Circular manufacturing emphasizes sustainability by minimizing waste and reusing materials throughout the production cycle, while smart manufacturing leverages advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to optimize efficiency and productivity. Both approaches transform traditional manufacturing by integrating innovation and resource management to enhance competitiveness in the global market. Discover how these manufacturing paradigms drive the future of industry.
Why it is important
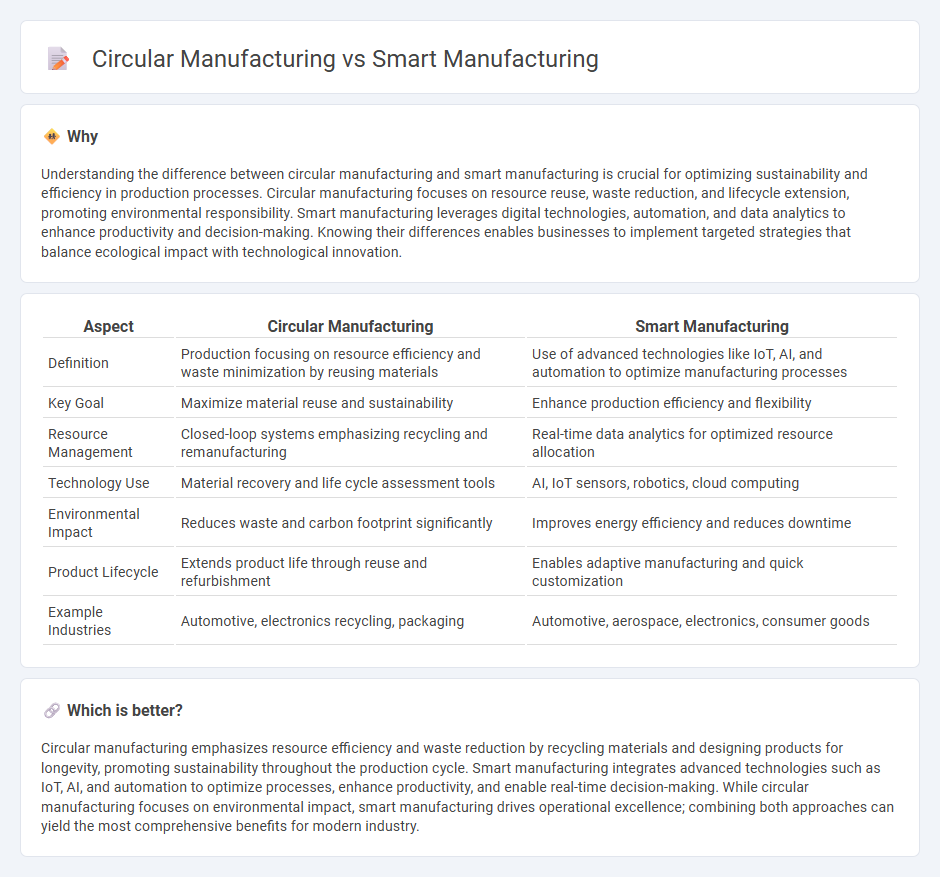
Understanding the difference between circular manufacturing and smart manufacturing is crucial for optimizing sustainability and efficiency in production processes. Circular manufacturing focuses on resource reuse, waste reduction, and lifecycle extension, promoting environmental responsibility. Smart manufacturing leverages digital technologies, automation, and data analytics to enhance productivity and decision-making. Knowing their differences enables businesses to implement targeted strategies that balance ecological impact with technological innovation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Manufacturing | Smart Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Production focusing on resource efficiency and waste minimization by reusing materials | Use of advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to optimize manufacturing processes |
| Key Goal | Maximize material reuse and sustainability | Enhance production efficiency and flexibility |
| Resource Management | Closed-loop systems emphasizing recycling and remanufacturing | Real-time data analytics for optimized resource allocation |
| Technology Use | Material recovery and life cycle assessment tools | AI, IoT sensors, robotics, cloud computing |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and carbon footprint significantly | Improves energy efficiency and reduces downtime |
| Product Lifecycle | Extends product life through reuse and refurbishment | Enables adaptive manufacturing and quick customization |
| Example Industries | Automotive, electronics recycling, packaging | Automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods |
Which is better?
Circular manufacturing emphasizes resource efficiency and waste reduction by recycling materials and designing products for longevity, promoting sustainability throughout the production cycle. Smart manufacturing integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to optimize processes, enhance productivity, and enable real-time decision-making. While circular manufacturing focuses on environmental impact, smart manufacturing drives operational excellence; combining both approaches can yield the most comprehensive benefits for modern industry.
Connection
Circular manufacturing and smart manufacturing are interconnected through the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and data analytics to optimize resource efficiency and reduce waste. Smart manufacturing enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, supporting circular economy principles by extending product lifecycles and facilitating material reuse. The synergy between these approaches enhances sustainable production processes and drives continuous improvement in manufacturing ecosystems.
Key Terms
IoT (for smart manufacturing)
Smart manufacturing leverages IoT technologies such as sensors, real-time data analytics, and connected devices to optimize production efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance predictive maintenance. Circular manufacturing integrates IoT to monitor material flow, track resource usage, and enable recycling processes that minimize waste and support sustainable product life cycles. Explore how IoT drives innovation in both manufacturing models to boost operational performance and environmental responsibility.
Closed-loop systems (for circular manufacturing)
Closed-loop systems in circular manufacturing emphasize the continuous reuse and recycling of materials, minimizing waste and resource consumption by integrating real-time data and automated feedback loops. Smart manufacturing uses advanced sensors, IoT, and AI to optimize production efficiency and product quality but primarily focuses on operational improvements rather than sustainability. Discover how closed-loop innovations drive the future of sustainable industrial practices.
Data analytics (for smart manufacturing)
Smart manufacturing leverages data analytics to optimize production processes, enhance predictive maintenance, and improve supply chain efficiency by analyzing real-time sensor data and machine learning algorithms. Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products and processes to minimize waste and enable recycling and reuse within a closed-loop system, emphasizing sustainability over operational data insights. Explore how data analytics transforms smart manufacturing to achieve higher productivity and reduced downtime.
Source and External Links
What Is Smart Manufacturing? - Smart manufacturing integrates data science and AI to create connected, knowledge-enabled processes that improve efficiency, productivity, and decision-making by using real-time data across factories and supply chains.
What Is Smart Manufacturing? - Smart manufacturing orchestrates business, physical, and digital processes with continuous monitoring, predictive analytics, and automation to enhance speed, quality, asset reliability, and profitability in manufacturing.
Smart manufacturing - Smart manufacturing employs computer-integrated systems and automation to boost adaptability, improve workplace safety, reduce human error, and optimize production efficiency through intelligent data analysis and connected devices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com