Microfactories offer compact, scalable production units designed for localized manufacturing, reducing lead times and logistics costs. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds products layer by layer, enabling complex designs and minimizing material waste. Explore how these innovative manufacturing approaches transform production efficiency and customization.
Why it is important
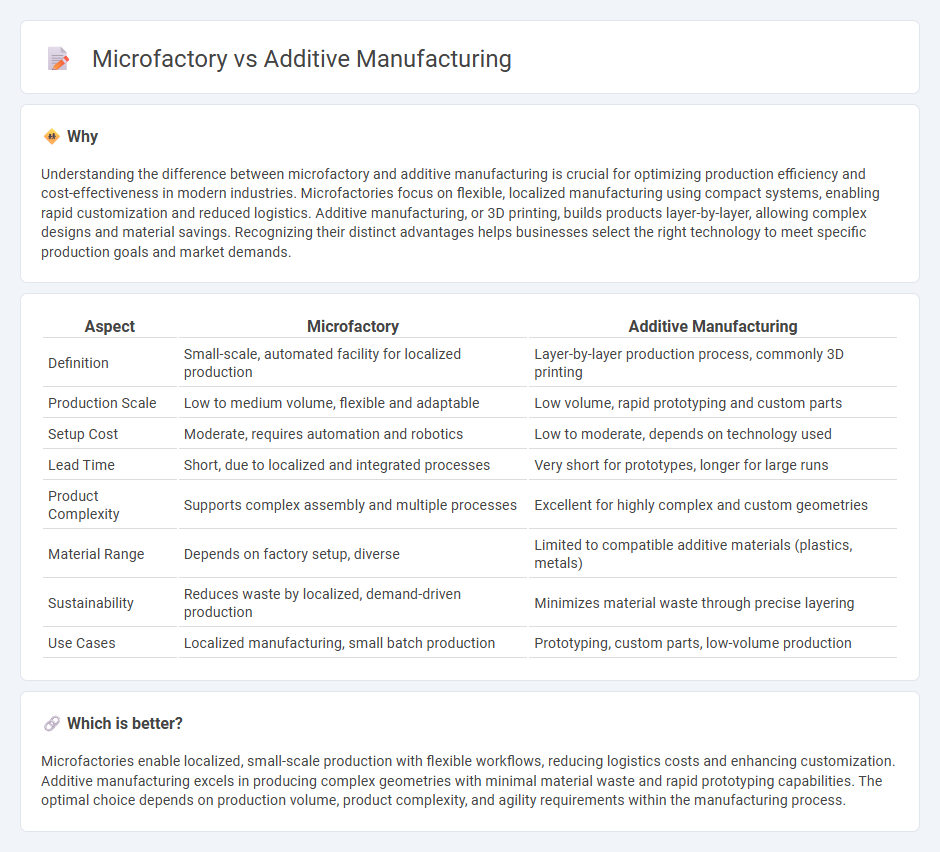
Understanding the difference between microfactory and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and cost-effectiveness in modern industries. Microfactories focus on flexible, localized manufacturing using compact systems, enabling rapid customization and reduced logistics. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, builds products layer-by-layer, allowing complex designs and material savings. Recognizing their distinct advantages helps businesses select the right technology to meet specific production goals and market demands.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfactory | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, automated facility for localized production | Layer-by-layer production process, commonly 3D printing |
| Production Scale | Low to medium volume, flexible and adaptable | Low volume, rapid prototyping and custom parts |
| Setup Cost | Moderate, requires automation and robotics | Low to moderate, depends on technology used |
| Lead Time | Short, due to localized and integrated processes | Very short for prototypes, longer for large runs |
| Product Complexity | Supports complex assembly and multiple processes | Excellent for highly complex and custom geometries |
| Material Range | Depends on factory setup, diverse | Limited to compatible additive materials (plastics, metals) |
| Sustainability | Reduces waste by localized, demand-driven production | Minimizes material waste through precise layering |
| Use Cases | Localized manufacturing, small batch production | Prototyping, custom parts, low-volume production |
Which is better?
Microfactories enable localized, small-scale production with flexible workflows, reducing logistics costs and enhancing customization. Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex geometries with minimal material waste and rapid prototyping capabilities. The optimal choice depends on production volume, product complexity, and agility requirements within the manufacturing process.
Connection
Microfactories leverage additive manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing to produce small-scale, customizable products with increased efficiency and reduced waste. Additive manufacturing enables microfactories to rapidly prototype and iterate designs, accelerating product development cycles. The integration of these technologies supports localized, on-demand production, minimizing supply chain dependencies and enhancing flexibility in manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, builds objects layer by layer from digital models, enabling rapid prototyping and complex geometries. Microfactories integrate 3D printing with automation, robotics, and real-time data analytics to create small-scale, highly flexible production units for localized manufacturing. Explore how combining additive manufacturing with microfactory systems can revolutionize efficient, customized production.
Distributed Production
Additive manufacturing enables localized production by fabricating complex parts layer-by-layer directly at or near the point of use, reducing supply chain dependencies. Microfactories integrate digital technologies and automation on a compact scale to support distributed production networks with flexible, scalable, and efficient manufacturing capabilities. Explore how these innovations are reshaping distributed production ecosystems and driving new business models.
Automation
Additive manufacturing leverages automated layer-by-layer material deposition to create complex parts with minimal human intervention, enhancing precision and reducing waste. Microfactories integrate automation across various production stages, enabling rapid, flexible manufacturing of diverse products within compact spaces. Explore the latest advancements in automation technologies driving these innovative manufacturing paradigms.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained - Additive manufacturing is the process of creating objects layer by layer from digital designs, typically using 3D printing, enabling rapid prototyping and functional product creation with diverse materials like polymers, metals, and biomaterials.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing (or 3D printing) builds parts layer by layer from digital designs, allowing complex, customized products while reducing waste, with applications from aerospace to biomedical implants.
What Is Additive Manufacturing? | 3D Printing Simulation - Additive manufacturing creates 3D objects from CAD models by layering materials using various printer technologies like powder bed fusion and material extrusion, optimizing for different materials and functions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com