Circular manufacturing focuses on sustainable production by minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency through recycling and reuse of materials. Flexible manufacturing emphasizes adaptability and efficiency, enabling rapid changes in production processes to meet varying customer demands. Explore more to understand how these manufacturing approaches transform industry practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and flexible manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and adapting production to market demands. Circular manufacturing focuses on sustainability by recycling materials and minimizing waste, while flexible manufacturing emphasizes rapid adaptability and customization of products. Companies leveraging circular manufacturing reduce environmental impact and comply with regulatory standards. Those prioritizing flexible manufacturing enhance responsiveness to consumer needs and improve competitiveness in dynamic markets.
Comparison Table
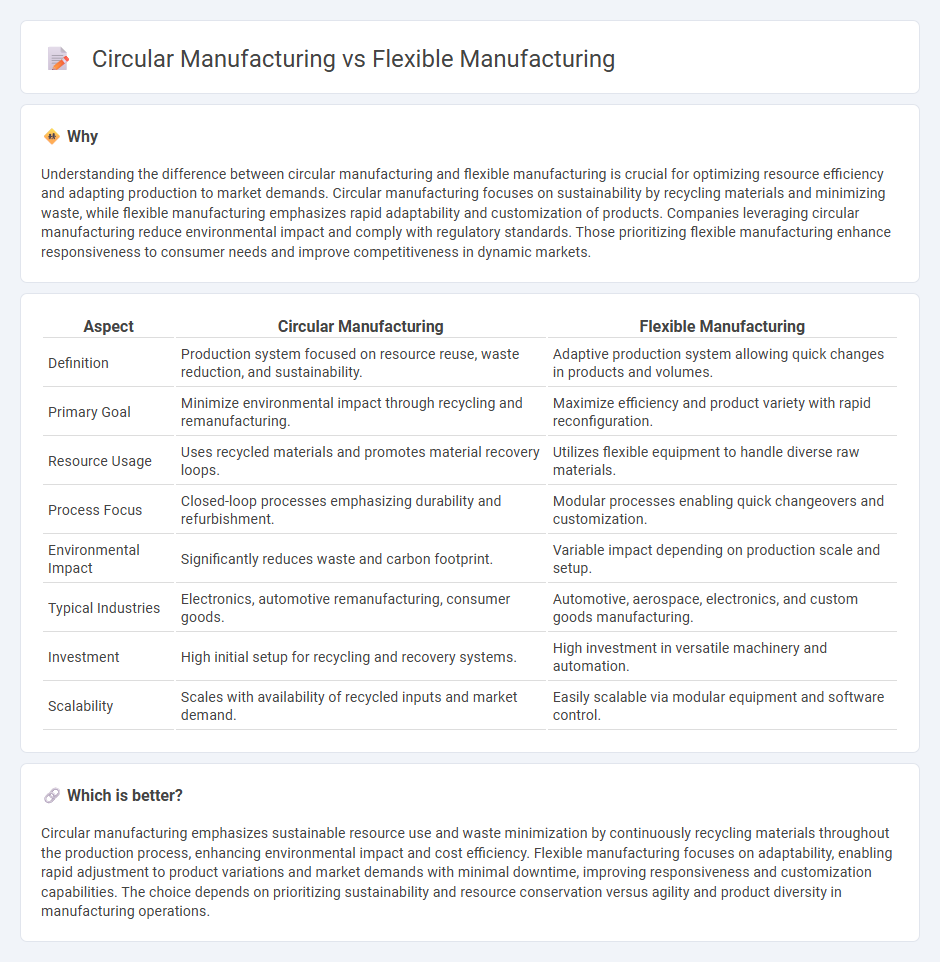
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Flexible Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production system focused on resource reuse, waste reduction, and sustainability. | Adaptive production system allowing quick changes in products and volumes. |
| Primary Goal | Minimize environmental impact through recycling and remanufacturing. | Maximize efficiency and product variety with rapid reconfiguration. |
| Resource Usage | Uses recycled materials and promotes material recovery loops. | Utilizes flexible equipment to handle diverse raw materials. |
| Process Focus | Closed-loop processes emphasizing durability and refurbishment. | Modular processes enabling quick changeovers and customization. |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly reduces waste and carbon footprint. | Variable impact depending on production scale and setup. |
| Typical Industries | Electronics, automotive remanufacturing, consumer goods. | Automotive, aerospace, electronics, and custom goods manufacturing. |
| Investment | High initial setup for recycling and recovery systems. | High investment in versatile machinery and automation. |
| Scalability | Scales with availability of recycled inputs and market demand. | Easily scalable via modular equipment and software control. |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing emphasizes sustainable resource use and waste minimization by continuously recycling materials throughout the production process, enhancing environmental impact and cost efficiency. Flexible manufacturing focuses on adaptability, enabling rapid adjustment to product variations and market demands with minimal downtime, improving responsiveness and customization capabilities. The choice depends on prioritizing sustainability and resource conservation versus agility and product diversity in manufacturing operations.
Connection
Circular manufacturing and flexible manufacturing both enhance sustainability by optimizing resource use and minimizing waste through adaptable production processes. Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products for reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling, while flexible manufacturing enables rapid adjustments in production lines to accommodate different materials and product variations. Together, they create resilient manufacturing systems that reduce environmental impact and improve resource efficiency.
Key Terms
**Flexible Manufacturing:**
Flexible manufacturing emphasizes adaptive production systems capable of efficiently handling varied product types and volumes through automation and reconfigurable machinery. This approach reduces downtime and increases responsiveness to market demand, optimizing resource use and minimizing waste in the manufacturing process. Explore more about how flexible manufacturing drives innovation and sustainability in modern industries.
Reconfigurability
Flexible manufacturing excels in reconfigurability by enabling rapid adaptation of production lines to different products, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency. Circular manufacturing incorporates reconfigurability to support sustainability by designing processes that facilitate resource reuse, waste reduction, and product lifecycle extension. Explore how reconfigurability in both paradigms drives innovation and resilience in modern manufacturing systems.
Automation
Flexible manufacturing leverages automated systems to quickly adapt production lines for varying product types, optimizing efficiency and minimizing downtime. Circular manufacturing integrates automation to enhance resource recovery and waste reduction, supporting sustainable production cycles through smart material handling and recycling processes. Explore how automation drives innovation in both manufacturing paradigms for enhanced productivity and sustainability.
Source and External Links
Flexible Manufacturing Systems - Autodesk - A flexible manufacturing system is a computer-controlled setup designed to adapt to changes in product details through routing or machine flexibility.
Flexible Manufacturing System - Wikipedia - A flexible manufacturing system allows for adaptability in manufacturing by offering routing and machine flexibility, improving efficiency and production adaptability.
What is Flexible Manufacturing - Big Sky Engineering, Inc. - Flexible manufacturing enables companies to adapt production operations to produce different parts for various markets without major retooling or equipment investments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com