Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances manufacturing efficiency by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, reducing human error and operational costs. Smart manufacturing integrates IoT, AI, and data analytics to create adaptive, self-optimizing production systems that improve quality, agility, and resource management. Discover how these technologies transform industrial operations and drive innovation.
Why it is important
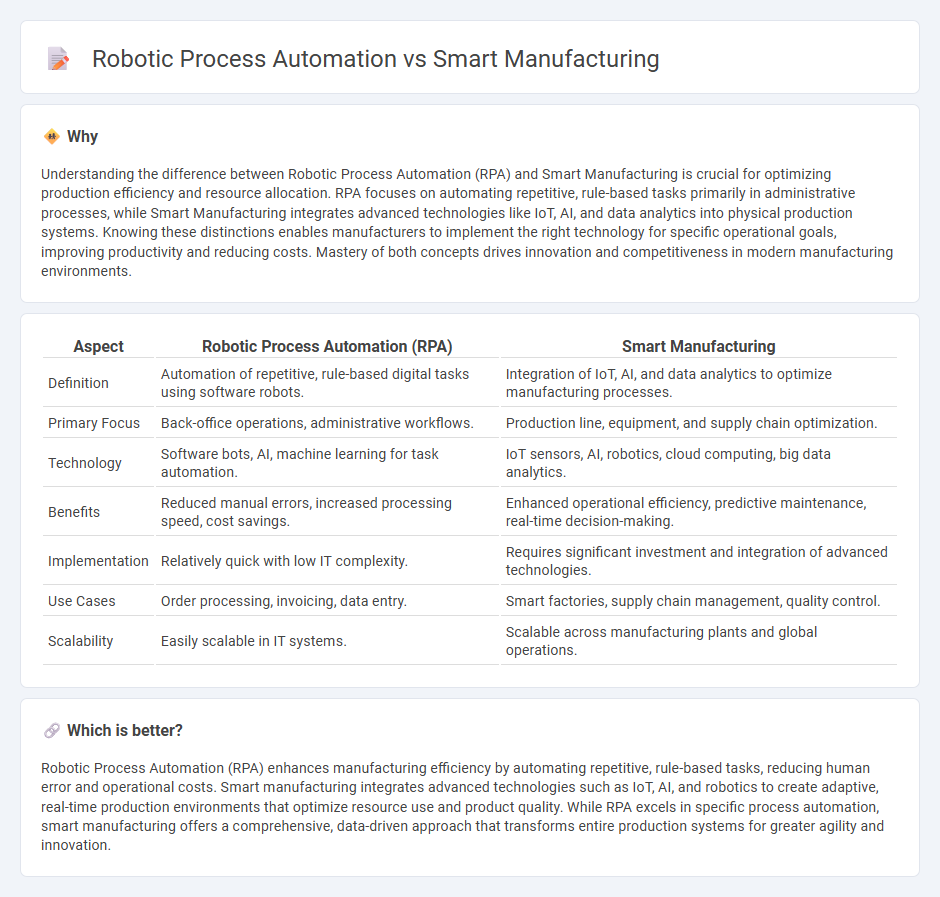
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Smart Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and resource allocation. RPA focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks primarily in administrative processes, while Smart Manufacturing integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and data analytics into physical production systems. Knowing these distinctions enables manufacturers to implement the right technology for specific operational goals, improving productivity and reducing costs. Mastery of both concepts drives innovation and competitiveness in modern manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Smart Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automation of repetitive, rule-based digital tasks using software robots. | Integration of IoT, AI, and data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes. |
| Primary Focus | Back-office operations, administrative workflows. | Production line, equipment, and supply chain optimization. |
| Technology | Software bots, AI, machine learning for task automation. | IoT sensors, AI, robotics, cloud computing, big data analytics. |
| Benefits | Reduced manual errors, increased processing speed, cost savings. | Enhanced operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, real-time decision-making. |
| Implementation | Relatively quick with low IT complexity. | Requires significant investment and integration of advanced technologies. |
| Use Cases | Order processing, invoicing, data entry. | Smart factories, supply chain management, quality control. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable in IT systems. | Scalable across manufacturing plants and global operations. |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances manufacturing efficiency by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, reducing human error and operational costs. Smart manufacturing integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and robotics to create adaptive, real-time production environments that optimize resource use and product quality. While RPA excels in specific process automation, smart manufacturing offers a comprehensive, data-driven approach that transforms entire production systems for greater agility and innovation.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances Smart Manufacturing by automating repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and increasing operational efficiency on the factory floor. Smart Manufacturing integrates IoT sensors, AI analytics, and RPA to enable real-time data-driven decision-making and adaptive production workflows. This synergy accelerates production cycles, optimizes resource utilization, and improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Key Terms
IoT Integration
Smart manufacturing leverages IoT integration to enable real-time data collection and machine-to-machine communication, enhancing production efficiency and predictive maintenance. Robotic process automation (RPA) primarily focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based digital tasks without extensive IoT capabilities. Explore the impact of IoT integration in transforming manufacturing processes and optimizing factory operations.
Workflow Automation
Smart manufacturing integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics to optimize production workflows, enabling real-time data analysis and adaptive control of manufacturing processes. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based digital tasks across business workflows but does not directly control physical manufacturing operations. Explore the distinct impacts of smart manufacturing and RPA on workflow automation to enhance operational efficiency and innovation.
Real-time Data Analytics
Smart manufacturing integrates real-time data analytics to optimize production processes by collecting and analyzing sensor data, enabling predictive maintenance and adaptive control systems. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages real-time analytics primarily for monitoring and improving workflow efficiency in administrative and repetitive digital tasks. Explore how real-time data analytics transforms both smart manufacturing and RPA to enhance operational performance and decision-making.
Source and External Links
What Is Smart Manufacturing? - Smart manufacturing integrates modern data science and artificial intelligence with factory processes to increase efficiency, connectivity, and real-time decision making, transforming traditional manufacturing into highly connected, productive, and sustainable operations.
What Is Smart Manufacturing? - It is an information-driven, event-driven orchestration of business, physical, and digital processes that enhances speed, agility, quality, and profitability through automation, predictive analytics, and continuous monitoring.
2025 Smart Manufacturing and Operations Survey - Smart manufacturing adoption focuses on sensors, automation, AI, and cloud computing to monitor manufacturing environments, increase productivity, and leverage standards for scalable data management and operational agility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com