Adaptive machining utilizes real-time data and advanced sensors to adjust machining processes dynamically, enhancing precision and reducing waste. Smart manufacturing integrates IoT, AI, and automation to optimize entire production lines, improving efficiency and flexibility at scale. Discover how these innovative approaches transform modern manufacturing for competitive advantage.
Why it is important
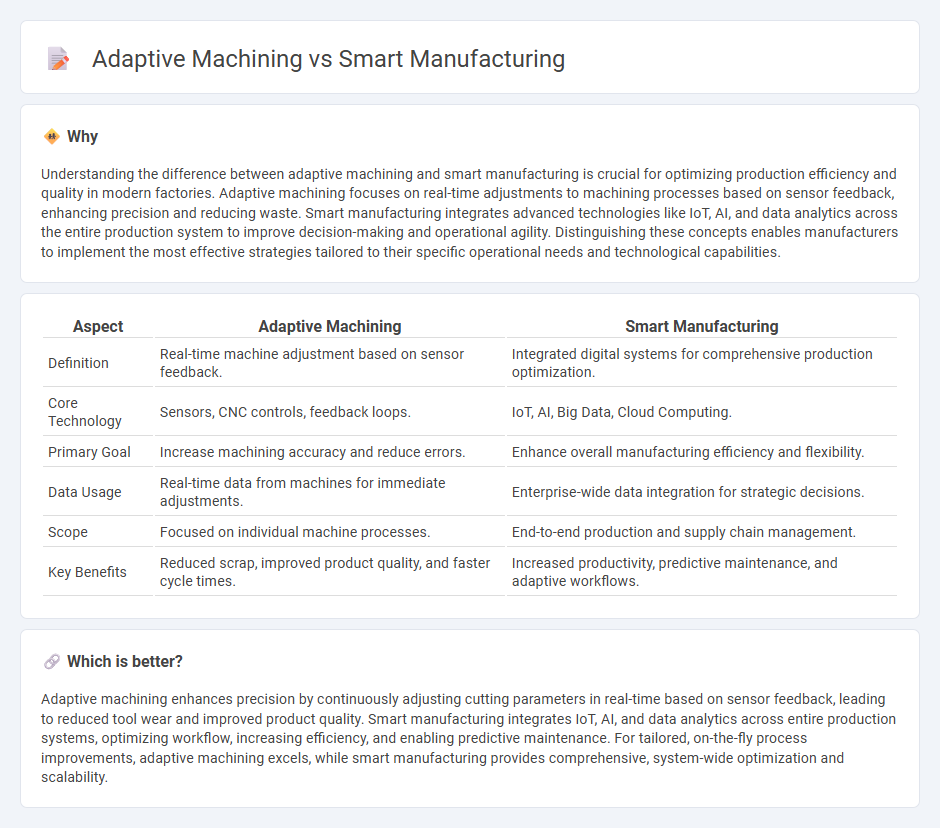
Understanding the difference between adaptive machining and smart manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and quality in modern factories. Adaptive machining focuses on real-time adjustments to machining processes based on sensor feedback, enhancing precision and reducing waste. Smart manufacturing integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and data analytics across the entire production system to improve decision-making and operational agility. Distinguishing these concepts enables manufacturers to implement the most effective strategies tailored to their specific operational needs and technological capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Adaptive Machining | Smart Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time machine adjustment based on sensor feedback. | Integrated digital systems for comprehensive production optimization. |
| Core Technology | Sensors, CNC controls, feedback loops. | IoT, AI, Big Data, Cloud Computing. |
| Primary Goal | Increase machining accuracy and reduce errors. | Enhance overall manufacturing efficiency and flexibility. |
| Data Usage | Real-time data from machines for immediate adjustments. | Enterprise-wide data integration for strategic decisions. |
| Scope | Focused on individual machine processes. | End-to-end production and supply chain management. |
| Key Benefits | Reduced scrap, improved product quality, and faster cycle times. | Increased productivity, predictive maintenance, and adaptive workflows. |
Which is better?
Adaptive machining enhances precision by continuously adjusting cutting parameters in real-time based on sensor feedback, leading to reduced tool wear and improved product quality. Smart manufacturing integrates IoT, AI, and data analytics across entire production systems, optimizing workflow, increasing efficiency, and enabling predictive maintenance. For tailored, on-the-fly process improvements, adaptive machining excels, while smart manufacturing provides comprehensive, system-wide optimization and scalability.
Connection
Adaptive machining leverages real-time data and sensor feedback to adjust machining processes dynamically, enhancing precision and reducing waste. Smart manufacturing integrates these adaptive techniques within a broader digital ecosystem, utilizing IoT, AI, and machine learning to optimize production efficiency and responsiveness. This connectivity enables seamless communication between machines and systems, driving intelligent decision-making and continuous process improvement.
Key Terms
IoT (Internet of Things)
Smart manufacturing integrates IoT technologies to enhance automation, data collection, and real-time monitoring across the entire production process, enabling predictive maintenance and improved operational efficiency. Adaptive machining leverages IoT sensors and data analytics to dynamically adjust machining parameters in response to real-time feedback, optimizing tool wear and product quality. Explore how IoT-driven strategies transform manufacturing by visiting our detailed analysis on smart manufacturing and adaptive machining.
Real-time feedback
Smart manufacturing leverages IoT sensors and AI analytics to provide real-time feedback that optimizes production efficiency and predicts maintenance needs. Adaptive machining utilizes immediate sensor data to dynamically adjust cutting parameters, improving precision and reducing material waste. Explore how real-time feedback technologies revolutionize these processes for enhanced operational performance.
Flexible automation
Smart manufacturing integrates IoT, AI, and big data analytics to optimize production efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality through real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Adaptive machining emphasizes flexible automation by utilizing CNC machines equipped with sensors and adaptive control systems, allowing dynamic adjustments to tool paths and cutting parameters in response to material variability and process feedback. Discover how these advanced technologies transform modern production systems for greater agility and performance.
Source and External Links
What Is Smart Manufacturing? | Oracle - Smart manufacturing combines modern data science and AI techniques to create highly connected, knowledge-enabled industrial processes that enhance productivity, sustainability, and economic performance by leveraging cloud technology and real-time data for better decision-making and system efficiency.
What Is Smart Manufacturing? - CESMII - Smart manufacturing integrates physical and digital processes using sensing, predictive analytics, and automation to improve manufacturing speed, quality, asset reliability, and cost-efficiency, resulting in enhanced profitability and innovation acceleration.
2025 Smart Manufacturing and Operations Survey - Deloitte - Smart manufacturing adoption focuses on sensors, data analytics, automation, and AI, with widespread use of cloud computing, IIoT, and 5G, enabling manufacturers to monitor environments in real-time and improve operational agility through standards and scalable architectures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com