Dark factories eliminate human presence by using fully automated systems and robotics to operate continuously, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs. The contrast between traditional automation, which may still require human oversight, and dark factory models highlights advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT integration. Explore how these innovations transform manufacturing processes and redefine industry standards.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a dark factory and automation is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and reducing operational costs. A dark factory operates fully automated without human presence, enabling 24/7 production in controlled environments. Automation refers to the integration of technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention, which can be partial or full depending on the factory setup. Recognizing these distinctions helps manufacturers implement the most effective strategies for productivity, safety, and scalability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Automation |
|---|---|---|
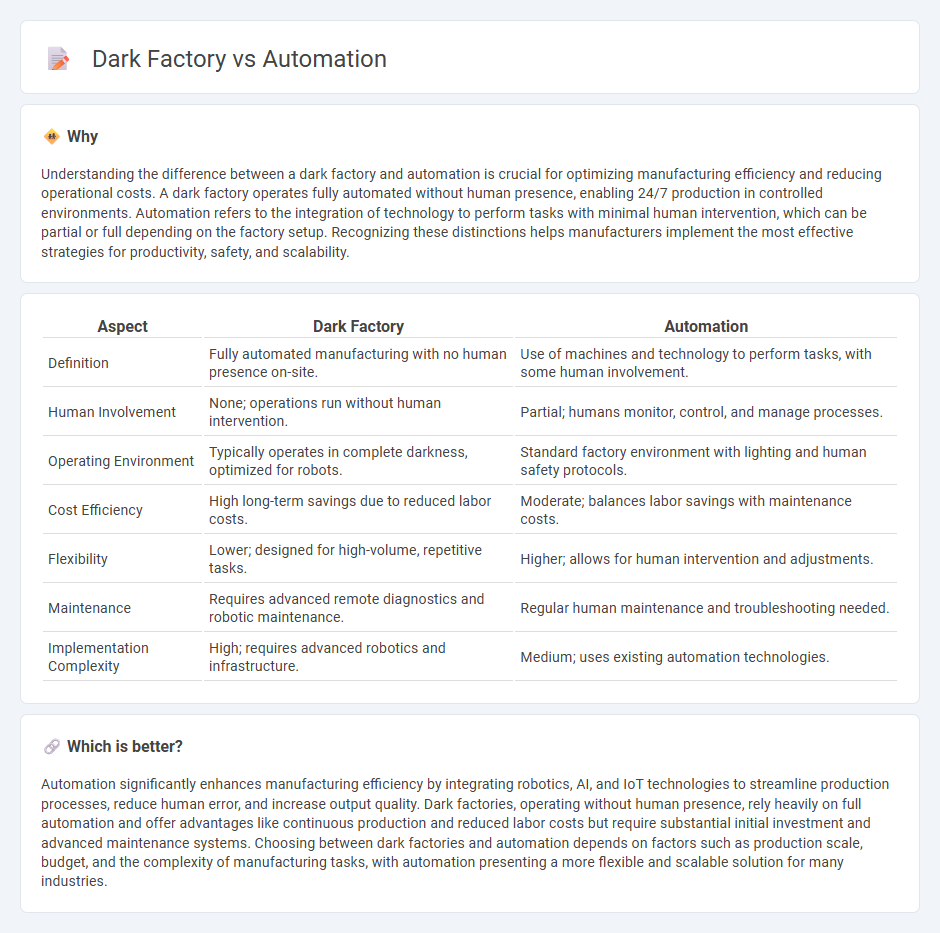
| Definition | Fully automated manufacturing with no human presence on-site. | Use of machines and technology to perform tasks, with some human involvement. |
| Human Involvement | None; operations run without human intervention. | Partial; humans monitor, control, and manage processes. |
| Operating Environment | Typically operates in complete darkness, optimized for robots. | Standard factory environment with lighting and human safety protocols. |
| Cost Efficiency | High long-term savings due to reduced labor costs. | Moderate; balances labor savings with maintenance costs. |
| Flexibility | Lower; designed for high-volume, repetitive tasks. | Higher; allows for human intervention and adjustments. |
| Maintenance | Requires advanced remote diagnostics and robotic maintenance. | Regular human maintenance and troubleshooting needed. |
| Implementation Complexity | High; requires advanced robotics and infrastructure. | Medium; uses existing automation technologies. |
Which is better?
Automation significantly enhances manufacturing efficiency by integrating robotics, AI, and IoT technologies to streamline production processes, reduce human error, and increase output quality. Dark factories, operating without human presence, rely heavily on full automation and offer advantages like continuous production and reduced labor costs but require substantial initial investment and advanced maintenance systems. Choosing between dark factories and automation depends on factors such as production scale, budget, and the complexity of manufacturing tasks, with automation presenting a more flexible and scalable solution for many industries.
Connection
Dark factories operate without human presence by utilizing fully automated systems and robotics, enhancing production efficiency and reducing operational costs. Advanced sensors, AI-driven machinery, and IoT integration enable continuous, error-free manufacturing processes in dark factories. This seamless connection between automation and dark factory design supports high scalability, precision, and 24/7 production capabilities.
Key Terms
Robotics
Robotics plays a pivotal role in both automation and dark factories, with automation encompassing a broad range of technologies that streamline processes through robotics integration, while dark factories operate entirely without human presence, relying exclusively on advanced robotic systems for continuous, 24/7 production. Dark factories utilize high-end robotics combined with AI-driven monitoring to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and minimize downtime, surpassing traditional automation setups that often still require human oversight. Explore how cutting-edge robotic innovations are transforming manufacturing by visiting our detailed insights on automation and dark factory technologies.
Lights-out Manufacturing
Lights-out manufacturing represents a fully automated production process where factories operate without human intervention, contrasting traditional automation that often requires human oversight. This dark factory setup leverages advanced robotics, AI, and IoT to achieve continuous, efficient, and error-free production cycles. Discover how lights-out manufacturing transforms industrial efficiency and reduces operational costs by exploring its full potential.
Human Intervention
Automation reduces human intervention by utilizing machines and software to perform repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency and consistency in production processes. Dark factories operate with minimal human presence, relying heavily on automated systems and sensors to monitor and control operations in real-time. Explore how optimizing human intervention can balance productivity and flexibility in modern manufacturing.
Source and External Links
Automation - Wikipedia - Automation is a broad term describing technologies that reduce human intervention in processes through predetermined decision criteria, often combining mechanical, electrical, electronic, and computer systems to improve efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings in industries such as manufacturing, aviation, and banking.
What Is Automation? - IBM - Automation applies technology, programs, robotics, or processes to achieve outcomes with minimal human input, enhancing productivity, profitability, efficiency, and customer satisfaction across various sectors including business process automation and industrial manufacturing.
Understanding Automation - Red Hat - Automation refers to using technology to perform tasks with reduced human assistance and is widely applied in IT, cloud management, business process automation, robotic process automation, industrial automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com