The digital thread integrates data across the entire manufacturing lifecycle, enabling real-time visibility and seamless communication between design, production, and quality assurance. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, builds parts layer by layer, allowing for complex geometries and rapid prototyping that traditional methods cannot achieve. Explore how these transformative technologies are revolutionizing manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
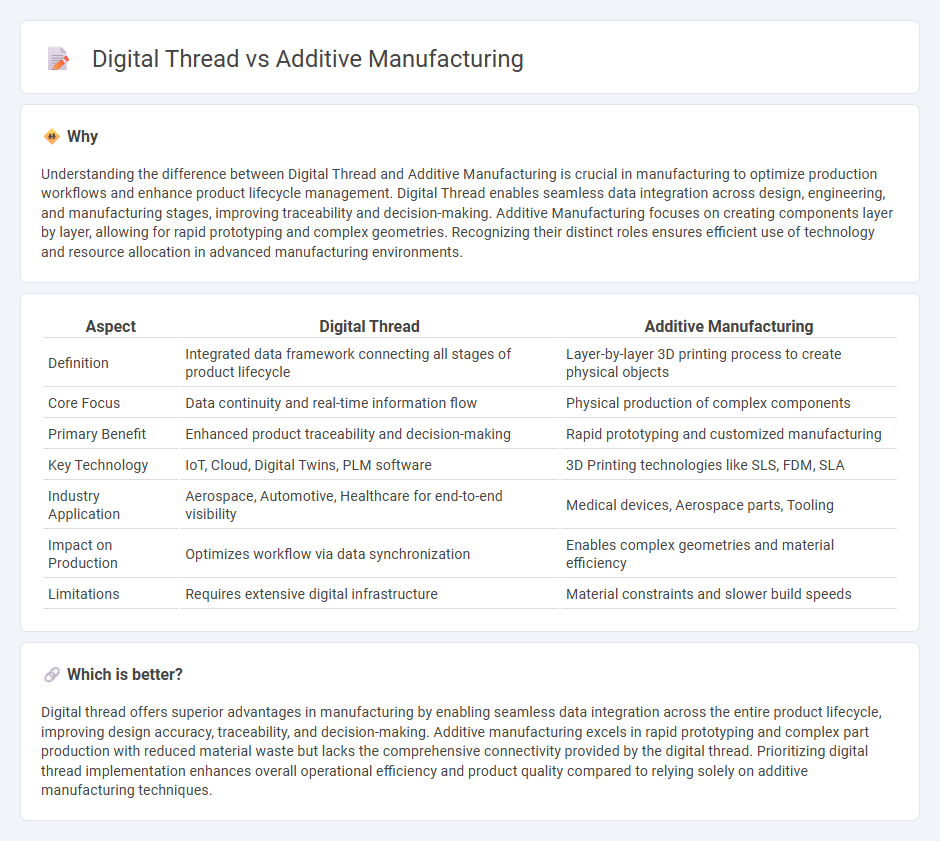
Understanding the difference between Digital Thread and Additive Manufacturing is crucial in manufacturing to optimize production workflows and enhance product lifecycle management. Digital Thread enables seamless data integration across design, engineering, and manufacturing stages, improving traceability and decision-making. Additive Manufacturing focuses on creating components layer by layer, allowing for rapid prototyping and complex geometries. Recognizing their distinct roles ensures efficient use of technology and resource allocation in advanced manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Thread | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated data framework connecting all stages of product lifecycle | Layer-by-layer 3D printing process to create physical objects |
| Core Focus | Data continuity and real-time information flow | Physical production of complex components |
| Primary Benefit | Enhanced product traceability and decision-making | Rapid prototyping and customized manufacturing |
| Key Technology | IoT, Cloud, Digital Twins, PLM software | 3D Printing technologies like SLS, FDM, SLA |
| Industry Application | Aerospace, Automotive, Healthcare for end-to-end visibility | Medical devices, Aerospace parts, Tooling |
| Impact on Production | Optimizes workflow via data synchronization | Enables complex geometries and material efficiency |
| Limitations | Requires extensive digital infrastructure | Material constraints and slower build speeds |
Which is better?
Digital thread offers superior advantages in manufacturing by enabling seamless data integration across the entire product lifecycle, improving design accuracy, traceability, and decision-making. Additive manufacturing excels in rapid prototyping and complex part production with reduced material waste but lacks the comprehensive connectivity provided by the digital thread. Prioritizing digital thread implementation enhances overall operational efficiency and product quality compared to relying solely on additive manufacturing techniques.
Connection
The digital thread integrates data from design, production, and supply chain stages, enabling real-time tracking and optimization in additive manufacturing processes. Additive manufacturing leverages the digital thread to create precise 3D-printed components with improved traceability and quality control. This connection enhances manufacturing efficiency, reduces errors, and accelerates product development cycles.
Key Terms
Layer-by-layer fabrication
Additive manufacturing, characterized by its layer-by-layer fabrication process, enables precise creation of complex geometries unattainable through traditional manufacturing methods. The digital thread serves as a comprehensive data framework that integrates design, production, and quality information to optimize and trace each additive layer in real-time. Explore how integrating additive manufacturing with a digital thread transforms product development and production efficiency.
Data continuity
Additive manufacturing relies on precise data continuity throughout design, production, and quality control stages to ensure part accuracy and performance. The digital thread integrates this data seamlessly across the entire product lifecycle, enabling real-time tracking and traceability from raw material to finished component. Explore how establishing a robust digital thread enhances additive manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Real-time monitoring
Real-time monitoring in additive manufacturing leverages sensors and IoT devices to track layer-by-layer deposition, ensuring precision and detecting defects immediately. The digital thread integrates this live data into a comprehensive product lifecycle framework, enhancing traceability and enabling predictive maintenance across supply chains. Discover how combining additive manufacturing with a digital thread revolutionizes production efficiency and quality control.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained - Additive manufacturing is the process of creating objects by building them one layer at a time, typically using 3D printing technology, which contrasts with traditional subtractive manufacturing methods.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Using digital designs, additive manufacturing fabricates three-dimensional products layer by layer, allowing for complex designs with less material waste and enabling new applications across industries like aerospace and healthcare.
The 7 categories of Additive Manufacturing - Additive manufacturing encompasses a variety of processes, officially classified into seven categories--including vat photopolymerization, material jetting, and binder jetting--each differing in how material layers are formed.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com