Dark factories utilize fully automated systems and robots to operate without human presence, significantly reducing labor costs and enhancing production efficiency. Remote monitoring leverages IoT sensors and real-time data analytics to oversee manufacturing processes from any location, ensuring rapid response to anomalies and optimized maintenance schedules. Discover how integrating dark factory concepts with remote monitoring can transform modern manufacturing for increased productivity and resilience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark factories and remote monitoring is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and workforce allocation. Dark factories operate fully automated without human presence, minimizing labor costs and errors, while remote monitoring involves human oversight through digital systems to ensure operational control and quick issue resolution. Recognizing these distinctions aids in implementing the appropriate technology infrastructure and investment strategies tailored to production goals. This knowledge supports enhanced productivity, safety, and scalability in modern manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
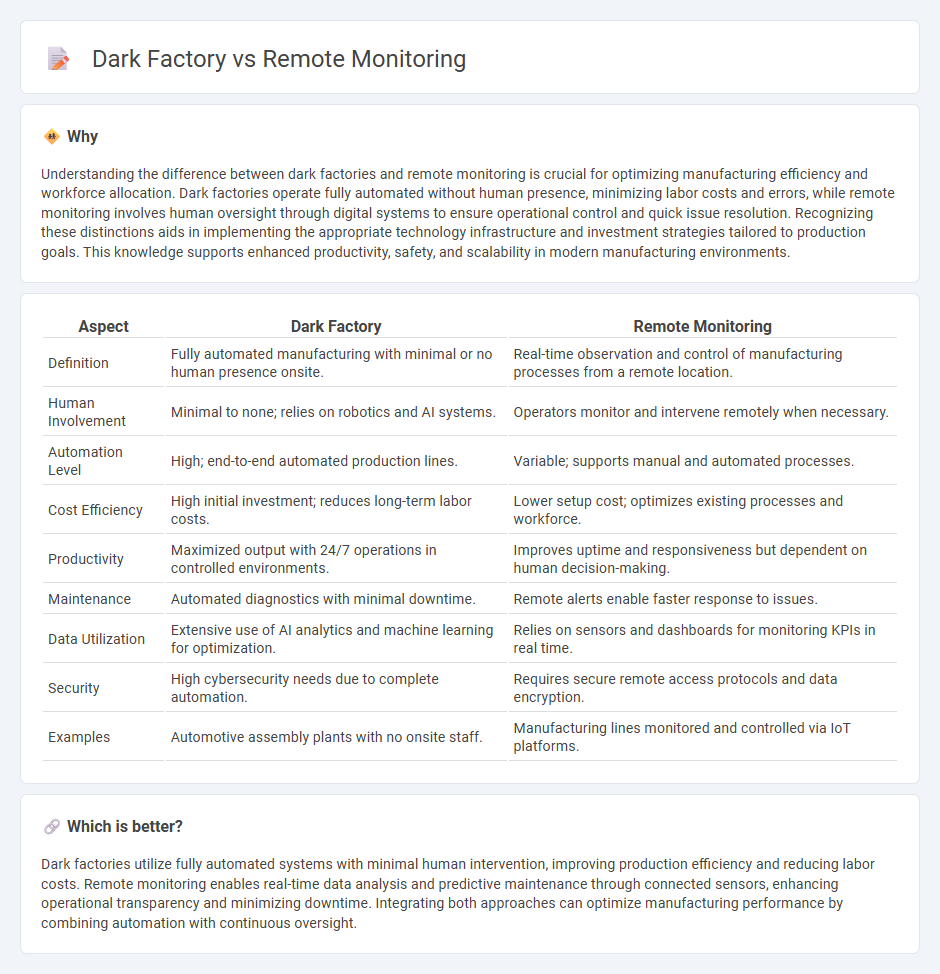
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Remote Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated manufacturing with minimal or no human presence onsite. | Real-time observation and control of manufacturing processes from a remote location. |
| Human Involvement | Minimal to none; relies on robotics and AI systems. | Operators monitor and intervene remotely when necessary. |
| Automation Level | High; end-to-end automated production lines. | Variable; supports manual and automated processes. |
| Cost Efficiency | High initial investment; reduces long-term labor costs. | Lower setup cost; optimizes existing processes and workforce. |
| Productivity | Maximized output with 24/7 operations in controlled environments. | Improves uptime and responsiveness but dependent on human decision-making. |
| Maintenance | Automated diagnostics with minimal downtime. | Remote alerts enable faster response to issues. |
| Data Utilization | Extensive use of AI analytics and machine learning for optimization. | Relies on sensors and dashboards for monitoring KPIs in real time. |
| Security | High cybersecurity needs due to complete automation. | Requires secure remote access protocols and data encryption. |
| Examples | Automotive assembly plants with no onsite staff. | Manufacturing lines monitored and controlled via IoT platforms. |
Which is better?
Dark factories utilize fully automated systems with minimal human intervention, improving production efficiency and reducing labor costs. Remote monitoring enables real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance through connected sensors, enhancing operational transparency and minimizing downtime. Integrating both approaches can optimize manufacturing performance by combining automation with continuous oversight.
Connection
Dark factories utilize advanced automation and robotics enabling continuous production without human presence, which relies heavily on remote monitoring systems to oversee operations in real-time. Remote monitoring employs IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics to track equipment performance, detect anomalies, and optimize workflows within dark factories. This integration enhances manufacturing efficiency, reduces downtime, and enables predictive maintenance at scale.
Key Terms
**Remote Monitoring:**
Remote monitoring enables real-time data collection and analysis from industrial equipment across multiple sites, enhancing predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. It leverages IoT sensors, cloud platforms, and AI algorithms to provide continuous visibility without on-site presence. Explore how remote monitoring transforms operational efficiency and drives smarter decision-making.
IoT Sensors
IoT sensors enable remote monitoring by transmitting real-time data on equipment performance and environmental conditions, enhancing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. In contrast, dark factories leverage IoT sensors for fully automated, human-free manufacturing environments, maximizing production uptime and minimizing labor costs. Explore the transformative impact of IoT sensors in optimizing industrial processes through remote monitoring and dark factory implementations.
Real-time Data Analytics
Remote monitoring leverages real-time data analytics to track equipment performance and environmental conditions from distant locations, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime. Dark factories utilize advanced real-time data analytics combined with automation to operate fully unattended, optimizing production efficiency and minimizing human error. Explore how integrating real-time data analytics transforms industrial operations by learning more about these cutting-edge technologies.
Source and External Links
What is RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management)? - AWS - Remote monitoring and management (RMM) enables IT administrators to observe, maintain, and troubleshoot IT infrastructure and IoT devices from a central location, facilitating proactive issue detection, security management, and cost savings.
What is remote monitoring in IoT? - Software AG - Remote monitoring in IoT uses connected sensors to provide real-time insights into equipment performance, allowing operators to detect problems early, track resource usage, and make informed decisions remotely.
Remote Patient Monitoring - CMS - Remote patient monitoring allows patients to collect health data (e.g., blood pressure, weight) using connected devices that transmit information to healthcare providers for ongoing condition management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com