Green steel production significantly reduces carbon emissions by using hydrogen or renewable energy instead of coal, contrasting with conventional steel that relies heavily on carbon-intensive blast furnaces. This innovative approach addresses climate change while maintaining steel's critical role in construction and manufacturing industries. Discover how green steel can transform industrial sustainability and meet future environmental standards.
Why it is important
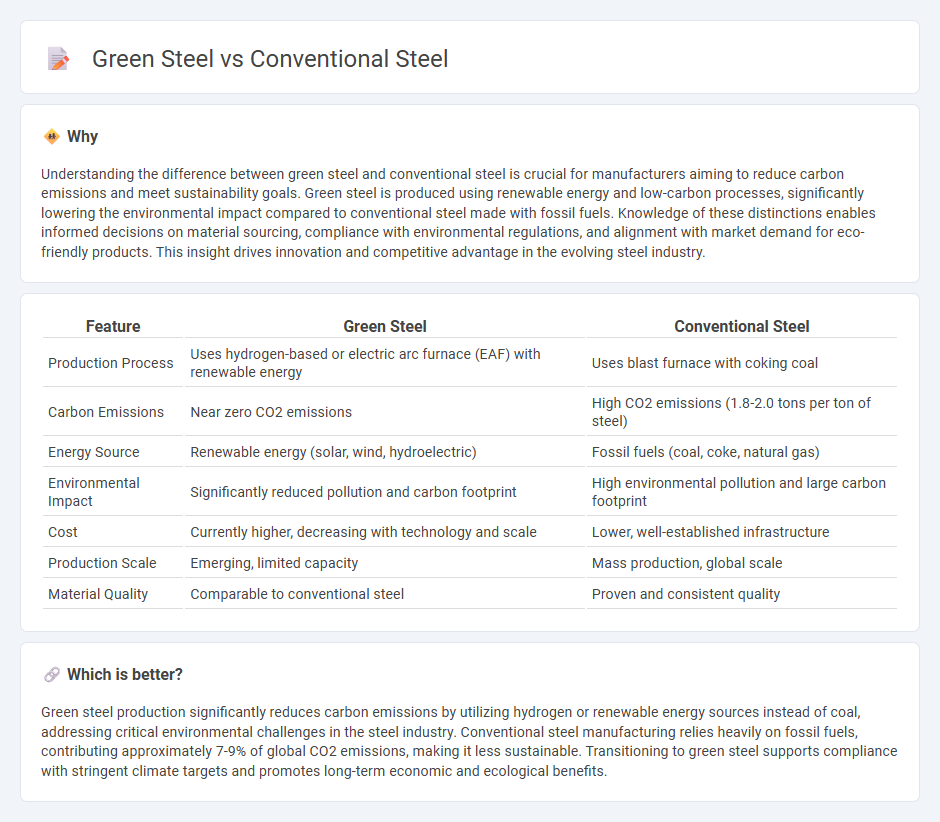
Understanding the difference between green steel and conventional steel is crucial for manufacturers aiming to reduce carbon emissions and meet sustainability goals. Green steel is produced using renewable energy and low-carbon processes, significantly lowering the environmental impact compared to conventional steel made with fossil fuels. Knowledge of these distinctions enables informed decisions on material sourcing, compliance with environmental regulations, and alignment with market demand for eco-friendly products. This insight drives innovation and competitive advantage in the evolving steel industry.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Green Steel | Conventional Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Production Process | Uses hydrogen-based or electric arc furnace (EAF) with renewable energy | Uses blast furnace with coking coal |
| Carbon Emissions | Near zero CO2 emissions | High CO2 emissions (1.8-2.0 tons per ton of steel) |
| Energy Source | Renewable energy (solar, wind, hydroelectric) | Fossil fuels (coal, coke, natural gas) |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly reduced pollution and carbon footprint | High environmental pollution and large carbon footprint |
| Cost | Currently higher, decreasing with technology and scale | Lower, well-established infrastructure |
| Production Scale | Emerging, limited capacity | Mass production, global scale |
| Material Quality | Comparable to conventional steel | Proven and consistent quality |
Which is better?
Green steel production significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing hydrogen or renewable energy sources instead of coal, addressing critical environmental challenges in the steel industry. Conventional steel manufacturing relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing approximately 7-9% of global CO2 emissions, making it less sustainable. Transitioning to green steel supports compliance with stringent climate targets and promotes long-term economic and ecological benefits.
Connection
Green steel and conventional steel are connected through the steel production process, where green steel utilizes renewable energy and hydrogen to reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional coal-based methods. Both types rely on iron ore as a primary raw material, but green steel integrates sustainable technologies to minimize environmental impact. This connection marks a transition in manufacturing toward decarbonizing the steel industry while maintaining production efficiency.
Key Terms
Carbon Emissions
Conventional steel production emits approximately 1.85 tons of CO2 per ton of steel, primarily due to coal-based blast furnaces, making it a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions. Green steel leverages hydrogen-based direct reduction and renewable energy, reducing carbon emissions by up to 90% compared to conventional methods. Discover detailed insights on the environmental benefits and innovations driving green steel.
Energy Source
Conventional steel production primarily relies on coal and coke as energy sources, resulting in significant carbon emissions. Green steel utilizes renewable energy such as hydrogen, solar, and wind power to drastically reduce its environmental impact. Discover more about the transformative energy innovations shaping the future of steel manufacturing.
Production Process
Conventional steel production primarily relies on blast furnaces and carbon-intensive coke, emitting significant CO2 during iron ore reduction. Green steel employs hydrogen-based direct reduction and renewable energy sources, drastically cutting greenhouse gas emissions in the production process. Explore detailed comparisons to understand the environmental impact and innovations in steel manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Conventional Steel - Corrosionpedia - Conventional steel is a type of steel with low carbon content, formulated for low yield strength and high hardening capabilities, often used in heavy building foundations.
Comparison between pre-engineered steel building and conventional steel building - Conventional steel buildings are traditional structures where steel components are individually designed and fabricated on-site using welding and cutting, resulting in higher labor, time, and cost compared to pre-engineered systems.
Conventional steel building - Pebtrade - Conventional steel buildings use rolled steel sections fabricated at the construction site and are suitable for multi-story projects beyond the limits of pre-engineered buildings, offering flexible architectural features and a one-stop-shop solution for builders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com