Process mining utilizes data-driven analytics to visualize and optimize manufacturing workflows by extracting insights from event logs, enhancing real-time decision-making and operational transparency. Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and variability in manufacturing processes through statistical methods and DMAIC cycles, improving product quality and efficiency. Explore the differences and benefits of process mining and Six Sigma to elevate manufacturing performance.
Why it is important
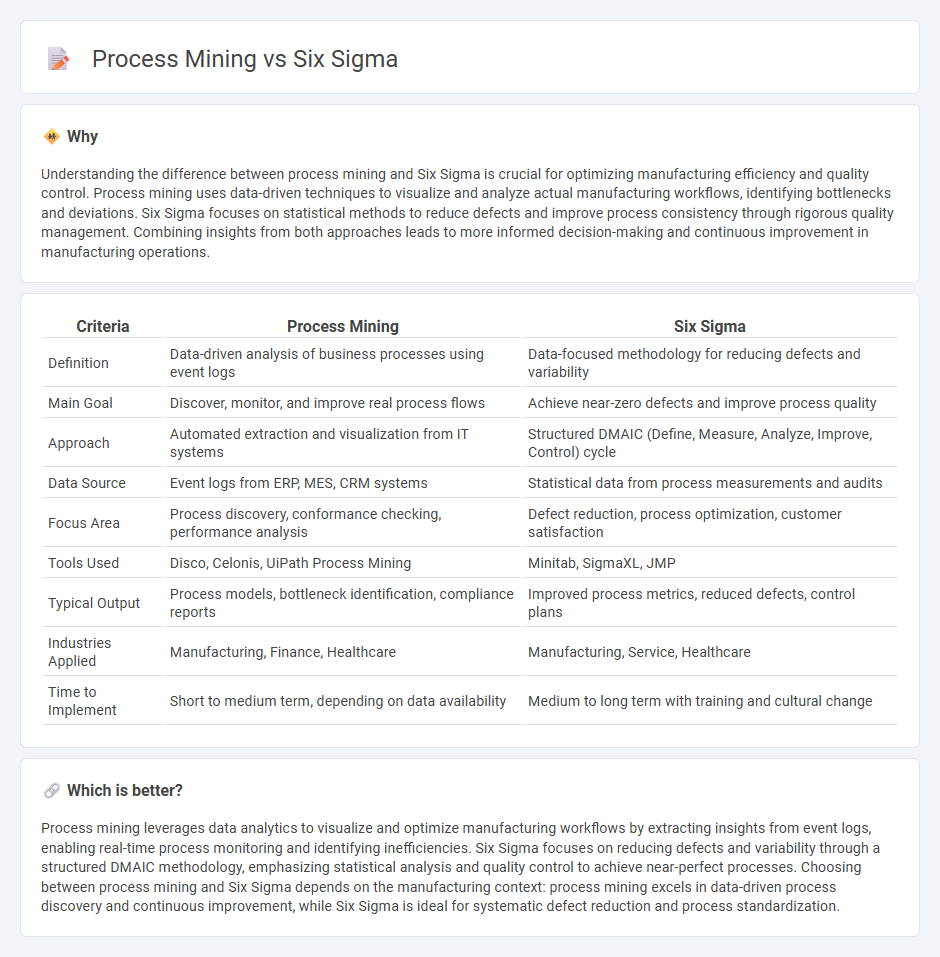
Understanding the difference between process mining and Six Sigma is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and quality control. Process mining uses data-driven techniques to visualize and analyze actual manufacturing workflows, identifying bottlenecks and deviations. Six Sigma focuses on statistical methods to reduce defects and improve process consistency through rigorous quality management. Combining insights from both approaches leads to more informed decision-making and continuous improvement in manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Process Mining | Six Sigma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data-driven analysis of business processes using event logs | Data-focused methodology for reducing defects and variability |
| Main Goal | Discover, monitor, and improve real process flows | Achieve near-zero defects and improve process quality |
| Approach | Automated extraction and visualization from IT systems | Structured DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) cycle |
| Data Source | Event logs from ERP, MES, CRM systems | Statistical data from process measurements and audits |
| Focus Area | Process discovery, conformance checking, performance analysis | Defect reduction, process optimization, customer satisfaction |
| Tools Used | Disco, Celonis, UiPath Process Mining | Minitab, SigmaXL, JMP |
| Typical Output | Process models, bottleneck identification, compliance reports | Improved process metrics, reduced defects, control plans |
| Industries Applied | Manufacturing, Finance, Healthcare | Manufacturing, Service, Healthcare |
| Time to Implement | Short to medium term, depending on data availability | Medium to long term with training and cultural change |
Which is better?
Process mining leverages data analytics to visualize and optimize manufacturing workflows by extracting insights from event logs, enabling real-time process monitoring and identifying inefficiencies. Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and variability through a structured DMAIC methodology, emphasizing statistical analysis and quality control to achieve near-perfect processes. Choosing between process mining and Six Sigma depends on the manufacturing context: process mining excels in data-driven process discovery and continuous improvement, while Six Sigma is ideal for systematic defect reduction and process standardization.
Connection
Process mining uncovers workflow inefficiencies by analyzing event logs, enabling data-driven decision-making in manufacturing operations. Six Sigma leverages these insights to apply statistical methods aimed at reducing defects and variability in production processes. Integrating process mining with Six Sigma accelerates continuous improvement by pinpointing root causes and optimizing quality control metrics.
Key Terms
DMAIC (Six Sigma)
Six Sigma's DMAIC framework--Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control--systematically improves processes by identifying defects and reducing variability through data-driven analysis. Process mining complements DMAIC by extracting insights from event logs to visualize workflows, detect bottlenecks, and uncover inefficiencies in real-time. Explore how integrating process mining with DMAIC enhances process optimization and operational excellence.
Event Logs (Process Mining)
Event logs are the core data source for process mining, capturing detailed records of business activities with timestamps, event types, and case identifiers, enabling comprehensive process visualization and analysis. Six Sigma relies on structured data and statistical methods to identify defects and optimize quality, but it lacks the granular real-time event data that process mining leverages for uncovering process inefficiencies. Explore how integrating Six Sigma with process mining can enhance process improvement by combining statistical rigor with actionable event log insights.
Process Optimization
Six Sigma emphasizes reducing process variation and improving quality through statistical analysis and DMAIC methodology, focusing heavily on defect reduction and efficiency enhancement. Process mining leverages data from event logs to visualize, analyze, and optimize actual process flows, uncovering bottlenecks and deviations that may not be visible through traditional methods. Explore how combining Six Sigma and process mining can drive comprehensive process optimization and elevate organizational performance.
Source and External Links
What is Lean Six Sigma? - ASQ - Six Sigma is a disciplined quality improvement method aimed at reducing process variation to eliminate defects, targeting 3.4 defects per million opportunities and improving customer satisfaction and business performance.
Six Sigma - Wikipedia - Introduced at Motorola in 1986, Six Sigma focuses on continuous efforts to stabilize and improve business and manufacturing processes by reducing variability, relying heavily on data-driven decision-making and management commitment.
What Is Six Sigma?: Transform Your Organization's Productivity - Six Sigma is a structured, data-driven methodology requiring leadership commitment and defined roles (such as Black Belts and Green Belts) to execute process improvements linked to strategic goals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com