Factory as a Service (FaaS) enables on-demand access to physical production facilities through digital platforms, allowing businesses to scale manufacturing without owning factories. Cloud manufacturing integrates distributed manufacturing resources and capabilities via cloud computing technologies to optimize production efficiency and collaboration. Explore the distinct advantages of FaaS and cloud manufacturing to revolutionize your production strategy.
Why it is important
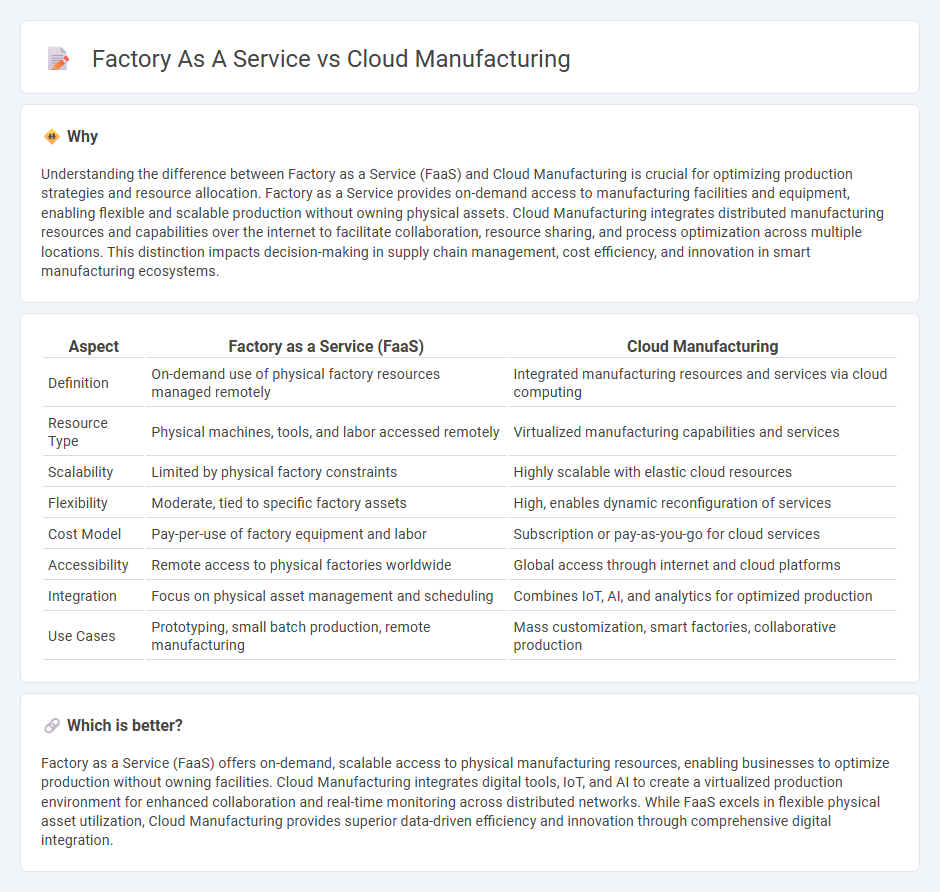
Understanding the difference between Factory as a Service (FaaS) and Cloud Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production strategies and resource allocation. Factory as a Service provides on-demand access to manufacturing facilities and equipment, enabling flexible and scalable production without owning physical assets. Cloud Manufacturing integrates distributed manufacturing resources and capabilities over the internet to facilitate collaboration, resource sharing, and process optimization across multiple locations. This distinction impacts decision-making in supply chain management, cost efficiency, and innovation in smart manufacturing ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Factory as a Service (FaaS) | Cloud Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-demand use of physical factory resources managed remotely | Integrated manufacturing resources and services via cloud computing |
| Resource Type | Physical machines, tools, and labor accessed remotely | Virtualized manufacturing capabilities and services |
| Scalability | Limited by physical factory constraints | Highly scalable with elastic cloud resources |
| Flexibility | Moderate, tied to specific factory assets | High, enables dynamic reconfiguration of services |
| Cost Model | Pay-per-use of factory equipment and labor | Subscription or pay-as-you-go for cloud services |
| Accessibility | Remote access to physical factories worldwide | Global access through internet and cloud platforms |
| Integration | Focus on physical asset management and scheduling | Combines IoT, AI, and analytics for optimized production |
| Use Cases | Prototyping, small batch production, remote manufacturing | Mass customization, smart factories, collaborative production |
Which is better?
Factory as a Service (FaaS) offers on-demand, scalable access to physical manufacturing resources, enabling businesses to optimize production without owning facilities. Cloud Manufacturing integrates digital tools, IoT, and AI to create a virtualized production environment for enhanced collaboration and real-time monitoring across distributed networks. While FaaS excels in flexible physical asset utilization, Cloud Manufacturing provides superior data-driven efficiency and innovation through comprehensive digital integration.
Connection
Factory as a Service (FaaS) leverages cloud manufacturing platforms to enable on-demand access to manufacturing resources, including machines, software, and expertise, through internet-based services. Cloud manufacturing provides a virtualized environment where manufacturing processes are distributed and managed remotely, facilitating real-time data exchange, scalability, and flexibility essential for FaaS operations. The integration of FaaS with cloud manufacturing enhances production efficiency, reduces capital investment, and supports customized, agile manufacturing workflows.
Key Terms
Cloud Manufacturing:
Cloud manufacturing leverages IoT, AI, and big data to create a flexible and scalable production environment where resources and capabilities are virtualized and shared over the internet. This approach enhances real-time collaboration, resource optimization, and rapid responsiveness to market demands compared to traditional Factory as a Service models. Explore how cloud manufacturing transforms industrial processes by integrating advanced digital technologies for increased efficiency and innovation.
Resource Virtualization
Resource virtualization in cloud manufacturing involves creating digital representations of physical assets to enable flexible, scalable resource allocation across multiple production sites. Factory as a Service (FaaS) focuses on delivering complete, on-demand manufacturing capabilities by integrating and virtualizing equipment, software, and human resources in a unified platform. Explore how resource virtualization reshapes manufacturing efficiency and scalability by learning more about these innovative models.
Service-Oriented Architecture
Cloud manufacturing leverages Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) to integrate and share distributed resources, enabling flexible, on-demand production services across multiple locations. Factory as a Service (FaaS) applies SOA principles to provide customers with customizable, scalable manufacturing capabilities through virtualized factory resources and workflows. Explore how SOA enhances resource interoperability and agility in both paradigms for smarter manufacturing solutions.
Source and External Links
Cloud manufacturing - Cloud manufacturing (CMfg) is a paradigm transforming manufacturing resources and capabilities into services managed and shared via cloud computing, IoT, virtualization, and advanced technologies, enabling on-demand, high-quality manufacturing across the entire product lifecycle.
What is Cloud Manufacturing & How Does It Work? - Cloud manufacturing leverages cloud-based computing systems accessed over the internet to operate and manage manufacturing, improving productivity, reducing costs, enabling remote access, and streamlining processes with integrated, automated technologies.
Cloud-enabled manufacturing - Manufacturing organizations adopting cloud computing aim to enhance productivity, quality, and sustainability, though many are still underutilizing cloud potential due to limited workload migration, fragmented strategies, and narrow cost-focused views.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com