Digital twin technology creates precise, real-time virtual replicas of physical manufacturing assets, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the physical environment, improving worker training and troubleshooting processes. Explore how integrating digital twins and augmented reality can revolutionize manufacturing workflows and productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital twin and augmented reality is crucial in manufacturing to optimize production processes and improve decision-making accuracy. Digital twins create a virtual replica of physical assets for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, while augmented reality overlays digital information onto the physical environment to enhance operator training and quality control. Leveraging these technologies correctly can lead to reduced downtime, increased efficiency, and more precise troubleshooting. Manufacturers who distinguish between these tools can implement targeted solutions that drive innovation and operational excellence.
Comparison Table
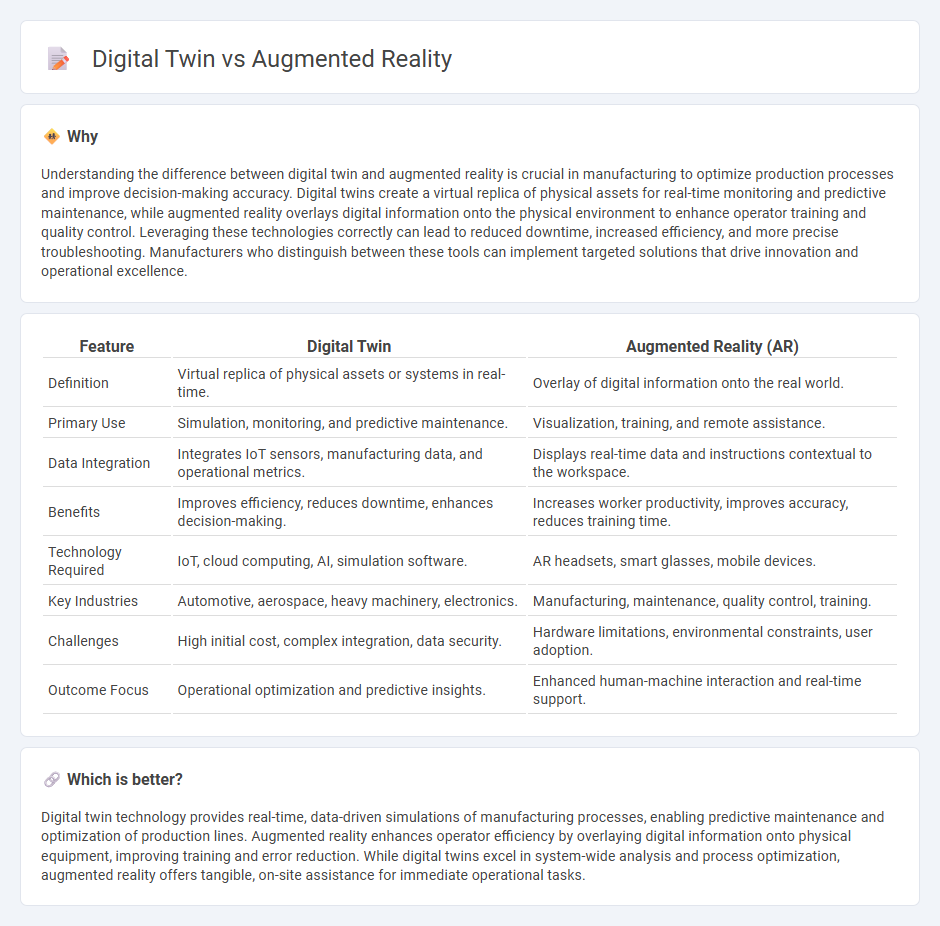
| Feature | Digital Twin | Augmented Reality (AR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets or systems in real-time. | Overlay of digital information onto the real world. |
| Primary Use | Simulation, monitoring, and predictive maintenance. | Visualization, training, and remote assistance. |
| Data Integration | Integrates IoT sensors, manufacturing data, and operational metrics. | Displays real-time data and instructions contextual to the workspace. |
| Benefits | Improves efficiency, reduces downtime, enhances decision-making. | Increases worker productivity, improves accuracy, reduces training time. |
| Technology Required | IoT, cloud computing, AI, simulation software. | AR headsets, smart glasses, mobile devices. |
| Key Industries | Automotive, aerospace, heavy machinery, electronics. | Manufacturing, maintenance, quality control, training. |
| Challenges | High initial cost, complex integration, data security. | Hardware limitations, environmental constraints, user adoption. |
| Outcome Focus | Operational optimization and predictive insights. | Enhanced human-machine interaction and real-time support. |
Which is better?
Digital twin technology provides real-time, data-driven simulations of manufacturing processes, enabling predictive maintenance and optimization of production lines. Augmented reality enhances operator efficiency by overlaying digital information onto physical equipment, improving training and error reduction. While digital twins excel in system-wide analysis and process optimization, augmented reality offers tangible, on-site assistance for immediate operational tasks.
Connection
Digital twin technology creates a virtual replica of physical manufacturing assets, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Augmented reality overlays digital information onto the physical environment, enhancing operator interaction with the digital twin for improved decision-making. Together, they optimize manufacturing processes by providing immersive insights and enabling proactive responses to machine performance and production anomalies.
Key Terms
Visualization
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing visualization by integrating interactive 3D models with physical environments in real-time. Digital twins create a virtual replica of a physical asset or system, enabling detailed visualization of performance, status, and simulations within a controlled digital environment. Explore the distinct visualization benefits of AR and digital twins to understand their applications across industries.
Simulation
Augmented reality (AR) enhances real-world environments by overlaying digital simulations, enabling users to interact with virtual objects in real time. Digital twin technology creates highly detailed, real-time virtual replicas of physical assets or systems for advanced simulation and predictive analysis. Explore further to understand how these simulation technologies transform industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and urban planning.
Data Integration
Augmented reality (AR) leverages real-time data integration from sensors and cameras to overlay virtual objects onto the physical environment, enhancing user interaction and situational awareness. Digital twins rely on extensive data integration from IoT devices, simulations, and historical records to create accurate, dynamic virtual replicas of physical assets for monitoring, analysis, and predictive maintenance. Explore the advanced data integration techniques that distinguish AR and digital twin technologies to fully understand their applications and benefits.
Source and External Links
Augmented reality - Wikipedia - Augmented reality (AR) overlays real-time 3D computer graphics onto the real world, blending digital content with the user's physical environment through devices like smartphones or headsets.
What is Augmented Reality? | IBM - AR integrates digital information in real time into a user's surroundings, using cameras and sensors on devices such as smartphones, tablets, or wearables to enhance perception without replacing reality.
What is augmented reality (AR)? | Definition from TechTarget - AR delivers visual, auditory, and other sensory information overlaid onto the real world via devices, altering the user's perception while keeping them grounded in their actual environment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com