Microfactories enable localized production with compact, flexible setups that reduce transportation costs and lead times. Dark factories operate fully autonomous, often without human presence, maximizing efficiency through advanced robotics and AI technologies. Explore how these innovative manufacturing approaches transform industry dynamics and operational strategies.
Why it is important
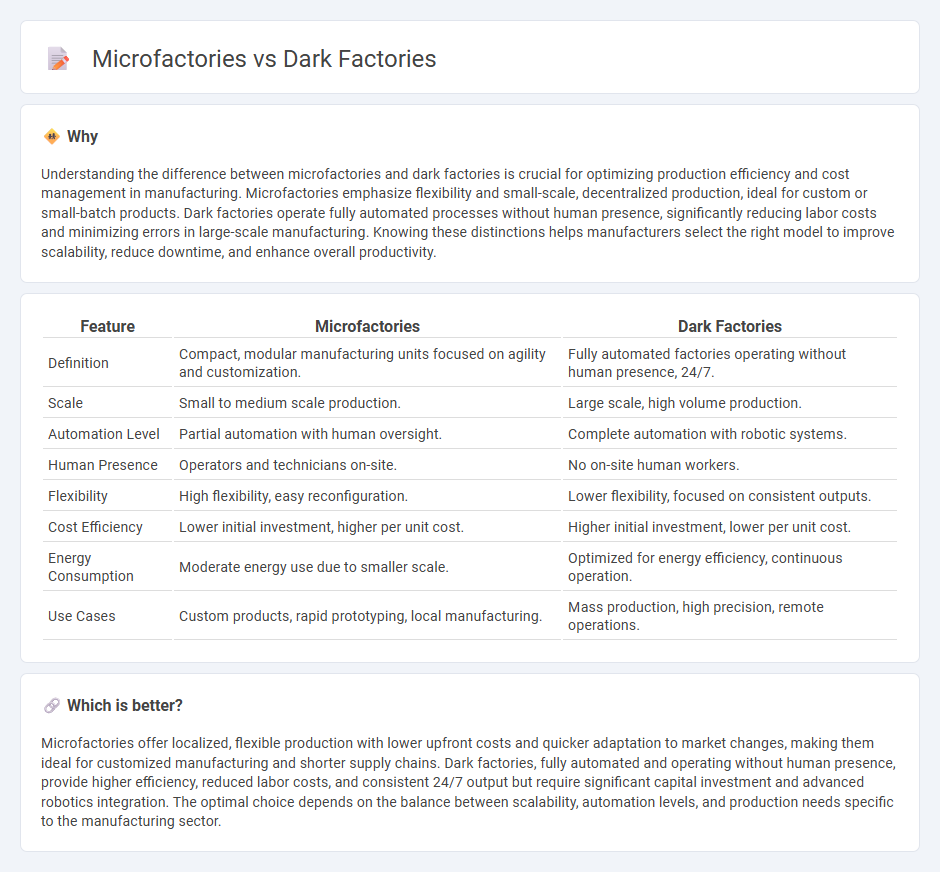
Understanding the difference between microfactories and dark factories is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost management in manufacturing. Microfactories emphasize flexibility and small-scale, decentralized production, ideal for custom or small-batch products. Dark factories operate fully automated processes without human presence, significantly reducing labor costs and minimizing errors in large-scale manufacturing. Knowing these distinctions helps manufacturers select the right model to improve scalability, reduce downtime, and enhance overall productivity.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Microfactories | Dark Factories |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compact, modular manufacturing units focused on agility and customization. | Fully automated factories operating without human presence, 24/7. |
| Scale | Small to medium scale production. | Large scale, high volume production. |
| Automation Level | Partial automation with human oversight. | Complete automation with robotic systems. |
| Human Presence | Operators and technicians on-site. | No on-site human workers. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, easy reconfiguration. | Lower flexibility, focused on consistent outputs. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial investment, higher per unit cost. | Higher initial investment, lower per unit cost. |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate energy use due to smaller scale. | Optimized for energy efficiency, continuous operation. |
| Use Cases | Custom products, rapid prototyping, local manufacturing. | Mass production, high precision, remote operations. |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer localized, flexible production with lower upfront costs and quicker adaptation to market changes, making them ideal for customized manufacturing and shorter supply chains. Dark factories, fully automated and operating without human presence, provide higher efficiency, reduced labor costs, and consistent 24/7 output but require significant capital investment and advanced robotics integration. The optimal choice depends on the balance between scalability, automation levels, and production needs specific to the manufacturing sector.
Connection
Microfactories and dark factories are connected through their shared emphasis on automation and compact, efficient production spaces. Microfactories utilize advanced robotics and AI to operate with minimal human intervention, aligning closely with dark factories, which function entirely without onsite human presence. Both concepts optimize manufacturing processes by reducing labor costs, increasing flexibility, and enabling continuous production cycles.
Key Terms
Automation
Dark factories leverage advanced automation technologies to operate entirely without human presence, utilizing robotic systems and AI to enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. Microfactories emphasize compact, flexible production with automation tailored for rapid scaling and customization, often integrating IoT and machine learning to optimize workflows. Explore the evolving landscape of automated manufacturing by learning more about how these innovative factory models transform industrial processes.
Scalability
Dark factories leverage full automation with minimal human intervention, enabling high scalability through continuous, 24/7 operation and reduced labor costs. Microfactories emphasize flexibility and rapid reconfiguration, ideal for smaller-scale production runs but limited in scaling compared to dark factories. Explore how these manufacturing models impact scalability and efficiency in detail.
Flexibility
Dark factories operate with minimal human intervention, leveraging automation and robotics for continuous, efficient production without lighting or breaks, enhancing scalability but limiting rapid adaptation. Microfactories emphasize high flexibility, enabling quick reconfiguration of machinery and workflows to accommodate diverse product types and smaller batches, ideal for customized manufacturing. Explore further to understand how these models impact production agility and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Dark Factory: The completely automated factory of the future - A dark factory is a fully automated production or logistics facility operated entirely by machines, autonomous robots, and digital technologies, capable of running 24/7 without human intervention, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing costs through IoT and AI integration.
China enters new era of 'Dark Factories' with no lights ... - China is rapidly adopting dark factories as part of its "Made in China 2025" initiative, with highly automated facilities that operate without human workers or lighting, powered by AI and robotics, leading the nation to become a leader in industrial automation.
What is "Lights Out" Dark Manufacturing? | ATS - Dark factories, also known as lights-out manufacturing facilities, rely on robotics, AI, and IoT systems to perform production with minimal or no human presence, improving efficiency, lowering costs, and addressing labor shortages through advanced automation and digital transformation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com