Zero defect manufacturing focuses on eliminating defects through rigorous quality control and precision processes to ensure consistently flawless products. Flexible manufacturing systems enhance adaptability by integrating automated machinery and computer-controlled operations, allowing rapid changes in production to meet diverse customer demands. Explore how these approaches can transform efficiency and product quality in modern manufacturing.
Why it is important
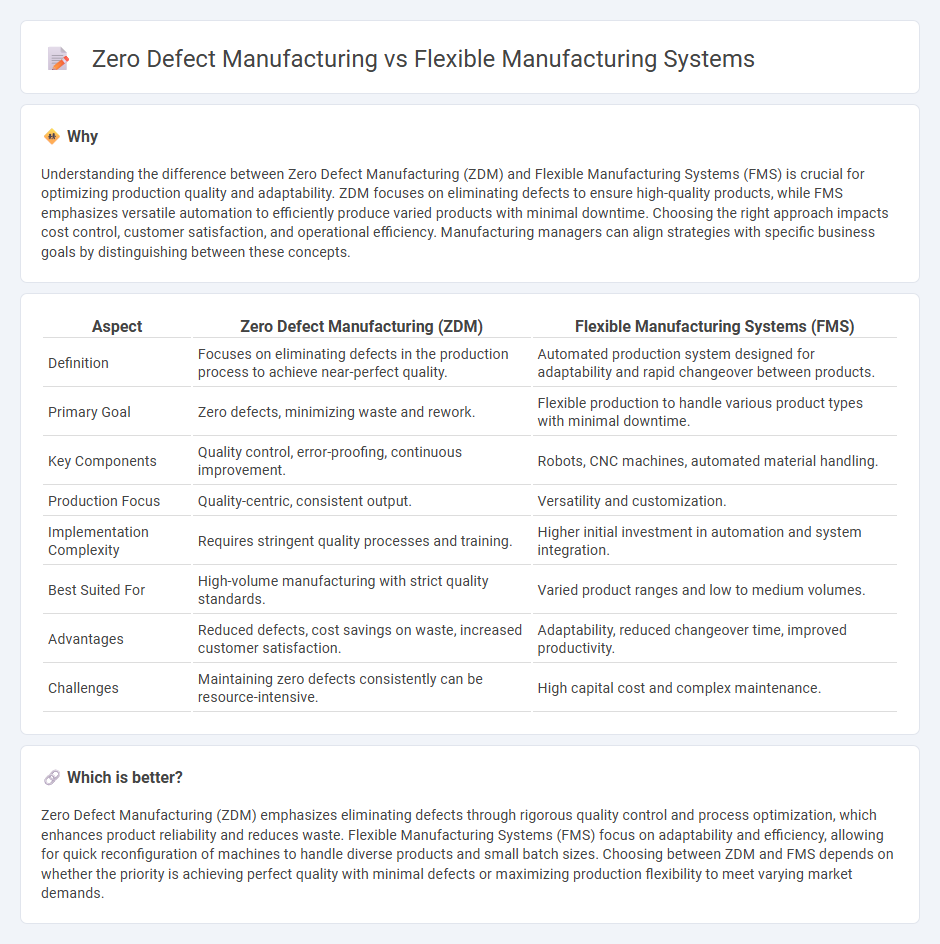
Understanding the difference between Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) and Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) is crucial for optimizing production quality and adaptability. ZDM focuses on eliminating defects to ensure high-quality products, while FMS emphasizes versatile automation to efficiently produce varied products with minimal downtime. Choosing the right approach impacts cost control, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Manufacturing managers can align strategies with specific business goals by distinguishing between these concepts.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) | Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on eliminating defects in the production process to achieve near-perfect quality. | Automated production system designed for adaptability and rapid changeover between products. |
| Primary Goal | Zero defects, minimizing waste and rework. | Flexible production to handle various product types with minimal downtime. |
| Key Components | Quality control, error-proofing, continuous improvement. | Robots, CNC machines, automated material handling. |
| Production Focus | Quality-centric, consistent output. | Versatility and customization. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires stringent quality processes and training. | Higher initial investment in automation and system integration. |
| Best Suited For | High-volume manufacturing with strict quality standards. | Varied product ranges and low to medium volumes. |
| Advantages | Reduced defects, cost savings on waste, increased customer satisfaction. | Adaptability, reduced changeover time, improved productivity. |
| Challenges | Maintaining zero defects consistently can be resource-intensive. | High capital cost and complex maintenance. |
Which is better?
Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) emphasizes eliminating defects through rigorous quality control and process optimization, which enhances product reliability and reduces waste. Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) focus on adaptability and efficiency, allowing for quick reconfiguration of machines to handle diverse products and small batch sizes. Choosing between ZDM and FMS depends on whether the priority is achieving perfect quality with minimal defects or maximizing production flexibility to meet varying market demands.
Connection
Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) and Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) are interconnected through their shared goal of enhancing production quality and efficiency. ZDM focuses on eliminating defects at every stage of the manufacturing process, while FMS enables rapid adaptation to varying product designs and volumes, ensuring consistent quality control across diverse operations. The integration of ZDM principles within FMS frameworks leads to streamlined workflows, reduced waste, and improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Key Terms
Flexible Manufacturing Systems:
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) optimize production by integrating computer-controlled machines and automated material handling, enabling rapid changeover and customization with minimal downtime. Unlike Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM), which emphasizes error reduction and quality control to eliminate defects, FMS prioritizes efficiency and flexibility in handling varying product types within a single facility. Discover how implementing FMS can transform your production scalability and productivity.
Automation
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) leverage advanced automation technologies to adapt quickly to product variations, enhancing production efficiency and reducing downtime. Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) emphasizes automated quality control and error-proofing mechanisms to eliminate defects throughout the production process. Explore how automation bridges the gap between flexibility and quality assurance in modern manufacturing.
CNC Machines
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) enhance CNC machine productivity by automating tool changes and part handling, enabling rapid adaptation to varied production demands while reducing lead times. Zero Defect Manufacturing (ZDM) on CNC machines focuses on quality control through real-time monitoring, error detection, and process optimization to minimize defects and improve yield. Explore more to understand how integrating FMS and ZDM elevates efficiency and quality in CNC machining environments.
Source and External Links
Flexible manufacturing system - A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a system with flexibility to adapt to changes in product types or operation sequences, consisting mainly of automated CNC machines, material handling, and central control, offering benefits like reduced costs, improved quality, and increased production rates.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) | What is ... - FMS is a computer-controlled system designed for adaptability through routing flexibility (changing operation sequences) and machine flexibility (using different machines for the same task), with various types including dedicated, sequential, engineered, random, and modular systems fitting diverse manufacturing needs.
What Are Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)? - Flexible Manufacturing Systems employ automation and come in types such as engineered, dedicated, sequential, random, and modular, with modular being the most advanced, offering versatility to switch manufacturing modes and adapt to varying product demands and volumes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com