Microfactories emphasize compact, flexible production units designed for rapid scalability and customization, while lean manufacturing focuses on maximizing efficiency by eliminating waste and optimizing workflows within traditional large-scale facilities. Both approaches aim to enhance productivity and reduce costs but differ in scale, operational strategy, and adaptability to market demands. Explore the benefits of microfactories and lean manufacturing to determine the best fit for your production goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between microfactory and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and scalability in the manufacturing sector. Microfactories focus on small-scale, localized production with advanced automation, enabling rapid customization and reduced lead times. Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste and enhancing process efficiency across large-scale operations to minimize costs and maximize value. Selecting the appropriate approach impacts operational agility, cost management, and innovation potential within manufacturing enterprises.
Comparison Table
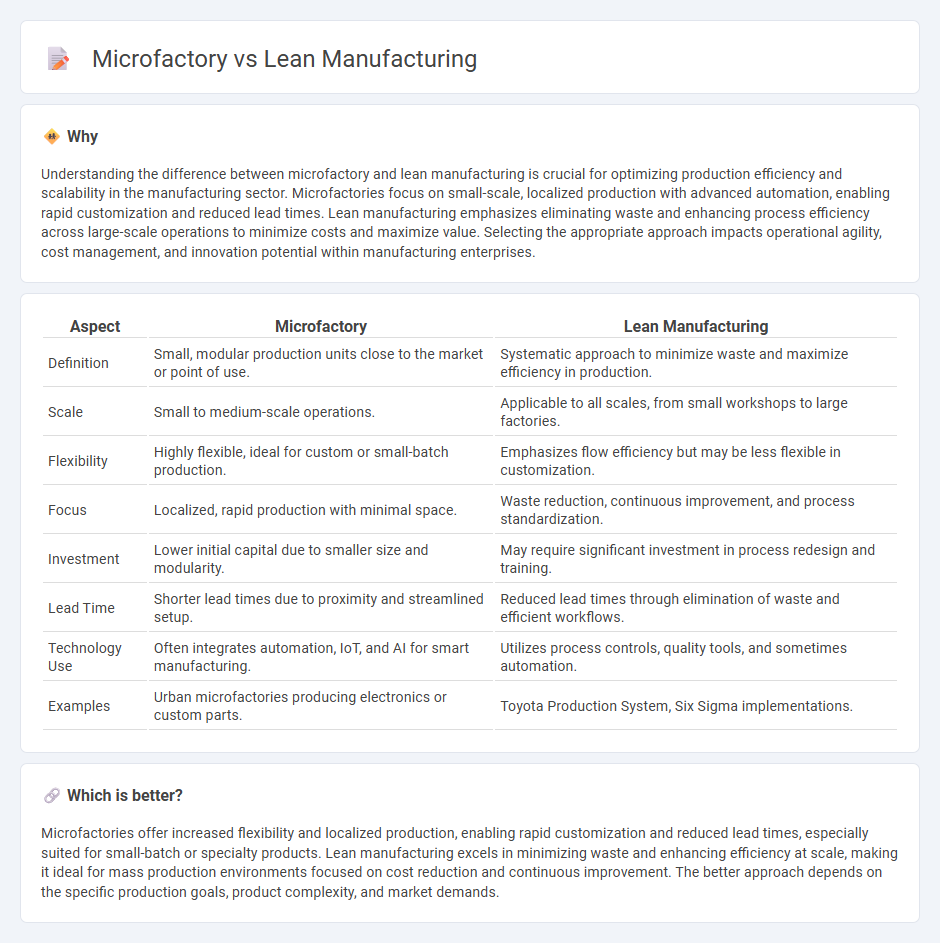
| Aspect | Microfactory | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small, modular production units close to the market or point of use. | Systematic approach to minimize waste and maximize efficiency in production. |
| Scale | Small to medium-scale operations. | Applicable to all scales, from small workshops to large factories. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, ideal for custom or small-batch production. | Emphasizes flow efficiency but may be less flexible in customization. |
| Focus | Localized, rapid production with minimal space. | Waste reduction, continuous improvement, and process standardization. |
| Investment | Lower initial capital due to smaller size and modularity. | May require significant investment in process redesign and training. |
| Lead Time | Shorter lead times due to proximity and streamlined setup. | Reduced lead times through elimination of waste and efficient workflows. |
| Technology Use | Often integrates automation, IoT, and AI for smart manufacturing. | Utilizes process controls, quality tools, and sometimes automation. |
| Examples | Urban microfactories producing electronics or custom parts. | Toyota Production System, Six Sigma implementations. |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer increased flexibility and localized production, enabling rapid customization and reduced lead times, especially suited for small-batch or specialty products. Lean manufacturing excels in minimizing waste and enhancing efficiency at scale, making it ideal for mass production environments focused on cost reduction and continuous improvement. The better approach depends on the specific production goals, product complexity, and market demands.
Connection
Microfactories embody lean manufacturing principles by minimizing waste, optimizing space, and streamlining production processes to enhance efficiency. Lean manufacturing techniques drive microfactories to focus on value-added activities and continuous improvement within compact, flexible setups. This integration allows manufacturers to achieve faster production cycles, lower costs, and improved product quality in small-scale, agile environments.
Key Terms
Lean Manufacturing:
Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste, improving process efficiency, and delivering maximum value by optimizing production workflows and minimizing resource usage. Techniques such as Just-In-Time (JIT), continuous improvement (Kaizen), and value stream mapping drive cost reduction and quality enhancement. Explore the core principles and benefits of lean manufacturing to transform your production strategy.
Just-in-Time (JIT)
Lean manufacturing emphasizes Just-in-Time (JIT) production to minimize inventory and reduce waste by producing only what is needed, when it is needed. Microfactories integrate JIT with compact, flexible manufacturing systems, allowing localized, rapid production close to demand points, enhancing responsiveness and reducing lead times. Explore how combining lean principles with microfactory design can revolutionize supply chain efficiency and operational agility.
Kaizen
Lean manufacturing emphasizes continuous improvement through Kaizen by systematically identifying and eliminating waste in large-scale production processes to enhance efficiency and product quality. Microfactories adopt Kaizen in a more flexible, localized environment, allowing rapid adjustments and real-time problem-solving within compact, automated setups. Explore how integrating Kaizen practices can optimize both lean manufacturing systems and microfactory operations for superior productivity.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production and supplier response times by eliminating non-value-adding activities, closely linked to just-in-time production and Toyota Production System principles that aim to reduce the seven wastes identified by Toyota engineers.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing minimizes waste and maximizes productivity in manufacturing systems, based on Toyota's production system and including continuous improvement (Kaizen) principles.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing maximizes productivity by eliminating waste, guided by five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection, aiming to do more with less.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com