Process mining leverages data from IT systems to visualize, analyze, and optimize manufacturing workflows by identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies in real-time. Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and improving value streams through continuous improvements and standardized procedures. Explore these methodologies further to understand how they can transform manufacturing efficiency and productivity.
Why it is important
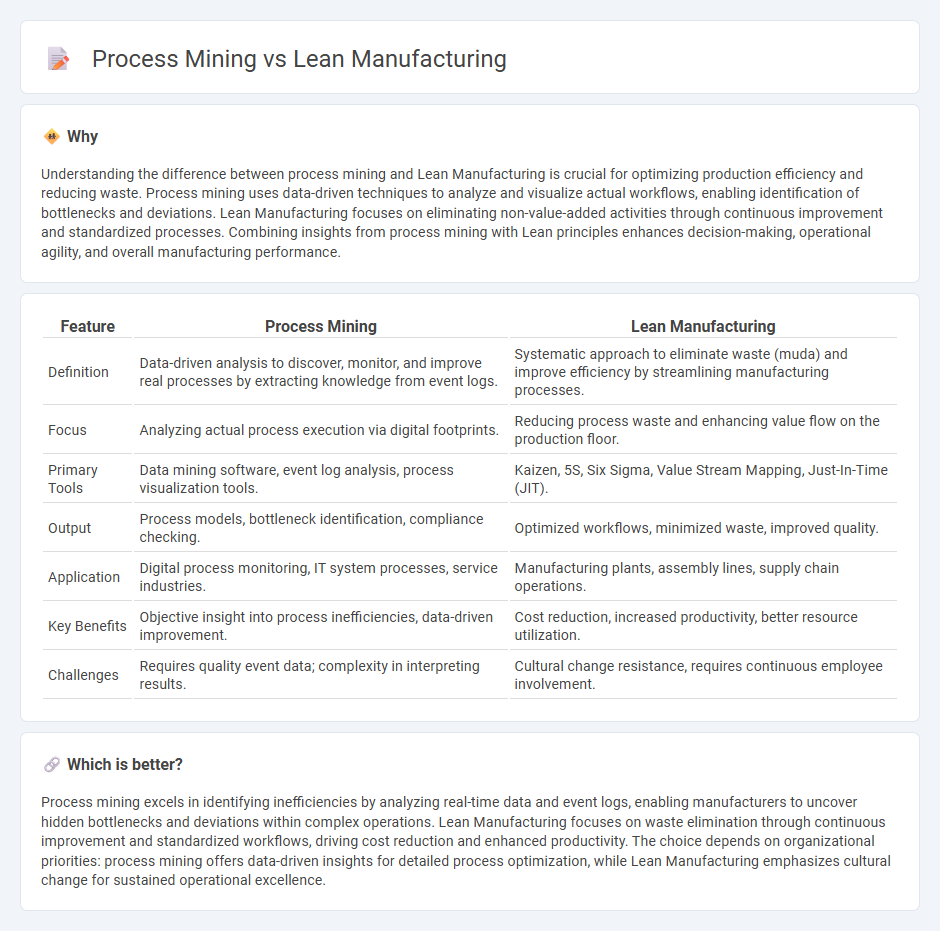
Understanding the difference between process mining and Lean Manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing waste. Process mining uses data-driven techniques to analyze and visualize actual workflows, enabling identification of bottlenecks and deviations. Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities through continuous improvement and standardized processes. Combining insights from process mining with Lean principles enhances decision-making, operational agility, and overall manufacturing performance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Process Mining | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data-driven analysis to discover, monitor, and improve real processes by extracting knowledge from event logs. | Systematic approach to eliminate waste (muda) and improve efficiency by streamlining manufacturing processes. |
| Focus | Analyzing actual process execution via digital footprints. | Reducing process waste and enhancing value flow on the production floor. |
| Primary Tools | Data mining software, event log analysis, process visualization tools. | Kaizen, 5S, Six Sigma, Value Stream Mapping, Just-In-Time (JIT). |
| Output | Process models, bottleneck identification, compliance checking. | Optimized workflows, minimized waste, improved quality. |
| Application | Digital process monitoring, IT system processes, service industries. | Manufacturing plants, assembly lines, supply chain operations. |
| Key Benefits | Objective insight into process inefficiencies, data-driven improvement. | Cost reduction, increased productivity, better resource utilization. |
| Challenges | Requires quality event data; complexity in interpreting results. | Cultural change resistance, requires continuous employee involvement. |
Which is better?
Process mining excels in identifying inefficiencies by analyzing real-time data and event logs, enabling manufacturers to uncover hidden bottlenecks and deviations within complex operations. Lean Manufacturing focuses on waste elimination through continuous improvement and standardized workflows, driving cost reduction and enhanced productivity. The choice depends on organizational priorities: process mining offers data-driven insights for detailed process optimization, while Lean Manufacturing emphasizes cultural change for sustained operational excellence.
Connection
Process mining enhances Lean Manufacturing by providing data-driven insights into workflow inefficiencies and bottlenecks through real-time event logs analysis. This integration enables manufacturers to identify non-value-added activities and streamline operations, ultimately reducing waste and improving cycle times. Combining process mining with Lean principles supports continuous improvement initiatives by validating process changes with empirical evidence.
Key Terms
Value Stream Mapping (Lean Manufacturing)
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) in Lean Manufacturing visually represents the flow of materials and information across production processes to identify waste and enhance value delivery. Process mining leverages event log data to analyze and optimize workflows by revealing bottlenecks, deviations, and inefficiencies in real-time. Explore how integrating VSM and process mining can drive superior operational efficiency and continuous improvement.
Waste Reduction (Lean Manufacturing)
Lean Manufacturing emphasizes systematic waste reduction by identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities across production processes, targeting the eight types of waste: defects, overproduction, waiting, non-utilized talent, transportation, inventory, motion, and excess processing. Process mining leverages data analytics and event logs to uncover inefficiencies and bottlenecks within workflows, enabling precise identification of waste patterns that Lean tools may overlook. Explore how integrating process mining with Lean Manufacturing can enhance waste reduction strategies and operational excellence.
Event Log Analysis (Process Mining)
Process mining, with its core technique of Event Log Analysis, provides a data-driven foundation to uncover inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and deviations within Lean Manufacturing processes. By extracting knowledge from event logs, organizations gain detailed visibility into real-time workflows and can validate or enhance Lean principles through empirical evidence. Explore how Event Log Analysis transforms Lean Manufacturing strategies for operational excellence.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method aimed at reducing production and supplier response times by eliminating waste, following principles from the Toyota Production System such as just-in-time inventory and quality control, with seven key wastes identified including overproduction and defects.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology that minimizes waste and maximizes productivity, emphasizing continuous improvement (Kaizen) and based on Toyota's system, influencing industries beyond manufacturing.
Lean Manufacturing: Understanding a New Manufacturing System - Lean manufacturing transitioned from mass production to a system with multi-skilled teams, prioritizing quality control, lower inventories, and continuous improvements often suggested by workers themselves.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com