Cloud manufacturing integrates distributed computing resources and IoT to optimize production processes through real-time data sharing and scalable infrastructure, enhancing flexibility and collaboration across global supply chains. Smart manufacturing leverages advanced automation, AI, and sensor technologies to enable predictive maintenance, improve product quality, and increase operational efficiency on the factory floor. Explore the distinct advantages and applications of cloud manufacturing and smart manufacturing to understand their impact on the future of industrial production.
Why it is important
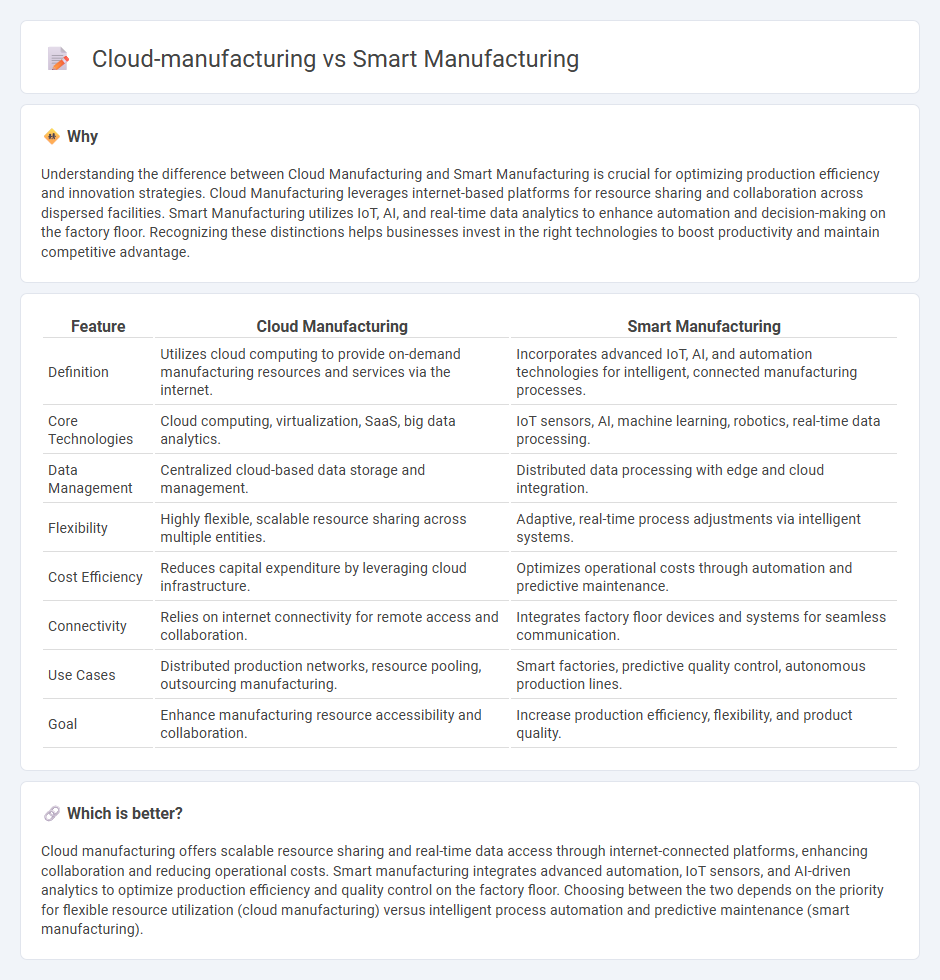
Understanding the difference between Cloud Manufacturing and Smart Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and innovation strategies. Cloud Manufacturing leverages internet-based platforms for resource sharing and collaboration across dispersed facilities. Smart Manufacturing utilizes IoT, AI, and real-time data analytics to enhance automation and decision-making on the factory floor. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses invest in the right technologies to boost productivity and maintain competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cloud Manufacturing | Smart Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Utilizes cloud computing to provide on-demand manufacturing resources and services via the internet. | Incorporates advanced IoT, AI, and automation technologies for intelligent, connected manufacturing processes. |
| Core Technologies | Cloud computing, virtualization, SaaS, big data analytics. | IoT sensors, AI, machine learning, robotics, real-time data processing. |
| Data Management | Centralized cloud-based data storage and management. | Distributed data processing with edge and cloud integration. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, scalable resource sharing across multiple entities. | Adaptive, real-time process adjustments via intelligent systems. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces capital expenditure by leveraging cloud infrastructure. | Optimizes operational costs through automation and predictive maintenance. |
| Connectivity | Relies on internet connectivity for remote access and collaboration. | Integrates factory floor devices and systems for seamless communication. |
| Use Cases | Distributed production networks, resource pooling, outsourcing manufacturing. | Smart factories, predictive quality control, autonomous production lines. |
| Goal | Enhance manufacturing resource accessibility and collaboration. | Increase production efficiency, flexibility, and product quality. |
Which is better?
Cloud manufacturing offers scalable resource sharing and real-time data access through internet-connected platforms, enhancing collaboration and reducing operational costs. Smart manufacturing integrates advanced automation, IoT sensors, and AI-driven analytics to optimize production efficiency and quality control on the factory floor. Choosing between the two depends on the priority for flexible resource utilization (cloud manufacturing) versus intelligent process automation and predictive maintenance (smart manufacturing).
Connection
Cloud manufacturing integrates IoT, AI, and big data to enable real-time data sharing, which forms the backbone of smart manufacturing systems for enhanced automation and decision-making. Smart manufacturing leverages cloud-based platforms to optimize production processes through predictive analytics and remote monitoring, driving efficiency and flexibility across the supply chain. This connectivity fosters adaptive manufacturing environments, reducing downtime and improving product quality by synchronizing physical and digital workflows.
Key Terms
IoT Integration
Smart manufacturing leverages IoT integration to enable real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and enhanced automation within factory environments. Cloud-manufacturing extends these capabilities by utilizing cloud computing for scalable data storage, remote monitoring, and collaborative supply chain management across distributed facilities. Explore how IoT integration transforms production efficiency and connectivity in both smart and cloud-manufacturing systems.
Data Centralization
Smart manufacturing integrates IoT devices and advanced analytics to optimize production processes on-site, creating localized data ecosystems. Cloud manufacturing centralizes data storage and computation in the cloud, enabling real-time global access and collaborative decision-making across distributed facilities. Explore how data centralization transforms manufacturing efficiency and agility by learning more about these innovative approaches.
Real-time Analytics
Smart manufacturing integrates IoT sensors and edge computing to enable real-time analytics directly on the factory floor, reducing latency and improving decision-making speed. Cloud manufacturing leverages centralized cloud platforms to process vast amounts of production data, offering scalability and advanced analytics capabilities but with potential latency issues. Explore how these approaches compare in optimizing real-time analytics for manufacturing efficiency and agility.
Source and External Links
What Is Smart Manufacturing? | Oracle - Smart manufacturing is the integration of modern data science and artificial intelligence to create highly connected, knowledge-enabled industrial enterprises that enhance productivity, sustainability, and economic performance by leveraging real-time data across factories and supply chains.
What Is Smart Manufacturing? - CESMII - Smart manufacturing is the information-driven, event-driven, and efficient orchestration of business, physical, and digital processes using integration, monitoring, predictive analytics, and automation to achieve measurable improvements in speed, quality, cost, and asset reliability.
Smart Manufacturing | Rockwell Automation | US - Smart manufacturing provides actionable information and insights to optimize productivity, quality, risk management, and sustainability, while offering the flexibility to quickly address issues, reduce downtime, and improve worker safety.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com