Lattice structure design focuses on interconnected networks forming geometric patterns to optimize strength-to-weight ratios, commonly used in aerospace and biomedical applications. Cellular structure design involves repeating units with enclosed volumes, providing enhanced energy absorption and thermal insulation properties essential in automotive and construction industries. Explore the differences and applications of these designs to improve manufacturing outcomes.
Why it is important
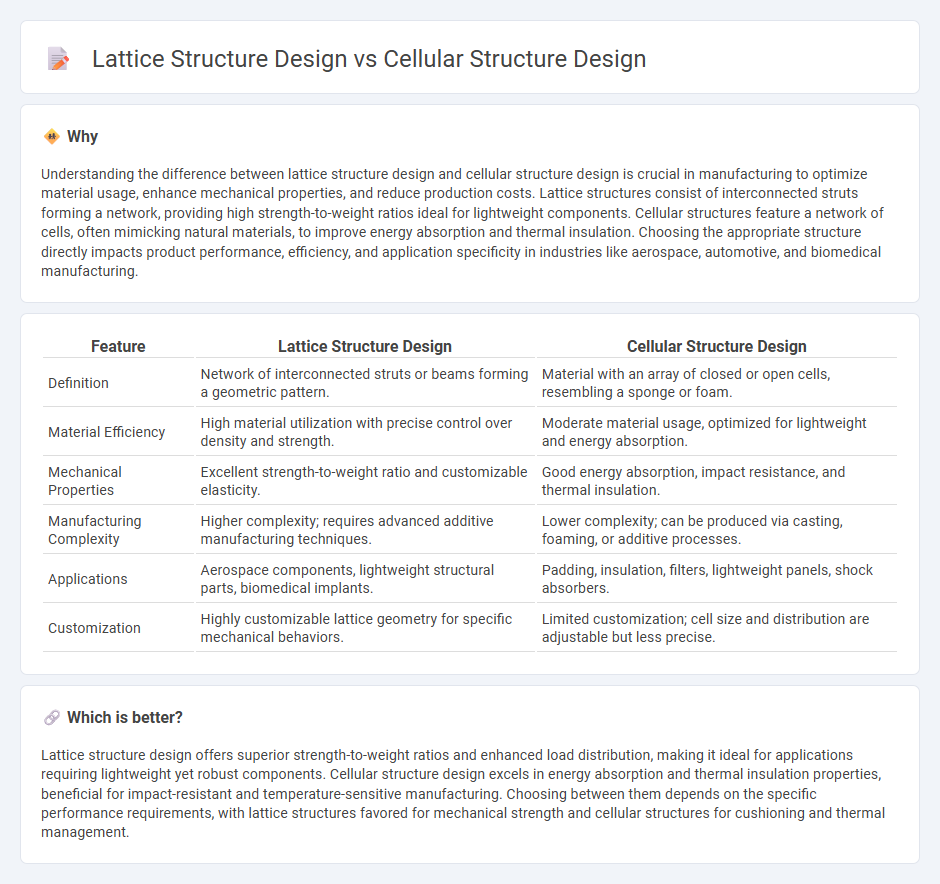
Understanding the difference between lattice structure design and cellular structure design is crucial in manufacturing to optimize material usage, enhance mechanical properties, and reduce production costs. Lattice structures consist of interconnected struts forming a network, providing high strength-to-weight ratios ideal for lightweight components. Cellular structures feature a network of cells, often mimicking natural materials, to improve energy absorption and thermal insulation. Choosing the appropriate structure directly impacts product performance, efficiency, and application specificity in industries like aerospace, automotive, and biomedical manufacturing.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lattice Structure Design | Cellular Structure Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of interconnected struts or beams forming a geometric pattern. | Material with an array of closed or open cells, resembling a sponge or foam. |
| Material Efficiency | High material utilization with precise control over density and strength. | Moderate material usage, optimized for lightweight and energy absorption. |
| Mechanical Properties | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio and customizable elasticity. | Good energy absorption, impact resistance, and thermal insulation. |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Higher complexity; requires advanced additive manufacturing techniques. | Lower complexity; can be produced via casting, foaming, or additive processes. |
| Applications | Aerospace components, lightweight structural parts, biomedical implants. | Padding, insulation, filters, lightweight panels, shock absorbers. |
| Customization | Highly customizable lattice geometry for specific mechanical behaviors. | Limited customization; cell size and distribution are adjustable but less precise. |
Which is better?
Lattice structure design offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced load distribution, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet robust components. Cellular structure design excels in energy absorption and thermal insulation properties, beneficial for impact-resistant and temperature-sensitive manufacturing. Choosing between them depends on the specific performance requirements, with lattice structures favored for mechanical strength and cellular structures for cushioning and thermal management.
Connection
Lattice structure design and cellular structure design are intrinsically connected through their focus on optimizing material distribution to enhance mechanical properties such as strength-to-weight ratio and energy absorption. Both design methodologies employ repetitive geometric patterns that reduce material use while maintaining structural integrity, making them essential in advanced manufacturing sectors like aerospace and biomedical implants. Computer-aided design (CAD) and additive manufacturing technologies play a critical role in fabricating these complex architectures with high precision and customizability.
Key Terms
Topology Optimization
Cellular structures feature interconnected voids and solid materials optimized for lightweight and high-strength applications, whereas lattice structures consist of repetitive unit cells designed for tailored mechanical performance through topology optimization. Topology optimization enhances both designs by strategically distributing material to maximize stiffness and minimize weight, crucial in aerospace, automotive, and biomedical industries. Discover how these advanced optimization techniques revolutionize structural efficiency and innovation.
Material Efficiency
Cellular structure design offers enhanced material efficiency by optimizing internal geometry to reduce weight while maintaining strength, widely used in aerospace and automotive industries for lightweight components. Lattice structure design focuses on repeating unit cells arranged in 3D patterns, maximizing load distribution and minimizing material usage, prominent in additive manufacturing for complex shapes. Explore how these innovative design methods transform material efficiency and product performance in cutting-edge engineering applications.
Mechanical Performance
Cellular structure design leverages hierarchical geometries to enhance energy absorption and impact resistance, while lattice structure design optimizes load distribution through periodic frameworks, resulting in high strength-to-weight ratios. Both approaches significantly improve mechanical performance by tailoring stiffness, strength, and deformation characteristics to specific applications such as aerospace and biomedical implants. Discover how advanced modeling and material selection further refine these designs for superior mechanical efficiency.
Source and External Links
Cellular Structures for Optimal Performance - Discusses cellular material structures like honeycombs and lattice structures that offer exceptional stiffness and strength at low weight, including new algorithms for creating uniform and conformal lattice meshes in 3D designs.
Design for Additive Manufacturing of Cellular Structures - CAD Journal - Presents a design method emphasizing unit cell approaches and optimization algorithms to improve stiffness and functional performance of cellular materials in additive manufacturing.
Functionally Graded Non-Periodic Cellular Structure Design and Optimization - Explores advanced non-periodic microstructure frameworks with smooth transitions for graded cellular designs, employing optimization for high-strength, lightweight parts with enhanced mechanical performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com