Digital twinning enables real-time simulation and monitoring of production processes by creating virtual replicas of physical assets, enhancing predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and optimizing workflows to maximize value and reduce costs throughout the production cycle. Explore how integrating digital twinning with lean principles can revolutionize manufacturing performance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital twinning and Lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and innovation. Digital twinning creates virtual replicas of physical assets to monitor and simulate performance in real-time, enhancing predictive maintenance and design improvements. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and streamlining processes to boost productivity and reduce costs. Knowing their distinct roles helps manufacturers leverage cutting-edge technology while maintaining operational excellence.
Comparison Table
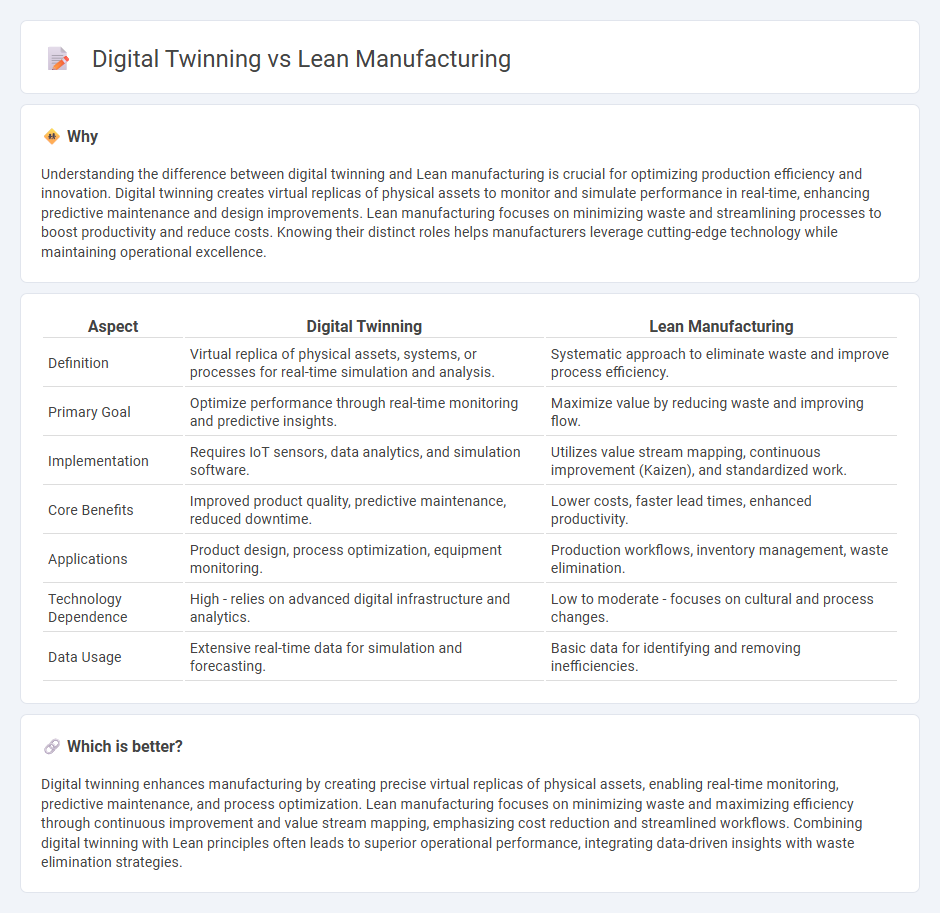
| Aspect | Digital Twinning | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets, systems, or processes for real-time simulation and analysis. | Systematic approach to eliminate waste and improve process efficiency. |
| Primary Goal | Optimize performance through real-time monitoring and predictive insights. | Maximize value by reducing waste and improving flow. |
| Implementation | Requires IoT sensors, data analytics, and simulation software. | Utilizes value stream mapping, continuous improvement (Kaizen), and standardized work. |
| Core Benefits | Improved product quality, predictive maintenance, reduced downtime. | Lower costs, faster lead times, enhanced productivity. |
| Applications | Product design, process optimization, equipment monitoring. | Production workflows, inventory management, waste elimination. |
| Technology Dependence | High - relies on advanced digital infrastructure and analytics. | Low to moderate - focuses on cultural and process changes. |
| Data Usage | Extensive real-time data for simulation and forecasting. | Basic data for identifying and removing inefficiencies. |
Which is better?
Digital twinning enhances manufacturing by creating precise virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency through continuous improvement and value stream mapping, emphasizing cost reduction and streamlined workflows. Combining digital twinning with Lean principles often leads to superior operational performance, integrating data-driven insights with waste elimination strategies.
Connection
Digital twinning enhances Lean manufacturing by providing real-time, data-driven simulations that identify inefficiencies and waste in production processes. This integration allows manufacturers to optimize workflows, reduce downtime, and accelerate continuous improvement cycles by visualizing potential changes before implementation. Leveraging digital twins supports Lean principles by enabling precise monitoring and adaptive control, ultimately driving higher productivity and cost savings.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction by eliminating non-value-added activities through techniques such as 5S, Kaizen, and Just-In-Time production, targeting defects, overproduction, and excess inventory. Digital twinning enhances waste reduction by creating real-time, virtual replicas of physical processes, enabling predictive maintenance, process optimization, and rapid identification of inefficiencies. Explore how combining lean principles with digital twinning technologies can revolutionize waste management strategies in modern manufacturing.
Real-time Simulation
Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste and optimizing workflows to enhance production efficiency, while digital twinning leverages real-time simulation to create virtual replicas of physical systems for predictive analysis and process improvements. Real-time simulation in digital twinning enables immediate data-driven decision-making, reducing downtime and enhancing responsiveness in manufacturing operations. Discover how integrating lean principles with digital twinning can revolutionize production efficiency and agility.
Process Optimization
Lean manufacturing enhances process optimization by minimizing waste, streamlining workflows, and improving efficiency through continuous improvement techniques such as value stream mapping and Just-In-Time production. Digital twinning advances process optimization by creating virtual replicas of physical systems, enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and predictive analytics to identify bottlenecks and optimize performance. Explore how integrating lean manufacturing principles with digital twin technology can revolutionize process optimization in your operations.
Source and External Links
Lean Manufacturing - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing waste and maximizing efficiency in production systems, closely related to the Toyota Production System.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology that minimizes waste while maximizing productivity, based on the Toyota Production System to improve efficiency and quality.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing is a production process that aims to maximize productivity by minimizing waste, using five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com