Digital twin technology creates a real-time, virtual replica of physical manufacturing processes, enabling continuous monitoring and optimization. Simulation models provide predictive analysis by testing hypothetical scenarios without live data integration. Explore how these tools revolutionize manufacturing efficiency and decision-making.
Why it is important
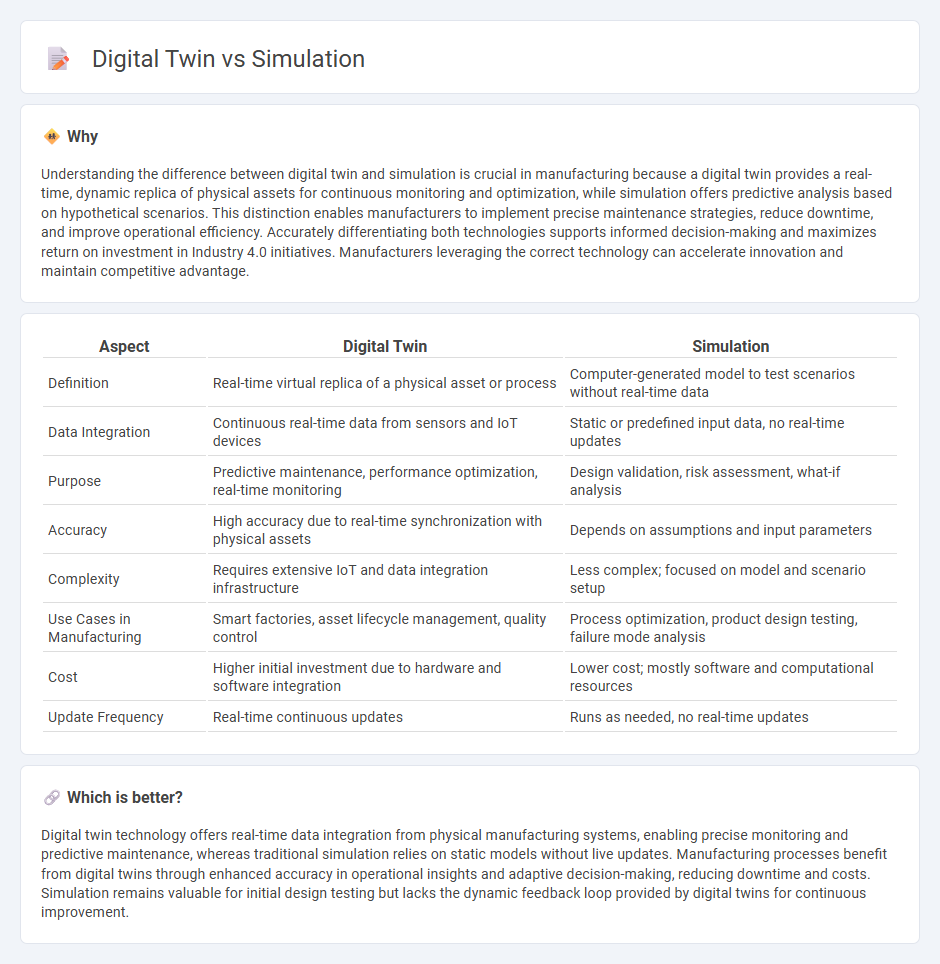
Understanding the difference between digital twin and simulation is crucial in manufacturing because a digital twin provides a real-time, dynamic replica of physical assets for continuous monitoring and optimization, while simulation offers predictive analysis based on hypothetical scenarios. This distinction enables manufacturers to implement precise maintenance strategies, reduce downtime, and improve operational efficiency. Accurately differentiating both technologies supports informed decision-making and maximizes return on investment in Industry 4.0 initiatives. Manufacturers leveraging the correct technology can accelerate innovation and maintain competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Twin | Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time virtual replica of a physical asset or process | Computer-generated model to test scenarios without real-time data |
| Data Integration | Continuous real-time data from sensors and IoT devices | Static or predefined input data, no real-time updates |
| Purpose | Predictive maintenance, performance optimization, real-time monitoring | Design validation, risk assessment, what-if analysis |
| Accuracy | High accuracy due to real-time synchronization with physical assets | Depends on assumptions and input parameters |
| Complexity | Requires extensive IoT and data integration infrastructure | Less complex; focused on model and scenario setup |
| Use Cases in Manufacturing | Smart factories, asset lifecycle management, quality control | Process optimization, product design testing, failure mode analysis |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to hardware and software integration | Lower cost; mostly software and computational resources |
| Update Frequency | Real-time continuous updates | Runs as needed, no real-time updates |
Which is better?
Digital twin technology offers real-time data integration from physical manufacturing systems, enabling precise monitoring and predictive maintenance, whereas traditional simulation relies on static models without live updates. Manufacturing processes benefit from digital twins through enhanced accuracy in operational insights and adaptive decision-making, reducing downtime and costs. Simulation remains valuable for initial design testing but lacks the dynamic feedback loop provided by digital twins for continuous improvement.
Connection
Digital twin technology creates a real-time virtual replica of physical manufacturing processes, enabling precise simulation and performance analysis. Simulation tools use these digital twins to predict system behaviors, optimize operations, and reduce downtime by identifying potential issues before they occur. Integrating digital twins with simulation enhances decision-making and accelerates innovation in manufacturing workflows.
Key Terms
Real-time Data Integration
Digital twins employ real-time data integration to create dynamic, constantly updated models of physical assets, enabling precise monitoring and predictive analysis. Simulations typically use static or pre-set data inputs, limiting their ability to reflect instantaneous changes in operational conditions. Explore how real-time data integration distinguishes digital twins from traditional simulations for enhanced decision-making.
Virtual Modeling
Virtual modeling in simulation creates simplified representations to analyze system behavior under various conditions, often focusing on specific scenarios. Digital twins provide dynamic, real-time replicas of physical assets by integrating sensor data and analytics for continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance. Explore how advanced virtual modeling techniques enhance the accuracy and functionality of digital twins.
Predictive Analytics
Simulation models replicate real-world processes using mathematical algorithms to forecast system behavior under various conditions, while digital twins integrate real-time sensor data for continuous monitoring and predictive analytics. Predictive analytics in digital twins enable proactive maintenance and operational optimization by analyzing live data streams and historical trends, surpassing traditional simulation's static scenario testing. Explore how leveraging digital twins enhances predictive capabilities and drives smarter decision-making in your industry.
Source and External Links
What is Simulation? | Ansys - Simulation is an imitative representation of a real-world process or system, used for predicting behavior, educating, troubleshooting, and optimizing designs without direct access to the actual system.
Simulation - Wikipedia - A simulation models a real-life or hypothetical situation on a computer, allowing study and prediction of system behavior by altering variables, and is widely applied in science, engineering, economics, and entertainment.
What is Simulation? What Does it Mean? (Definition and Examples) - Simulation mimics the operation of existing or proposed systems to test different scenarios, optimize performance, improve safety, and train personnel, especially when the real system is inaccessible or too dangerous.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com