Additive manufacturing builds parts layer by layer through 3D printing technology, enabling complex geometries and customization with minimal material waste. Stamping involves shaping metal sheets using high-pressure dies, offering high-speed mass production and precise repeatability for large-scale manufacturing. Explore the advantages and applications of additive manufacturing versus stamping to optimize your production process.
Why it is important
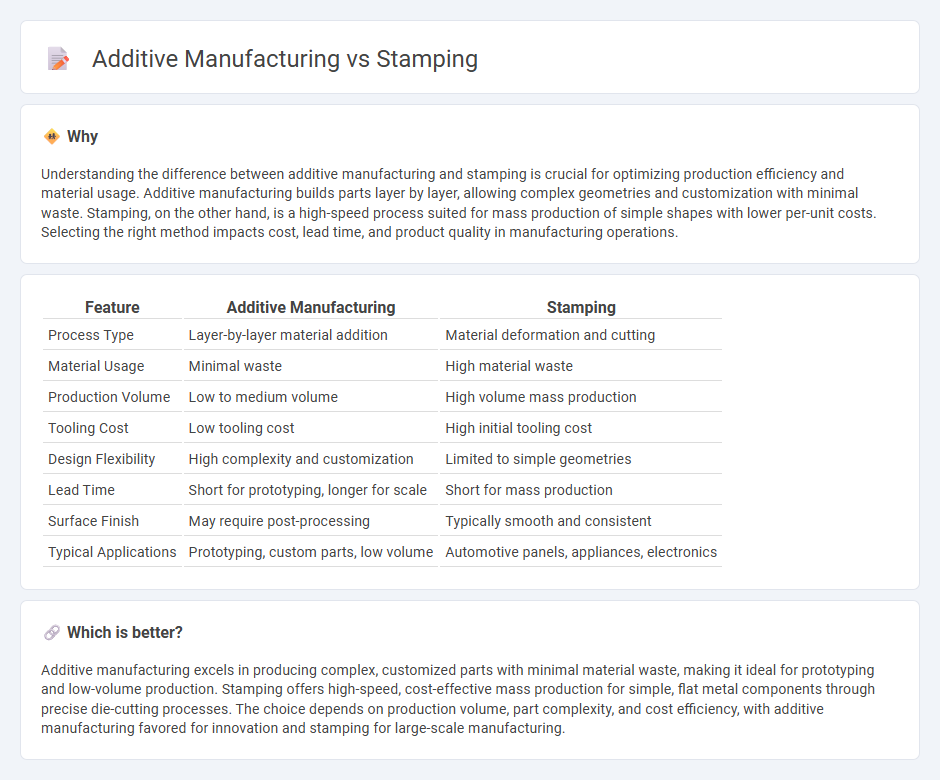
Understanding the difference between additive manufacturing and stamping is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and material usage. Additive manufacturing builds parts layer by layer, allowing complex geometries and customization with minimal waste. Stamping, on the other hand, is a high-speed process suited for mass production of simple shapes with lower per-unit costs. Selecting the right method impacts cost, lead time, and product quality in manufacturing operations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Additive Manufacturing | Stamping |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Layer-by-layer material addition | Material deformation and cutting |
| Material Usage | Minimal waste | High material waste |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume | High volume mass production |
| Tooling Cost | Low tooling cost | High initial tooling cost |
| Design Flexibility | High complexity and customization | Limited to simple geometries |
| Lead Time | Short for prototyping, longer for scale | Short for mass production |
| Surface Finish | May require post-processing | Typically smooth and consistent |
| Typical Applications | Prototyping, custom parts, low volume | Automotive panels, appliances, electronics |
Which is better?
Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex, customized parts with minimal material waste, making it ideal for prototyping and low-volume production. Stamping offers high-speed, cost-effective mass production for simple, flat metal components through precise die-cutting processes. The choice depends on production volume, part complexity, and cost efficiency, with additive manufacturing favored for innovation and stamping for large-scale manufacturing.
Connection
Additive manufacturing and stamping are connected through their complementary roles in the production process, where additive manufacturing creates complex prototypes or customized parts, and stamping efficiently produces high volumes of standardized components from metal sheets. The integration of both processes enhances manufacturing flexibility and reduces overall lead times by combining rapid prototyping with mass production. This synergy supports industries such as automotive and aerospace in achieving cost-effective, scalable, and precise fabrication.
Key Terms
Die (Stamping)
Die stamping relies on high-precision steel dies to shape metal sheets through pressure, enabling mass production of consistent parts with tight tolerances and minimal material waste. The robust die tooling supports rapid cycle times and durability for large-scale automotive and appliance manufacturing. Explore more about die stamping's efficiency and design capabilities by diving deeper into its role in modern manufacturing.
Layer-by-Layer (Additive Manufacturing)
Layer-by-layer additive manufacturing (AM) builds objects through sequential material deposition, offering precise control over complex geometries and internal structures, unlike stamping which shapes metal sheets via deformation in a single step. AM excels in producing customized, lightweight parts with reduced material waste, supporting industries such as aerospace and healthcare by enabling intricate designs that stamping cannot achieve. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits of layer-by-layer additive manufacturing to optimize your production strategy.
Material Utilization
Stamping achieves high material utilization by shaping metal sheets through precise cutting and forming, minimizing waste in large-scale production. Additive manufacturing builds parts layer by layer, optimizing material use for complex geometries but often resulting in longer production times and higher costs per unit. Explore the benefits and limitations of each method to determine the best approach for your manufacturing needs.
Source and External Links
What Is Metal Stamping? | ESI Engineering - Metal stamping, also called pressing, is a manufacturing process where flat sheet metal is shaped by a stamping press using various techniques like punching, blanking, bending, coining, embossing, and flanging to form the metal into desired shapes.
Everything You Need to Know about Stamping - Scrapbook.com - Stamping in crafting involves using tools such as stamping presses to apply ink evenly on stamps for clean, precise, and repeated images on surfaces like paper, emphasizing the application of firm, even pressure without rocking the stamp.
What is Stamping? Types & Processes - Keyence - Stamping is a traditional metal processing method dating back thousands of years, evolving from manual hammering to advanced industrial methods that produce precision metal parts used in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com