Lights out factories use fully automated systems to operate without human intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs. Discrete manufacturing involves producing distinct items such as automobiles, electronics, or machinery, often requiring human oversight at various stages. Explore how these manufacturing models transform production processes and drive innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between lights out factories and discrete manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and automation strategies. Lights out factories operate fully autonomously without human intervention, ideal for continuous processes and reducing labor costs. Discrete manufacturing involves distinct parts and assemblies, requiring more manual oversight for customization and quality control. This distinction guides resource allocation and technology investment for improved manufacturing outcomes.
Comparison Table
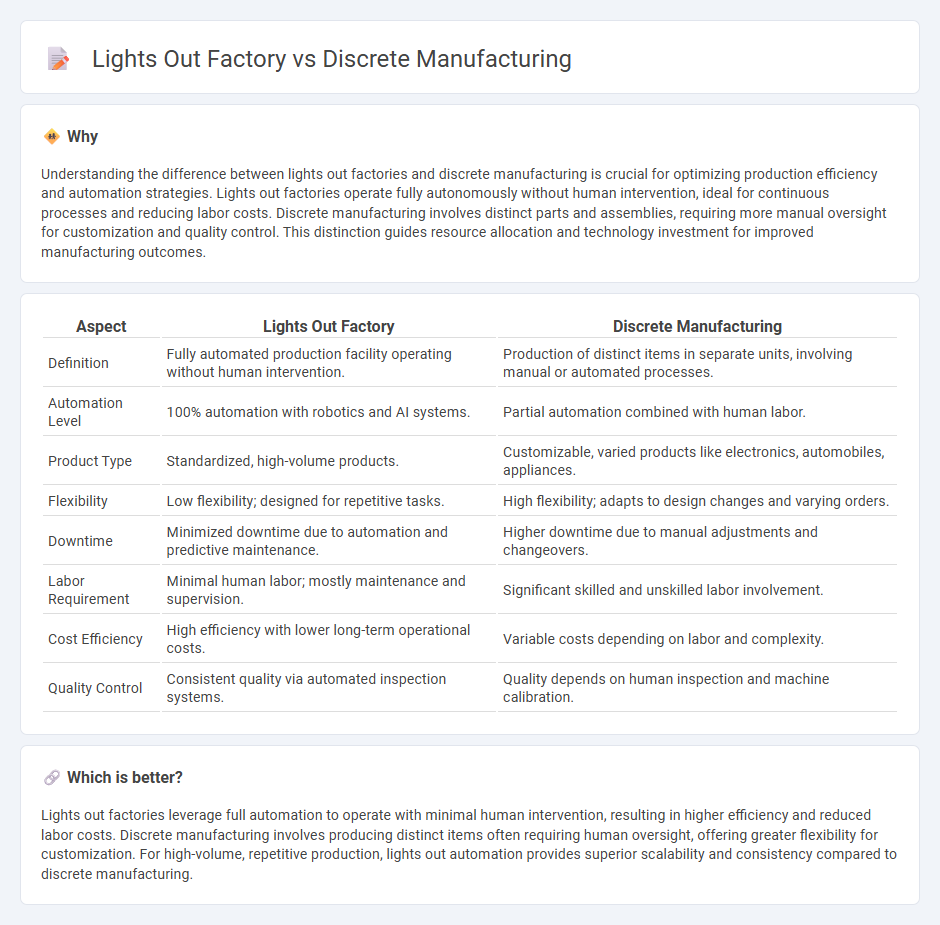
| Aspect | Lights Out Factory | Discrete Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated production facility operating without human intervention. | Production of distinct items in separate units, involving manual or automated processes. |
| Automation Level | 100% automation with robotics and AI systems. | Partial automation combined with human labor. |
| Product Type | Standardized, high-volume products. | Customizable, varied products like electronics, automobiles, appliances. |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility; designed for repetitive tasks. | High flexibility; adapts to design changes and varying orders. |
| Downtime | Minimized downtime due to automation and predictive maintenance. | Higher downtime due to manual adjustments and changeovers. |
| Labor Requirement | Minimal human labor; mostly maintenance and supervision. | Significant skilled and unskilled labor involvement. |
| Cost Efficiency | High efficiency with lower long-term operational costs. | Variable costs depending on labor and complexity. |
| Quality Control | Consistent quality via automated inspection systems. | Quality depends on human inspection and machine calibration. |
Which is better?
Lights out factories leverage full automation to operate with minimal human intervention, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced labor costs. Discrete manufacturing involves producing distinct items often requiring human oversight, offering greater flexibility for customization. For high-volume, repetitive production, lights out automation provides superior scalability and consistency compared to discrete manufacturing.
Connection
Lights out factories in discrete manufacturing utilize full automation and robotics to enable continuous, unattended production processes, reducing human intervention and operational costs. Discrete manufacturing benefits from lights out operations by improving precision, increasing throughput, and ensuring consistent quality in producing distinct items such as electronics, automotive components, and machinery. Integrating smart sensors and IoT technology in lights out factories enhances real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, optimizing product lifecycle management and minimizing downtime.
Key Terms
Batch Production
Batch production in discrete manufacturing involves producing a set quantity of distinct items, allowing customization and quality control between batches. Lights-out factories automate this process, minimizing human intervention by utilizing robotics and AI to run continuous, unattended production cycles, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing downtime. Discover how integrating lights-out automation can transform traditional batch production workflows.
Automation
Discrete manufacturing relies on human intervention for assembly and quality control, integrating automation primarily in repetitive or hazardous tasks to improve precision and efficiency. Lights-out factories operate with fully autonomous systems, leveraging advanced robotics, AI, and IoT for continuous, unattended production cycles that minimize human presence. Explore how automation transforms manufacturing by bridging discrete processes and lights-out capabilities for smarter, more agile operations.
Unattended Operations
Discrete manufacturing involves producing distinct items like cars or electronics, requiring human oversight for complexity and customization. Lights out factories operate fully autonomously with unattended operations, relying on advanced robotics and AI to maintain continuous production without human intervention. Explore how unattended operations transform efficiency and workforce dynamics in modern manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Discrete manufacturing - Wikipedia - Discrete manufacturing is the production of distinct, identifiable items such as automobiles, furniture, and smartphones, characterized by individual or separate unit production that can be either low volume/high complexity or high volume/low complexity.
Discrete vs. Process Manufacturing - How Do They Differ? - MRPeasy - Discrete manufacturing produces goods out of individual components and sub-assemblies, using bills of materials and routings to manage assembly, with examples including car manufacturers assembling thousands of parts on production lines.
Discrete Manufacturing - Oracle Help Center - Discrete manufacturing involves producing specific quantities of single items using work orders with routing instructions, commonly applied in make-to-stock or make-to-order environments for products like cars, electronics, and furniture.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com