Machine vision enhances manufacturing accuracy by enabling automated inspection and real-time quality control through advanced imaging technology. Robotics focuses on automating physical tasks such as assembly, welding, and material handling, boosting productivity and consistency on production lines. Discover how integrating machine vision and robotics can revolutionize your manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
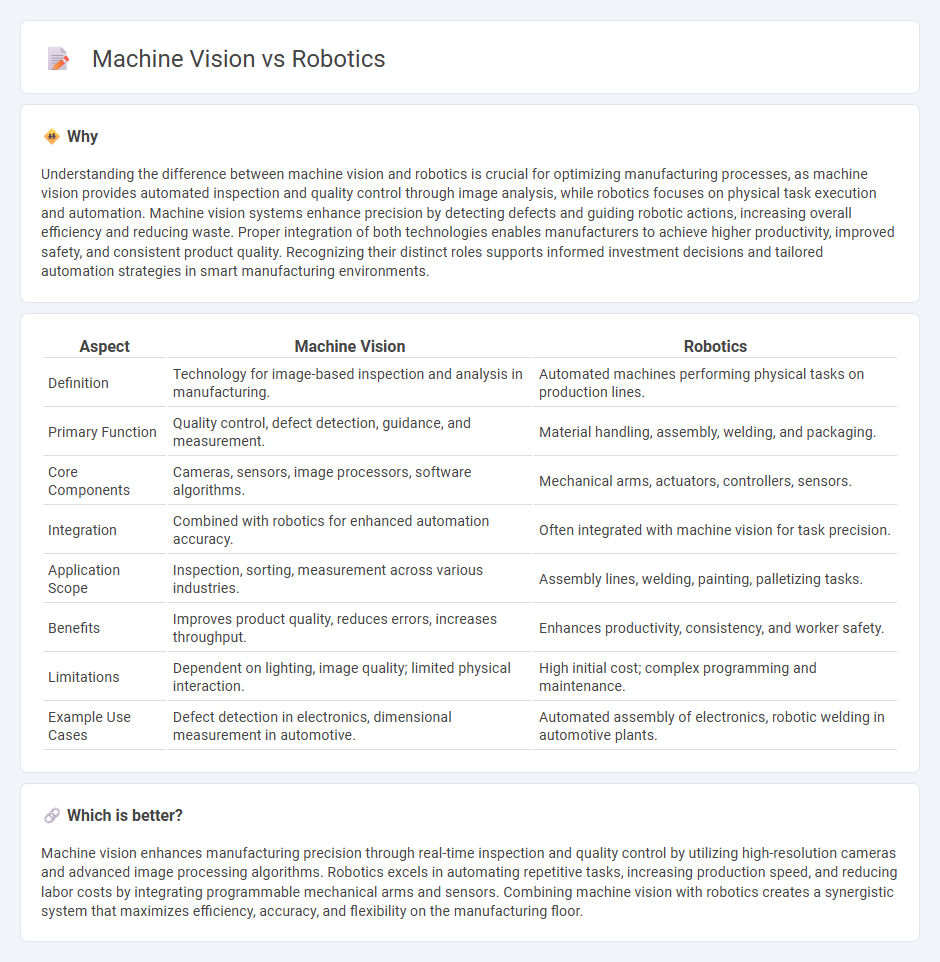
Understanding the difference between machine vision and robotics is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as machine vision provides automated inspection and quality control through image analysis, while robotics focuses on physical task execution and automation. Machine vision systems enhance precision by detecting defects and guiding robotic actions, increasing overall efficiency and reducing waste. Proper integration of both technologies enables manufacturers to achieve higher productivity, improved safety, and consistent product quality. Recognizing their distinct roles supports informed investment decisions and tailored automation strategies in smart manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Machine Vision | Robotics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology for image-based inspection and analysis in manufacturing. | Automated machines performing physical tasks on production lines. |
| Primary Function | Quality control, defect detection, guidance, and measurement. | Material handling, assembly, welding, and packaging. |
| Core Components | Cameras, sensors, image processors, software algorithms. | Mechanical arms, actuators, controllers, sensors. |
| Integration | Combined with robotics for enhanced automation accuracy. | Often integrated with machine vision for task precision. |
| Application Scope | Inspection, sorting, measurement across various industries. | Assembly lines, welding, painting, palletizing tasks. |
| Benefits | Improves product quality, reduces errors, increases throughput. | Enhances productivity, consistency, and worker safety. |
| Limitations | Dependent on lighting, image quality; limited physical interaction. | High initial cost; complex programming and maintenance. |
| Example Use Cases | Defect detection in electronics, dimensional measurement in automotive. | Automated assembly of electronics, robotic welding in automotive plants. |
Which is better?
Machine vision enhances manufacturing precision through real-time inspection and quality control by utilizing high-resolution cameras and advanced image processing algorithms. Robotics excels in automating repetitive tasks, increasing production speed, and reducing labor costs by integrating programmable mechanical arms and sensors. Combining machine vision with robotics creates a synergistic system that maximizes efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility on the manufacturing floor.
Connection
Machine vision systems provide robots with the ability to perceive and interpret their environment through cameras and sensors, enabling precise object recognition and quality inspection in manufacturing processes. Robotics utilize this visual data to perform tasks such as assembly, sorting, and defect detection with enhanced accuracy and speed. Integration of machine vision and robotics significantly improves automation efficiency, reduces human error, and supports advanced manufacturing techniques like Industry 4.0.
Key Terms
Automation
Robotics integrates mechanical systems and AI to perform complex automated tasks with precision, while machine vision enables robots to interpret visual data for real-time decision-making and quality control in manufacturing. The synergy between robotics and machine vision drives advancements in automation by enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability across industries such as automotive, electronics, and logistics. Explore how combining these technologies transforms automation processes and boosts operational productivity.
Image Processing
Robotics integrates machine vision to enhance image processing, enabling robots to interpret visual data for tasks such as object recognition, alignment, and quality control in manufacturing. Machine vision systems rely on advanced algorithms and cameras to analyze images, facilitating precise decision-making and automation. Explore further to understand how these technologies revolutionize industrial operations and improve efficiency.
Feedback Control
Robotics integrates sensors and actuators with feedback control systems to enable precise and adaptive movement, allowing robots to adjust actions based on real-time data. Machine vision provides critical visual feedback by processing images to detect objects, measure distances, and identify defects, enhancing robotic system accuracy. Explore deeper into the synergy between robotics and machine vision feedback control to optimize automation efficiency.
Source and External Links
Robotics: What Are Robots? - This page provides an overview of robotics, including the design, construction, and application of robots across various industries.
Robotics - Wikipedia - This article covers the interdisciplinary study and practice of robotics, focusing on the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Robotics | Definition, Applications, & Facts - This page defines robotics and explores its applications, including how robots perform tasks traditionally done by humans.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com