Industrial symbiosis enhances manufacturing efficiency by enabling waste or byproducts from one facility to serve as raw materials for another, reducing resource consumption and minimizing environmental impact. Eco-industrial parks integrate multiple manufacturing facilities in a shared space designed for collaborative resource management, energy sharing, and waste reduction to achieve sustainable industrial ecosystems. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of industrial symbiosis and eco-industrial parks to revolutionize sustainable manufacturing.
Why it is important
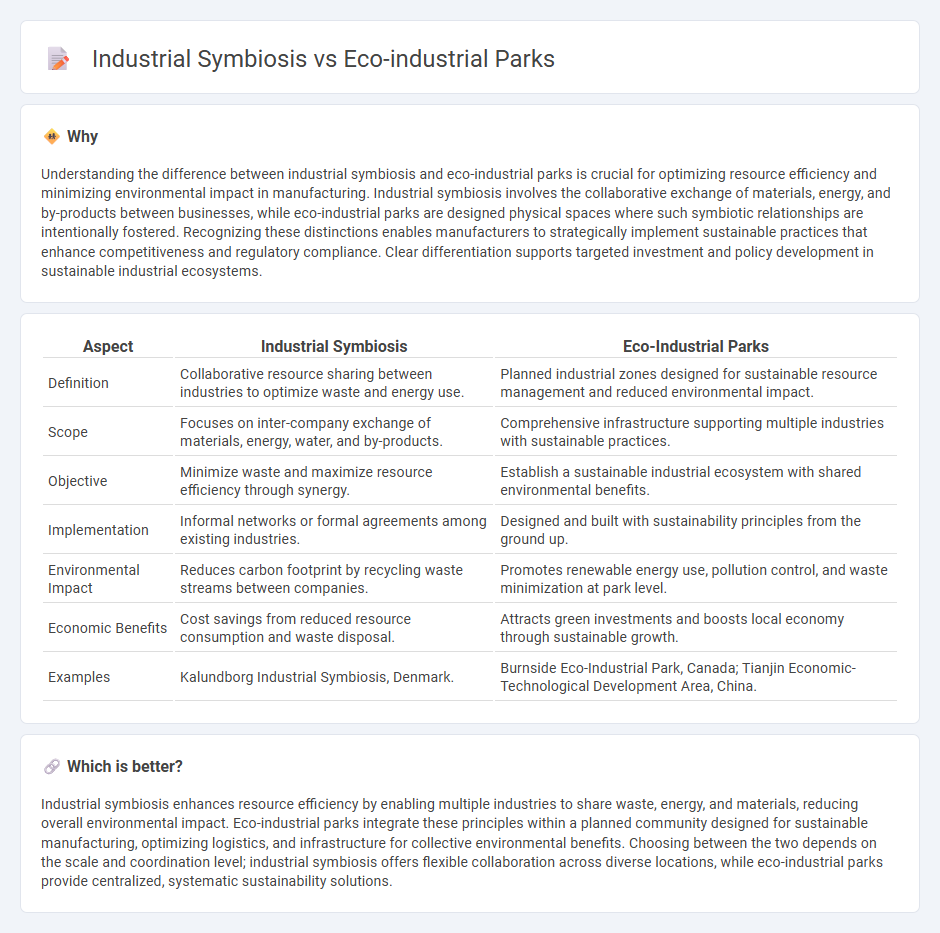
Understanding the difference between industrial symbiosis and eco-industrial parks is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact in manufacturing. Industrial symbiosis involves the collaborative exchange of materials, energy, and by-products between businesses, while eco-industrial parks are designed physical spaces where such symbiotic relationships are intentionally fostered. Recognizing these distinctions enables manufacturers to strategically implement sustainable practices that enhance competitiveness and regulatory compliance. Clear differentiation supports targeted investment and policy development in sustainable industrial ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Symbiosis | Eco-Industrial Parks |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative resource sharing between industries to optimize waste and energy use. | Planned industrial zones designed for sustainable resource management and reduced environmental impact. |
| Scope | Focuses on inter-company exchange of materials, energy, water, and by-products. | Comprehensive infrastructure supporting multiple industries with sustainable practices. |
| Objective | Minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency through synergy. | Establish a sustainable industrial ecosystem with shared environmental benefits. |
| Implementation | Informal networks or formal agreements among existing industries. | Designed and built with sustainability principles from the ground up. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint by recycling waste streams between companies. | Promotes renewable energy use, pollution control, and waste minimization at park level. |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings from reduced resource consumption and waste disposal. | Attracts green investments and boosts local economy through sustainable growth. |
| Examples | Kalundborg Industrial Symbiosis, Denmark. | Burnside Eco-Industrial Park, Canada; Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area, China. |
Which is better?
Industrial symbiosis enhances resource efficiency by enabling multiple industries to share waste, energy, and materials, reducing overall environmental impact. Eco-industrial parks integrate these principles within a planned community designed for sustainable manufacturing, optimizing logistics, and infrastructure for collective environmental benefits. Choosing between the two depends on the scale and coordination level; industrial symbiosis offers flexible collaboration across diverse locations, while eco-industrial parks provide centralized, systematic sustainability solutions.
Connection
Industrial symbiosis involves the collaboration of diverse industries to optimize resource use by exchanging waste, energy, and materials. Eco-industrial parks are designed environments where industrial symbiosis is facilitated, enabling businesses to collectively reduce environmental impact and improve economic performance. This connection promotes sustainable manufacturing by minimizing resource consumption and enhancing waste valorization within the park.
Key Terms
**Eco-industrial parks:**
Eco-industrial parks are planned clusters of businesses designed to promote resource efficiency and environmental sustainability through shared infrastructure, waste recycling, and energy optimization. These parks facilitate collaboration among companies to reduce environmental impact, lower operational costs, and enhance economic performance by utilizing industrial symbiosis principles within a defined geographic area. Discover how eco-industrial parks drive sustainable industrial development and circular economy strategies.
Resource Efficiency
Eco-industrial parks optimize resource efficiency by integrating multiple industries within a shared infrastructure, enabling the reuse of energy, water, and materials to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact. Industrial symbiosis enhances this efficiency by facilitating direct exchanges of by-products, energy, and resources between separate enterprises, creating a circular flow of materials that significantly lowers input requirements. Explore how these strategies transform industrial landscapes and advance sustainable development goals.
Shared Infrastructure
Eco-industrial parks (EIPs) and industrial symbiosis both emphasize shared infrastructure to enhance resource efficiency and reduce environmental impact. EIPs focus on integrated planning and management of infrastructure such as energy grids, water systems, and waste treatment facilities to optimize collective resource use. Explore more about how shared infrastructure drives sustainability in industrial ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Eco-industrial park - An eco-industrial park (EIP) is an industrial park where businesses collaborate to reduce waste and pollution, share resources efficiently, and promote sustainable development, resulting in economic and environmental benefits through systemic cooperation and design integration.
Eco-Industrial Parks - EIPs are business communities on a shared site that achieve enhanced economic, environmental, and social performance by working collectively to improve resource productivity, adopt green technologies, and strengthen social responsibility.
Global Eco-Industrial Park Programme - This program aims to increase resource productivity and improve the economic, social, and environmental performance of industrial parks by adopting strategies for sustainable and inclusive industrial development beyond traditional models.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com