Green steel production utilizes hydrogen or electric arc furnace methods powered by renewable energy, significantly reducing carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnace steel, which relies on coal-based coke for iron ore reduction and produces substantial CO2. Innovations in green steel manufacturing, such as direct reduced iron (DRI) technology combined with renewable energy, are key to decarbonizing the steel industry. Discover how these advancements are transforming steel production towards a sustainable future.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between green steel and blast furnace steel is crucial for evaluating environmental impact and sustainability in manufacturing. Green steel is produced using renewable energy and produces significantly lower carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnace steel. This knowledge helps manufacturers reduce their carbon footprint and comply with evolving regulations. Choosing green steel supports global efforts to combat climate change and promotes a more sustainable industrial future.
Comparison Table
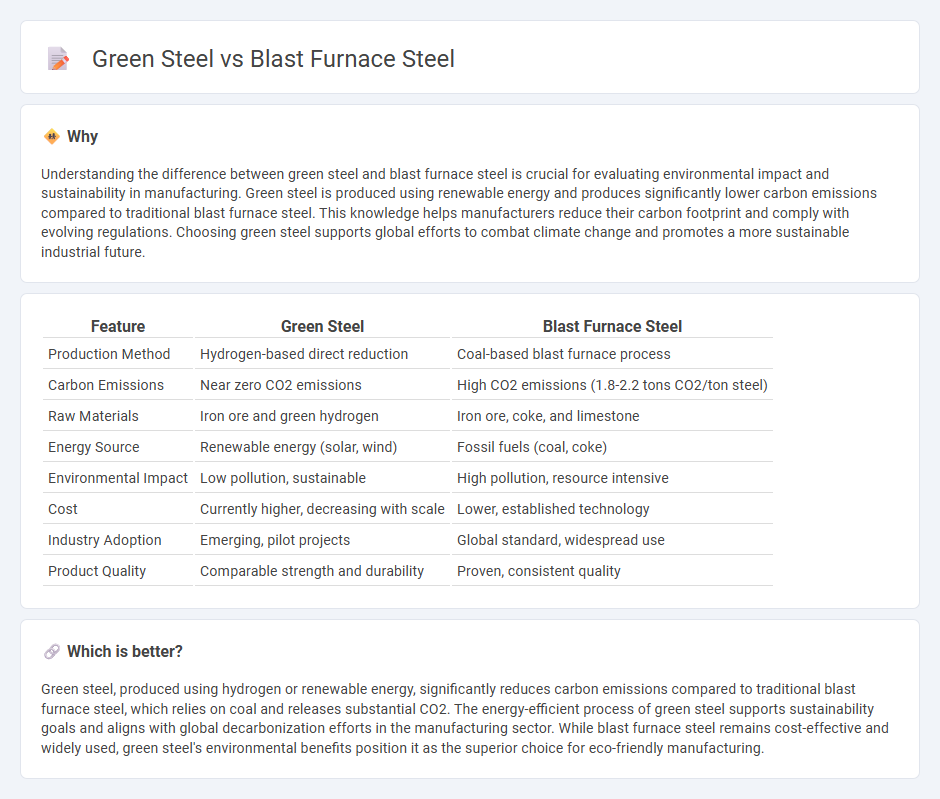
| Feature | Green Steel | Blast Furnace Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Production Method | Hydrogen-based direct reduction | Coal-based blast furnace process |
| Carbon Emissions | Near zero CO2 emissions | High CO2 emissions (1.8-2.2 tons CO2/ton steel) |
| Raw Materials | Iron ore and green hydrogen | Iron ore, coke, and limestone |
| Energy Source | Renewable energy (solar, wind) | Fossil fuels (coal, coke) |
| Environmental Impact | Low pollution, sustainable | High pollution, resource intensive |
| Cost | Currently higher, decreasing with scale | Lower, established technology |
| Industry Adoption | Emerging, pilot projects | Global standard, widespread use |
| Product Quality | Comparable strength and durability | Proven, consistent quality |
Which is better?
Green steel, produced using hydrogen or renewable energy, significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnace steel, which relies on coal and releases substantial CO2. The energy-efficient process of green steel supports sustainability goals and aligns with global decarbonization efforts in the manufacturing sector. While blast furnace steel remains cost-effective and widely used, green steel's environmental benefits position it as the superior choice for eco-friendly manufacturing.
Connection
Green steel production utilizes hydrogen or electric arc furnaces to reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnace steel, which relies on coal-based coke for iron ore reduction. Blast furnace steel remains dominant for large-scale manufacturing but faces increasing environmental regulations driving the shift toward green steel technologies. The integration of green steel innovations aims to decarbonize the steel industry while maintaining the mechanical properties and scalability offered by blast furnace processes.
Key Terms
Carbon emissions
Blast furnace steel production emits approximately 1.8 to 2.2 tons of CO2 per ton of steel, primarily due to the combustion of coke as both a fuel and reducing agent. Green steel significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing hydrogen or renewable energy sources in direct reduction processes, potentially cutting CO2 emissions by up to 95%. Discover more about how green steel technologies are transforming sustainable manufacturing.
Renewable energy
Blast furnace steel production primarily relies on coal as a reducing agent, leading to significant carbon emissions, whereas green steel uses renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydrogen to drastically reduce its carbon footprint. The integration of renewable energy in green steel manufacturing not only decreases reliance on fossil fuels but also supports global decarbonization goals. Explore how renewable energy advancements are transforming the steel industry toward sustainable production.
Iron ore reduction
Blast furnace steel production relies heavily on carbon-intensive reduction of iron ore using coke, resulting in significant CO2 emissions. Green steel utilizes hydrogen or renewable energy sources to reduce iron ore, drastically lowering the environmental footprint by minimizing carbon output. Explore more about how innovative iron ore reduction technologies are revolutionizing sustainable steel manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Blast Furnace Process - A blast furnace is a large steel cylinder lined with refractory material that uses coke, iron ore, and limestone to produce molten iron, which is then processed further into steel.
Blast furnace - Wikipedia - The blast furnace smelts iron ore, coke, and limestone together under a blast of hot air, yielding pig iron, the key raw material for steel production.
Blast furnace | Definition, Temperature, Diagrams, & Facts | Britannica - Blast furnaces heat iron ore, coke, and limestone in a continuous process to form pig iron, which is later refined into steel.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com