Zero Defect Manufacturing focuses on eliminating defects through strict quality control and error prevention techniques, ensuring products meet exact specifications. Smart Manufacturing integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and data analytics to optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and enable real-time decision-making. Discover how these innovative approaches transform industrial operations and drive competitive advantage.
Why it is important
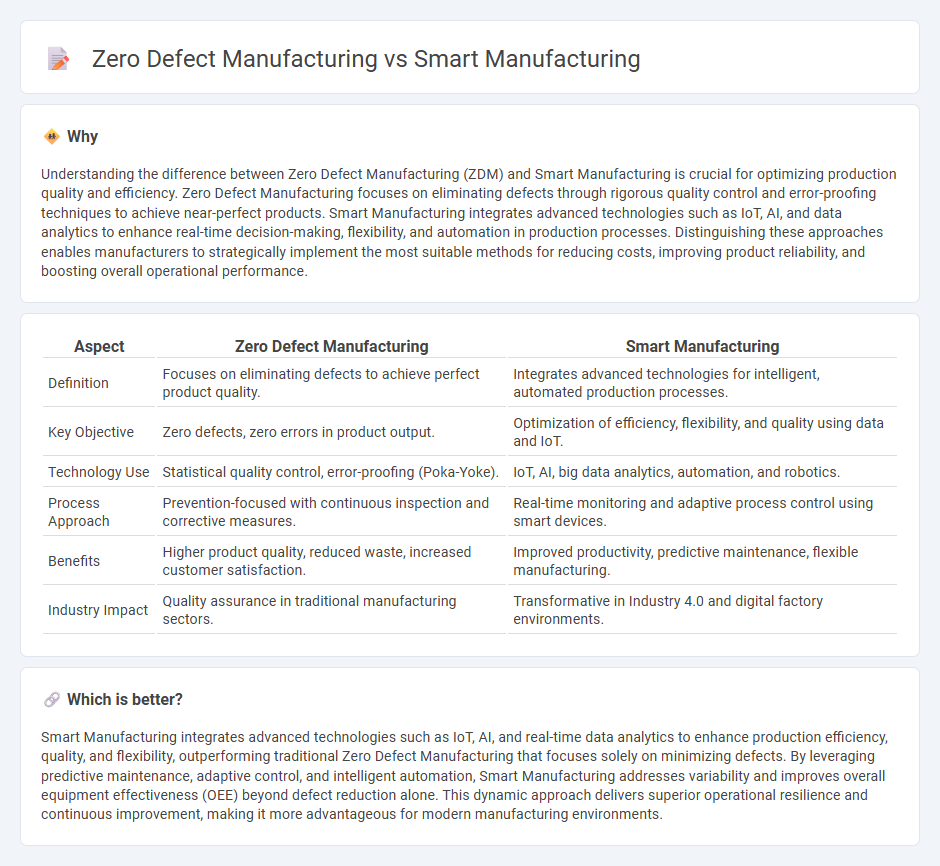
Understanding the difference between Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) and Smart Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production quality and efficiency. Zero Defect Manufacturing focuses on eliminating defects through rigorous quality control and error-proofing techniques to achieve near-perfect products. Smart Manufacturing integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and data analytics to enhance real-time decision-making, flexibility, and automation in production processes. Distinguishing these approaches enables manufacturers to strategically implement the most suitable methods for reducing costs, improving product reliability, and boosting overall operational performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Defect Manufacturing | Smart Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on eliminating defects to achieve perfect product quality. | Integrates advanced technologies for intelligent, automated production processes. |
| Key Objective | Zero defects, zero errors in product output. | Optimization of efficiency, flexibility, and quality using data and IoT. |
| Technology Use | Statistical quality control, error-proofing (Poka-Yoke). | IoT, AI, big data analytics, automation, and robotics. |
| Process Approach | Prevention-focused with continuous inspection and corrective measures. | Real-time monitoring and adaptive process control using smart devices. |
| Benefits | Higher product quality, reduced waste, increased customer satisfaction. | Improved productivity, predictive maintenance, flexible manufacturing. |
| Industry Impact | Quality assurance in traditional manufacturing sectors. | Transformative in Industry 4.0 and digital factory environments. |
Which is better?
Smart Manufacturing integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics to enhance production efficiency, quality, and flexibility, outperforming traditional Zero Defect Manufacturing that focuses solely on minimizing defects. By leveraging predictive maintenance, adaptive control, and intelligent automation, Smart Manufacturing addresses variability and improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) beyond defect reduction alone. This dynamic approach delivers superior operational resilience and continuous improvement, making it more advantageous for modern manufacturing environments.
Connection
Zero defect manufacturing (ZDM) and smart manufacturing are interconnected through the integration of advanced technologies like IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and real-time quality monitoring systems. Smart manufacturing utilizes data-driven automation and predictive maintenance to minimize errors, directly supporting the goal of ZDM to produce flawless products. The synergy between these approaches enhances operational efficiency, reduces waste, and improves overall product quality in modern production environments.
Key Terms
Automation
Smart manufacturing leverages advanced automation technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics to optimize production processes, enhance flexibility, and reduce operational costs. Zero defect manufacturing emphasizes precision automation and real-time quality control systems to eliminate defects, ensuring the highest product standards and minimizing waste. Explore how integrating smart automation can drive zero defect outcomes and transform manufacturing efficiency.
Predictive Analytics
Smart Manufacturing leverages predictive analytics to optimize production processes by anticipating equipment failures and minimizing downtime, enhancing overall efficiency. Zero Defect Manufacturing focuses on predictive analytics to detect and prevent defects before they occur, ensuring high product quality and reducing waste. Explore how predictive analytics transforms both methodologies to drive precision and productivity in modern manufacturing.
Quality Control
Smart Manufacturing leverages IoT sensors, AI algorithms, and real-time data analytics to enhance production efficiency while minimizing defects. Zero Defect Manufacturing prioritizes stringent quality control processes and defect prevention strategies to achieve near-perfect product standards and reduce waste. Explore how integrating Smart Manufacturing technologies with Zero Defect methodologies can revolutionize your quality control systems.
Source and External Links
What Is Smart Manufacturing? - CESMII - Information-driven, event-driven, and collaborative orchestration of business, physical, and digital processes for measurable improvements in manufacturing performance and profitability.
What Is Smart Manufacturing? | Oracle - The convergence of data science and artificial intelligence with manufacturing to create highly connected, knowledge-enabled enterprises that enhance productivity, sustainability, and economic performance using real-time data and cloud technology.
Smart manufacturing - Wikipedia - Computer-integrated manufacturing characterized by high adaptability, rapid design changes, and the use of advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, and cyber-physical systems to improve resource efficiency and integrate customers and business partners in value processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com