Machine vision enhances manufacturing processes by providing real-time visual data for automated inspection and quality control, improving accuracy and reducing defects. Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling simulation, monitoring, and predictive maintenance to optimize equipment performance and minimize downtime. Explore how integrating machine vision with digital twins revolutionizes smart manufacturing for greater efficiency.
Why it is important
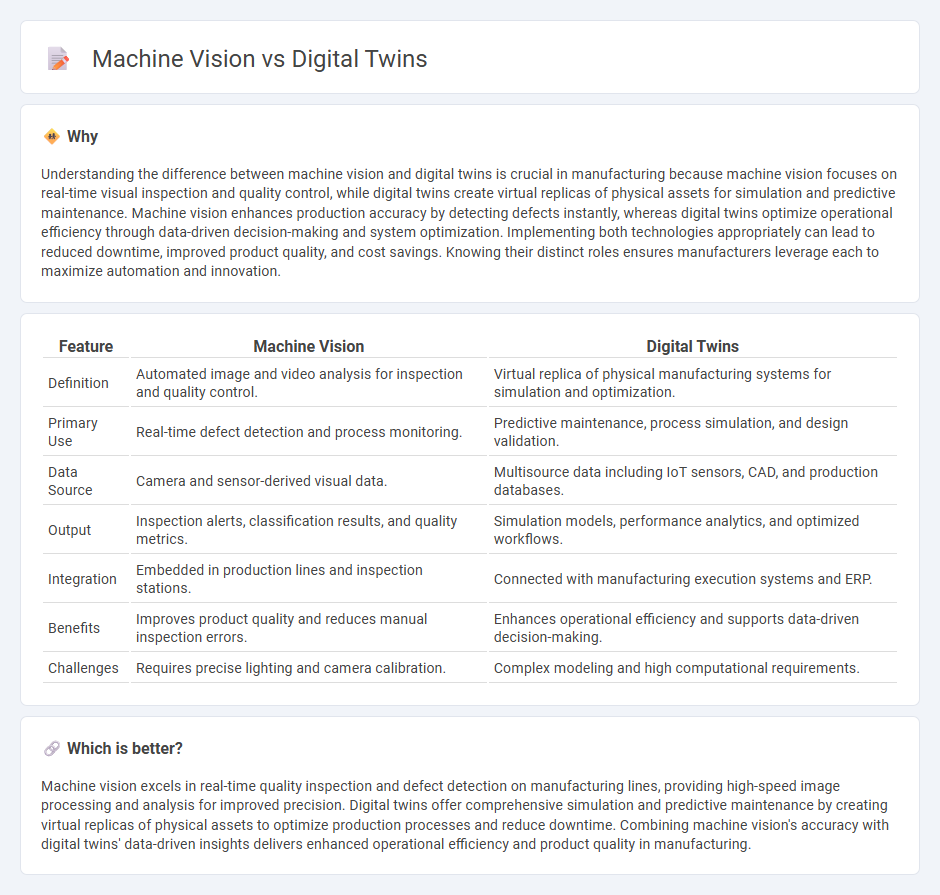
Understanding the difference between machine vision and digital twins is crucial in manufacturing because machine vision focuses on real-time visual inspection and quality control, while digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets for simulation and predictive maintenance. Machine vision enhances production accuracy by detecting defects instantly, whereas digital twins optimize operational efficiency through data-driven decision-making and system optimization. Implementing both technologies appropriately can lead to reduced downtime, improved product quality, and cost savings. Knowing their distinct roles ensures manufacturers leverage each to maximize automation and innovation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Machine Vision | Digital Twins |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated image and video analysis for inspection and quality control. | Virtual replica of physical manufacturing systems for simulation and optimization. |
| Primary Use | Real-time defect detection and process monitoring. | Predictive maintenance, process simulation, and design validation. |
| Data Source | Camera and sensor-derived visual data. | Multisource data including IoT sensors, CAD, and production databases. |
| Output | Inspection alerts, classification results, and quality metrics. | Simulation models, performance analytics, and optimized workflows. |
| Integration | Embedded in production lines and inspection stations. | Connected with manufacturing execution systems and ERP. |
| Benefits | Improves product quality and reduces manual inspection errors. | Enhances operational efficiency and supports data-driven decision-making. |
| Challenges | Requires precise lighting and camera calibration. | Complex modeling and high computational requirements. |
Which is better?
Machine vision excels in real-time quality inspection and defect detection on manufacturing lines, providing high-speed image processing and analysis for improved precision. Digital twins offer comprehensive simulation and predictive maintenance by creating virtual replicas of physical assets to optimize production processes and reduce downtime. Combining machine vision's accuracy with digital twins' data-driven insights delivers enhanced operational efficiency and product quality in manufacturing.
Connection
Machine vision captures real-time visual data of manufacturing processes, enabling precise quality control and defect detection. Digital twins use this data to create accurate virtual replicas of production lines, facilitating simulation and optimization of operations. Integrating machine vision with digital twins enhances predictive maintenance and accelerates decision-making in smart manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Simulation
Digital twins create dynamic virtual models of physical systems, enabling real-time simulation and predictive analysis to optimize performance and maintenance. Machine vision primarily involves image processing and analysis for quality control and automated inspection, offering limited simulation capabilities. Explore the full potential of digital twins in enhancing simulation technology for advanced industrial applications.
Image Processing
Digital twins utilize image processing by integrating real-time visual data to create dynamic, virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling predictive maintenance and performance optimization. Machine vision systems focus on analyzing and interpreting images for quality control, defect detection, and automated inspection in manufacturing processes. Explore how the synergy between digital twins and machine vision enhances industrial automation and operational efficiency.
Real-time Monitoring
Digital twins provide a dynamic virtual replica of physical assets, enabling real-time monitoring through continuous data synchronization and simulation of operational conditions. Machine vision captures and analyzes visual data instantly to detect anomalies and guide automation processes on the production line. Explore how integrating both technologies can enhance real-time monitoring efficiency and decision-making.
Source and External Links
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated data-driven virtual representation of real-world entities and processes, synchronized with the physical counterpart to enable holistic understanding, continuous improvement, decision-making, and intervention through real-time and historical data.
What Is a Digital Twin? | IBM - A digital twin is a virtual model that accurately reflects a physical object throughout its lifecycle, using real-time sensor data and simulation to analyze performance and optimize the physical entity dynamically.
Digital twin - Wikipedia - Digital twins serve as digital counterparts to physical products or systems for simulation, monitoring, maintenance, and predictive analytics, originating from NASA's space program and expanding into manufacturing and business process virtualization.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com