Lattice structure design offers enhanced material efficiency and weight reduction by utilizing a network of interconnected nodes and struts, optimizing load distribution in complex geometries. Truss structure design focuses on triangular units that provide strength and rigidity, commonly employed in bridges and frameworks due to their predictable mechanical behavior and ease of fabrication. Explore the advantages and applications of each design to determine the optimal solution for your manufacturing needs.
Why it is important
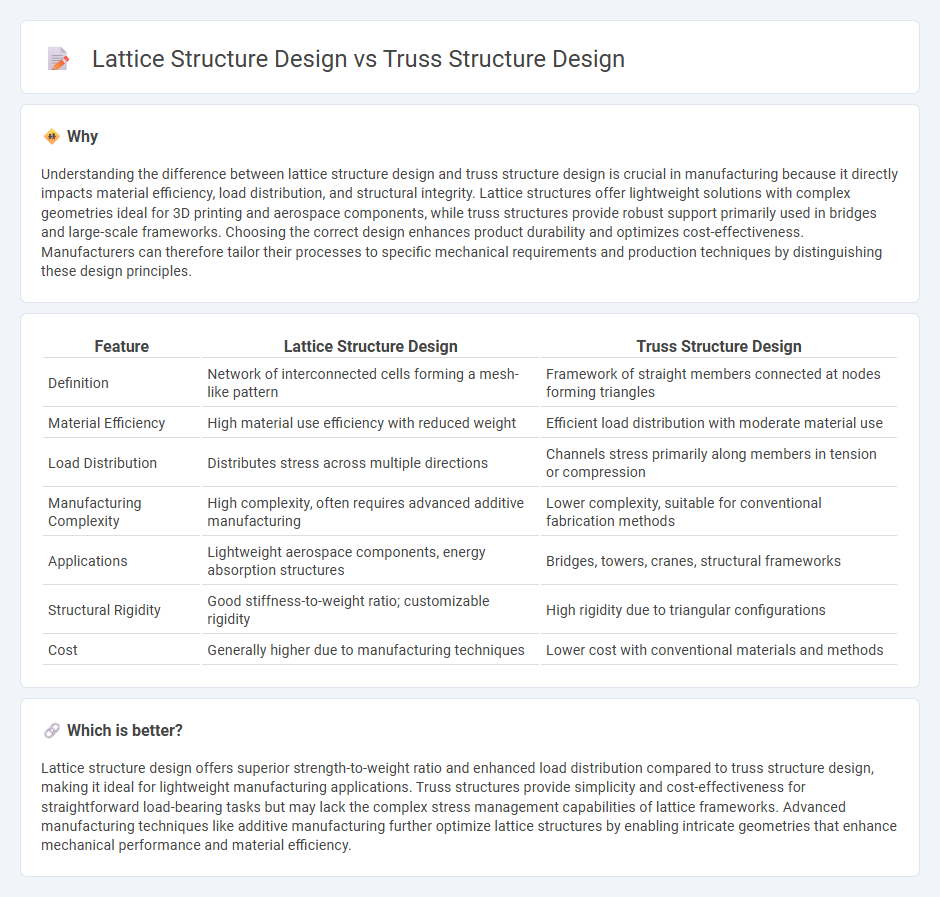
Understanding the difference between lattice structure design and truss structure design is crucial in manufacturing because it directly impacts material efficiency, load distribution, and structural integrity. Lattice structures offer lightweight solutions with complex geometries ideal for 3D printing and aerospace components, while truss structures provide robust support primarily used in bridges and large-scale frameworks. Choosing the correct design enhances product durability and optimizes cost-effectiveness. Manufacturers can therefore tailor their processes to specific mechanical requirements and production techniques by distinguishing these design principles.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lattice Structure Design | Truss Structure Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of interconnected cells forming a mesh-like pattern | Framework of straight members connected at nodes forming triangles |
| Material Efficiency | High material use efficiency with reduced weight | Efficient load distribution with moderate material use |
| Load Distribution | Distributes stress across multiple directions | Channels stress primarily along members in tension or compression |
| Manufacturing Complexity | High complexity, often requires advanced additive manufacturing | Lower complexity, suitable for conventional fabrication methods |
| Applications | Lightweight aerospace components, energy absorption structures | Bridges, towers, cranes, structural frameworks |
| Structural Rigidity | Good stiffness-to-weight ratio; customizable rigidity | High rigidity due to triangular configurations |
| Cost | Generally higher due to manufacturing techniques | Lower cost with conventional materials and methods |
Which is better?
Lattice structure design offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced load distribution compared to truss structure design, making it ideal for lightweight manufacturing applications. Truss structures provide simplicity and cost-effectiveness for straightforward load-bearing tasks but may lack the complex stress management capabilities of lattice frameworks. Advanced manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing further optimize lattice structures by enabling intricate geometries that enhance mechanical performance and material efficiency.
Connection
Lattice structure design and truss structure design are interconnected through their shared emphasis on optimizing load distribution and material efficiency in manufacturing. Both designs utilize geometric patterns of interconnected elements to enhance structural strength while minimizing weight, crucial for applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries. Advances in computer-aided design (CAD) and additive manufacturing technologies have further integrated these concepts, enabling precise fabrication of complex lattice and truss structures for improved performance and cost-effectiveness.
Key Terms
Load Distribution
Truss structure design efficiently distributes loads through interconnected triangular units, enhancing stability and minimizing material use by channeling forces along the members primarily in tension and compression. Lattice structure design, composed of crisscrossed elements, provides multidirectional load paths and greater surface area for load transfer but may require more complex analysis for optimal weight-to-strength balance. Explore the detailed comparisons and applications of these designs to optimize structural performance.
Material Utilization
Truss structure design optimizes material utilization by distributing loads through triangular units, which enhances strength while minimizing weight and material use. Lattice structure design employs a network of crisscrossed elements that provide stiffness and support, often resulting in higher material consumption compared to trusses. Explore the detailed differences in material efficiency and applications of both structures to understand their design advantages.
Structural Efficiency
Truss structure design maximizes structural efficiency by distributing loads through interconnected triangular units, providing high strength-to-weight ratios ideal for bridges and roofs. Lattice structure design employs a grid-like network of slender elements optimized for lightweight frameworks and aesthetic versatility in architectural applications. Explore further to understand the material performance and cost-effectiveness of these engineered frameworks.
Source and External Links
HOW TO DESIGN A TRUSS - The process involves determining the truss span and spacing, calculating design loading, and selecting the structural depth to control deflection, with an example of a 20m span truss design for a sports facility roof.
What is a Truss? Common Types of Trusses - Explains truss components like top chord, bottom chord, webs, and their benefits, emphasizing material efficiency through axial tension and compression forces, with common truss types to maximize structural performance.
Trusses - Basic Concepts of Structural Design for ... - Defines a truss as a system of two-force members arranged triangularly with pinned joints, loaded only at joints, carrying mainly tension and compression, essential for stability and efficient load distribution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com