Industrial Internet integrates sensors and big data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes by connecting machines and systems in real-time. Digital Twin creates virtual replicas of physical assets or processes to simulate, predict, and enhance performance throughout the product lifecycle. Discover how these technologies revolutionize smart manufacturing for improved efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
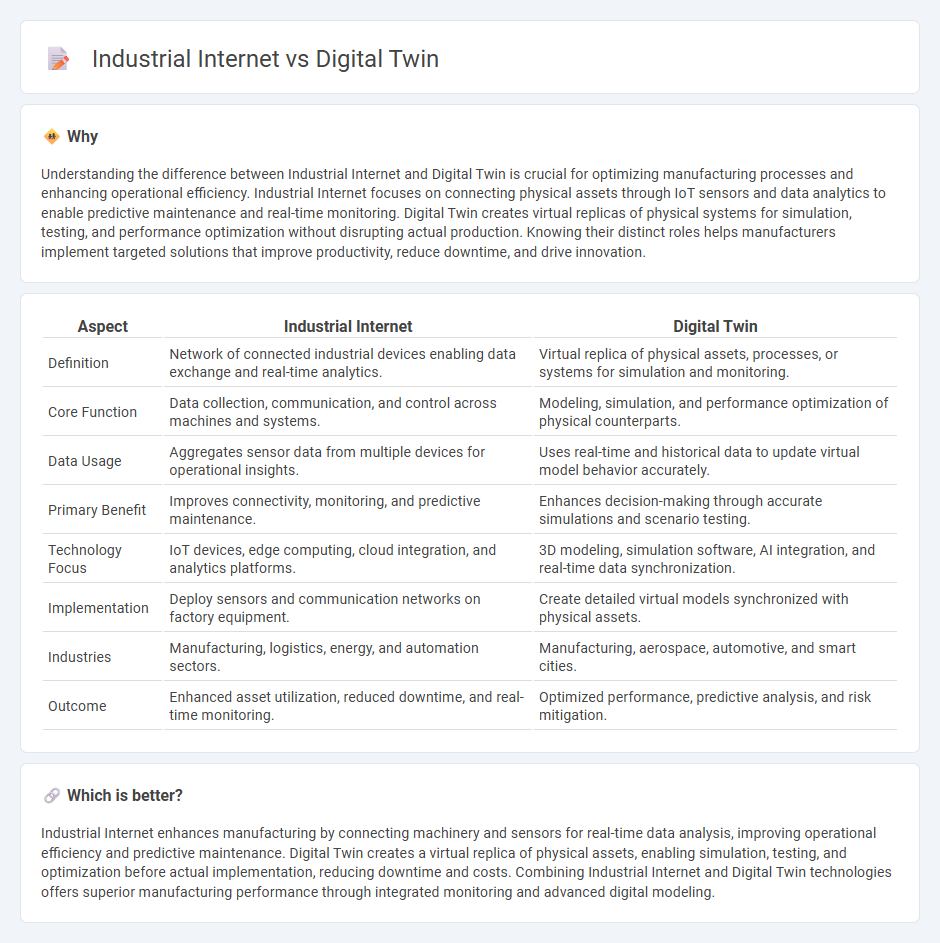
Understanding the difference between Industrial Internet and Digital Twin is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and enhancing operational efficiency. Industrial Internet focuses on connecting physical assets through IoT sensors and data analytics to enable predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring. Digital Twin creates virtual replicas of physical systems for simulation, testing, and performance optimization without disrupting actual production. Knowing their distinct roles helps manufacturers implement targeted solutions that improve productivity, reduce downtime, and drive innovation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Industrial Internet | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of connected industrial devices enabling data exchange and real-time analytics. | Virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems for simulation and monitoring. |
| Core Function | Data collection, communication, and control across machines and systems. | Modeling, simulation, and performance optimization of physical counterparts. |
| Data Usage | Aggregates sensor data from multiple devices for operational insights. | Uses real-time and historical data to update virtual model behavior accurately. |
| Primary Benefit | Improves connectivity, monitoring, and predictive maintenance. | Enhances decision-making through accurate simulations and scenario testing. |
| Technology Focus | IoT devices, edge computing, cloud integration, and analytics platforms. | 3D modeling, simulation software, AI integration, and real-time data synchronization. |
| Implementation | Deploy sensors and communication networks on factory equipment. | Create detailed virtual models synchronized with physical assets. |
| Industries | Manufacturing, logistics, energy, and automation sectors. | Manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and smart cities. |
| Outcome | Enhanced asset utilization, reduced downtime, and real-time monitoring. | Optimized performance, predictive analysis, and risk mitigation. |
Which is better?
Industrial Internet enhances manufacturing by connecting machinery and sensors for real-time data analysis, improving operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. Digital Twin creates a virtual replica of physical assets, enabling simulation, testing, and optimization before actual implementation, reducing downtime and costs. Combining Industrial Internet and Digital Twin technologies offers superior manufacturing performance through integrated monitoring and advanced digital modeling.
Connection
The industrial internet leverages IoT sensors and real-time data analytics to create a dynamic digital twin, an exact virtual replica of physical manufacturing processes. This integration enables continuous monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimization of production lines by simulating scenarios virtually before applying changes onsite. As a result, manufacturers achieve enhanced operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and accelerated innovation cycles.
Key Terms
Virtual Representation
Digital Twin technology offers precise virtual representation by creating real-time, dynamic replicas of physical industrial assets, enabling enhanced monitoring and predictive maintenance. The Industrial Internet integrates vast networks of sensors and devices, collecting extensive data streams that provide broader insights but often lack the detailed, synchronized virtual models characteristic of Digital Twins. Explore deeper insights into how virtual representation drives efficiency and innovation in modern industrial applications.
Real-time Data Integration
Digital Twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time data integration from sensors, machines, and systems to enhance monitoring and predictive maintenance. Industrial Internet leverages connected devices and big data analytics to optimize operational efficiency and asset performance across interconnected industrial networks. Explore the latest innovations in real-time data integration to unlock transformative benefits for industrial processes.
Connected Devices
Connected devices form the backbone of both digital twin technology and the industrial internet, enabling real-time data exchange and system optimization. Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets, utilizing sensor data from connected devices to simulate performance and predict maintenance needs. Explore how integrating connected devices drives innovation and efficiency in smart industrial environments.
Source and External Links
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated, data-driven virtual model that mirrors real-world entities or processes, constantly syncing with them for simulation, monitoring, and decision-making.
What is Digital Twin Technology? - AWS - Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical objects or systems, updated in real time with sensor data to simulate behavior, predict issues, and optimize performance throughout their lifecycle.
What Is a Digital Twin? | IBM - A digital twin is a dynamic virtual copy of a physical object, using live data, simulations, and analytics to enable better understanding and proactive management of the real-world counterpart.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com