Edge computing processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making crucial for modern manufacturing automation. Data centers centralize storage and computation, offering robust processing power and large-scale data management essential for enterprise-level analytics. Explore further to understand how each approach impacts manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
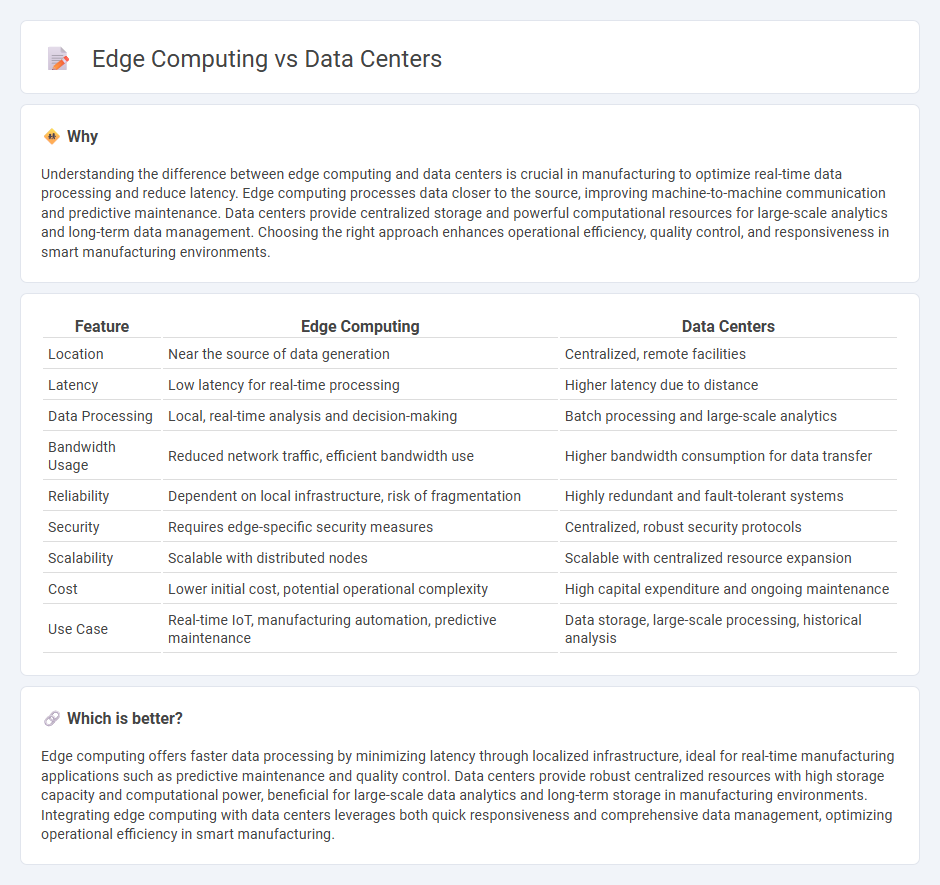
Understanding the difference between edge computing and data centers is crucial in manufacturing to optimize real-time data processing and reduce latency. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, improving machine-to-machine communication and predictive maintenance. Data centers provide centralized storage and powerful computational resources for large-scale analytics and long-term data management. Choosing the right approach enhances operational efficiency, quality control, and responsiveness in smart manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Computing | Data Centers |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Near the source of data generation | Centralized, remote facilities |
| Latency | Low latency for real-time processing | Higher latency due to distance |
| Data Processing | Local, real-time analysis and decision-making | Batch processing and large-scale analytics |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduced network traffic, efficient bandwidth use | Higher bandwidth consumption for data transfer |
| Reliability | Dependent on local infrastructure, risk of fragmentation | Highly redundant and fault-tolerant systems |
| Security | Requires edge-specific security measures | Centralized, robust security protocols |
| Scalability | Scalable with distributed nodes | Scalable with centralized resource expansion |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, potential operational complexity | High capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance |
| Use Case | Real-time IoT, manufacturing automation, predictive maintenance | Data storage, large-scale processing, historical analysis |
Which is better?
Edge computing offers faster data processing by minimizing latency through localized infrastructure, ideal for real-time manufacturing applications such as predictive maintenance and quality control. Data centers provide robust centralized resources with high storage capacity and computational power, beneficial for large-scale data analytics and long-term storage in manufacturing environments. Integrating edge computing with data centers leverages both quick responsiveness and comprehensive data management, optimizing operational efficiency in smart manufacturing.
Connection
Edge computing enhances manufacturing efficiency by processing data at or near the source, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making on the factory floor. Data centers support this infrastructure by providing centralized storage, powerful analytics, and computational resources to manage large-scale manufacturing data securely. The integration of edge devices with data centers enables seamless data flow and optimized operations in Industry 4.0 environments.
Key Terms
Latency
Data centers often face higher latency due to centralized processing and long-distance data transmission, which can impact real-time applications. Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, enhancing response times for IoT devices and time-sensitive services. Explore how latency improvements in edge computing transform network performance and user experience.
Data Processing Location
Data centers centralize data processing in large, remote facilities equipped with high-performance servers and extensive cooling systems, enabling efficient handling of massive workloads and complex computations. Edge computing shifts data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use by utilizing local devices such as IoT sensors, gateways, or edge servers for real-time analytics and faster decision-making. Explore how optimizing data processing locations enhances performance and scalability in modern IT infrastructures.
Scalability
Data centers offer centralized scalability by enabling massive resource pooling and high-density computing power, which supports large-scale applications and enterprise workloads. Edge computing enhances scalability by distributing processing closer to data sources, reducing latency and bandwidth usage while enabling real-time data handling at the network edge. Explore the detailed comparison to understand which scalability approach best suits your business needs.
Source and External Links
What Is a Data Center? | Importance & Types - A data center is a physical facility with servers, storage, and networking equipment that organizations use to store, manage, and distribute data, increasingly leveraging cloud services for scalability and security.
Data center - Data centers are buildings or dedicated spaces housing computer systems, with critical infrastructure for power, connectivity, and environmental controls, and vary from onsite to hyperscale and edge centers depending on their purpose.
What Is a Data Center? - Historically on-premises IT spaces, data centers have evolved with cloud computing into remote or virtualized facilities supporting multiple customers and scalable, on-demand IT resources.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com