Edge computing processes data locally near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth use, which is crucial for real-time manufacturing operations and IoT devices. Centralized data processing relies on a central server or cloud, offering robust analytical power and easier data management but can introduce delays due to data transmission. Explore how these approaches impact manufacturing efficiency and decision-making in detail.
Why it is important
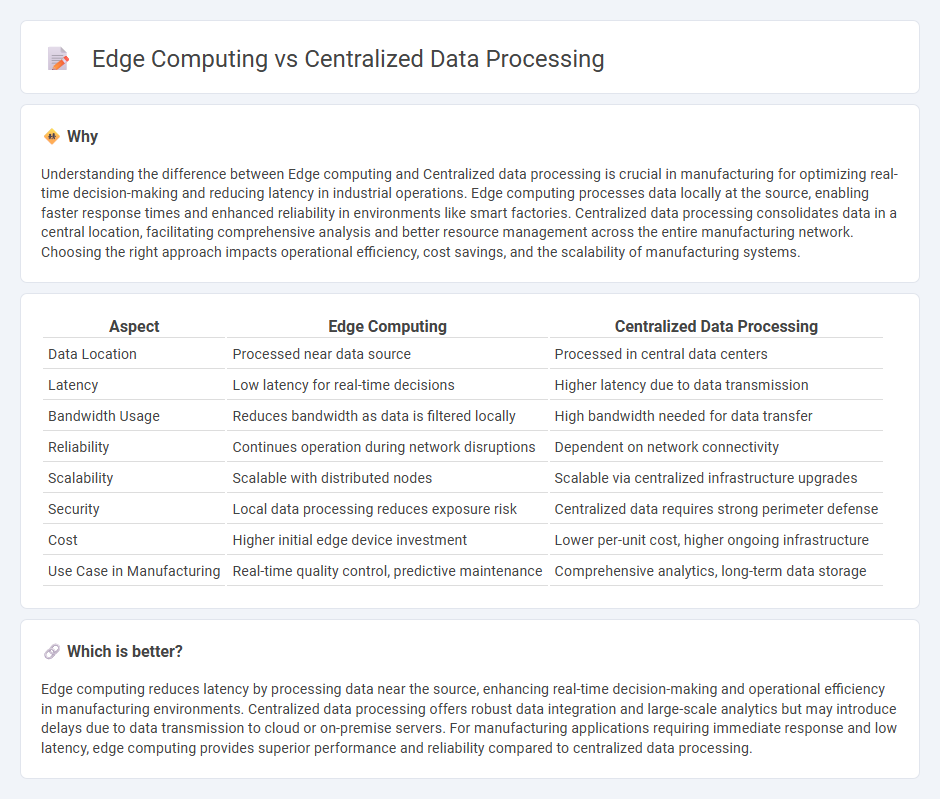
Understanding the difference between Edge computing and Centralized data processing is crucial in manufacturing for optimizing real-time decision-making and reducing latency in industrial operations. Edge computing processes data locally at the source, enabling faster response times and enhanced reliability in environments like smart factories. Centralized data processing consolidates data in a central location, facilitating comprehensive analysis and better resource management across the entire manufacturing network. Choosing the right approach impacts operational efficiency, cost savings, and the scalability of manufacturing systems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Edge Computing | Centralized Data Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Location | Processed near data source | Processed in central data centers |
| Latency | Low latency for real-time decisions | Higher latency due to data transmission |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduces bandwidth as data is filtered locally | High bandwidth needed for data transfer |
| Reliability | Continues operation during network disruptions | Dependent on network connectivity |
| Scalability | Scalable with distributed nodes | Scalable via centralized infrastructure upgrades |
| Security | Local data processing reduces exposure risk | Centralized data requires strong perimeter defense |
| Cost | Higher initial edge device investment | Lower per-unit cost, higher ongoing infrastructure |
| Use Case in Manufacturing | Real-time quality control, predictive maintenance | Comprehensive analytics, long-term data storage |
Which is better?
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data near the source, enhancing real-time decision-making and operational efficiency in manufacturing environments. Centralized data processing offers robust data integration and large-scale analytics but may introduce delays due to data transmission to cloud or on-premise servers. For manufacturing applications requiring immediate response and low latency, edge computing provides superior performance and reliability compared to centralized data processing.
Connection
Edge computing enhances manufacturing efficiency by processing data locally from machines and sensors, reducing latency and bandwidth use before sending critical information to centralized data processing systems. Centralized data centers aggregate and analyze this data on a larger scale, enabling advanced analytics, predictive maintenance, and real-time decision-making across the entire manufacturing facility. The integration of edge computing with centralized data processing ensures seamless data flow, optimized operations, and improved responsiveness in manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Latency
Edge computing significantly reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, minimizing the delay caused by transmitting information to centralized data centers. Centralized data processing often experiences higher latency due to the distance data must travel and potential network congestion. Explore the benefits of low-latency edge solutions to enhance real-time decision-making and application performance.
Bandwidth
Centralized data processing relies heavily on transmitting vast amounts of data to central servers, which can strain bandwidth and increase latency, particularly with IoT devices generating continuous data streams. Edge computing minimizes bandwidth usage by processing data locally at or near the data source, reducing the volume of data sent to central systems and enhancing real-time responsiveness. Explore how these bandwidth implications impact your network infrastructure and performance optimization strategies.
Real-time analytics
Centralized data processing involves aggregating data in a central repository, enabling comprehensive real-time analytics but often facing latency challenges due to data transmission delays. Edge computing processes data closer to the source, significantly reducing latency and enhancing real-time analytics capabilities for time-sensitive applications such as IoT and autonomous systems. Explore how leveraging edge computing can transform your real-time analytics strategy by visiting our detailed insights.
Source and External Links
What is Centralized Data Processing with Example - IT Release - Centralized data processing involves all data management, storage, and computation taking place on a single server or mainframe, with multiple clients (like smartphones, laptops) connecting to this central unit for data retrieval and analysis.
Benefits of Centralized Data Management for Decision-Making - Centralized data management integrates an organization's data into one system, improving decision-making by providing real-time, cohesive access to data across departments and external sources.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Centralized Data Processing - Centralized data processing offers easy resource management, advanced security, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with older systems as all processes run on a single server connected to various nodes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com