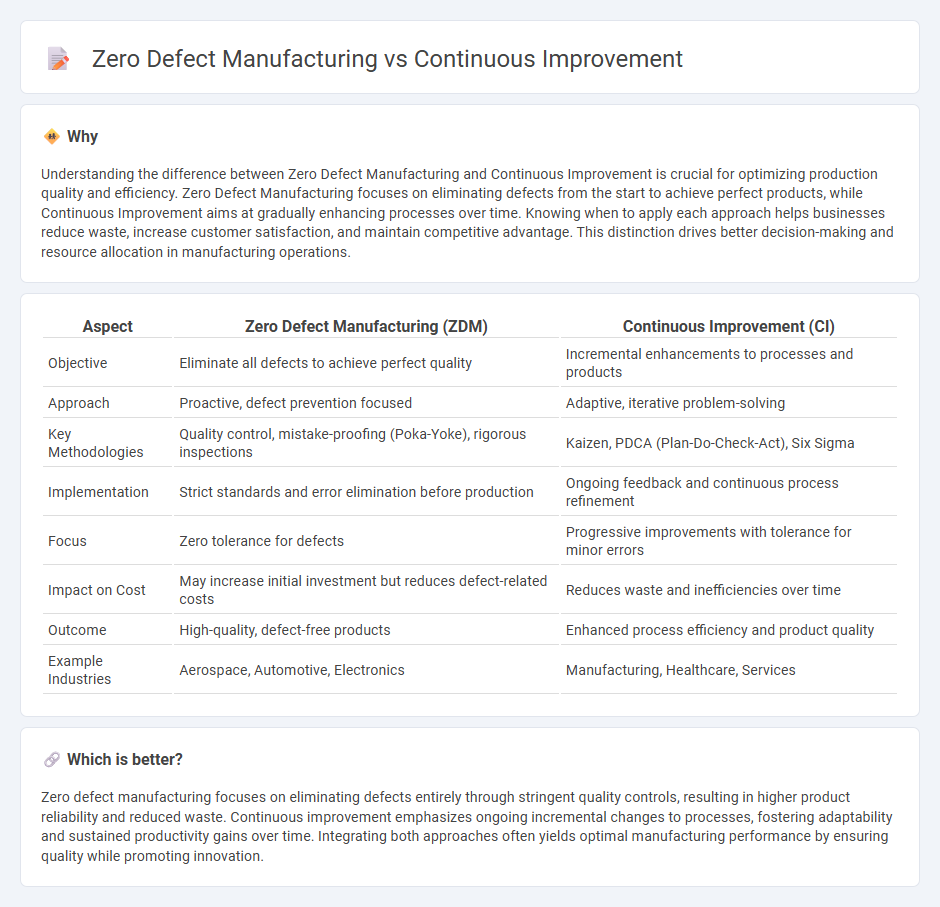
Understanding the difference between Zero Defect Manufacturing and Continuous Improvement is crucial for optimizing production quality and efficiency. Zero Defect Manufacturing focuses on eliminating defects from the start to achieve perfect products, while Continuous Improvement aims at gradually enhancing processes over time. Knowing when to apply each approach helps businesses reduce waste, increase customer satisfaction, and maintain competitive advantage. This distinction drives better decision-making and resource allocation in manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) | Continuous Improvement (CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Eliminate all defects to achieve perfect quality | Incremental enhancements to processes and products |
| Approach | Proactive, defect prevention focused | Adaptive, iterative problem-solving |
| Key Methodologies | Quality control, mistake-proofing (Poka-Yoke), rigorous inspections | Kaizen, PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act), Six Sigma |
| Implementation | Strict standards and error elimination before production | Ongoing feedback and continuous process refinement |
| Focus | Zero tolerance for defects | Progressive improvements with tolerance for minor errors |
| Impact on Cost | May increase initial investment but reduces defect-related costs | Reduces waste and inefficiencies over time |
| Outcome | High-quality, defect-free products | Enhanced process efficiency and product quality |
| Example Industries | Aerospace, Automotive, Electronics | Manufacturing, Healthcare, Services |
Which is better?
Zero defect manufacturing focuses on eliminating defects entirely through stringent quality controls, resulting in higher product reliability and reduced waste. Continuous improvement emphasizes ongoing incremental changes to processes, fostering adaptability and sustained productivity gains over time. Integrating both approaches often yields optimal manufacturing performance by ensuring quality while promoting innovation.
Connection
Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) and Continuous Improvement share a fundamental connection through their mutual emphasis on quality enhancement and waste reduction in production processes. ZDM targets the elimination of defects at every stage, requiring a systematic approach that continuously analyzes and refines workflows, which aligns with the Continuous Improvement philosophy of ongoing process optimization. Implementing tools like Six Sigma or Total Quality Management (TQM) facilitates the integration of ZDM principles within a continuous improvement framework, driving operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Key Terms
Kaizen
Continuous Improvement emphasizes incremental enhancements by fostering a culture of Kaizen, where employees consistently contribute to process optimizations. Zero Defect Manufacturing aims to eliminate errors entirely through rigorous quality management systems, setting a standard for defect-free production. Explore how integrating Kaizen into these methodologies can elevate manufacturing excellence and operational efficiency.
Six Sigma
Continuous Improvement in Six Sigma emphasizes incremental process enhancements by identifying and eliminating defects through DMAIC methodology, fostering long-term operational excellence. Zero Defect Manufacturing aims for flawless production by preventing errors from the outset, striving for near-perfect quality levels with a proactive defect prevention mindset. Explore the detailed strategies and benefits of both approaches in the Six Sigma framework to elevate your manufacturing quality.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Continuous Improvement in Total Quality Management emphasizes iterative enhancements in processes to boost efficiency and product quality, leveraging methods like PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycles. Zero Defect Manufacturing aims for perfection by preventing defects through rigorous standards and error-proofing techniques such as poka-yoke and Six Sigma. Explore the differences and synergies between these TQM approaches to optimize your quality management strategy.
Source and External Links
Continual Improvement Process - This process involves ongoing efforts to enhance products, services, or processes through incremental or breakthrough improvements, focusing on efficiency and effectiveness.
Continuous Improvement Model - This model uses the PDCA cycle to continuously improve processes by identifying opportunities, implementing changes, checking results, and acting based on feedback.
Continuous Improvement aka "Kaizen" - This philosophy involves making small, incremental changes to eliminate waste and increase efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction, often linked to lean manufacturing principles.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com