Cloud manufacturing leverages cloud computing technologies to optimize production processes, enabling real-time collaboration and resource sharing across global networks. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, focuses on layer-by-layer material deposition to create complex, customized parts with minimal waste. Explore how these innovative approaches transform modern manufacturing by enhancing efficiency and flexibility.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cloud manufacturing and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and resource allocation. Cloud manufacturing leverages internet-based platforms to share manufacturing resources and data, enabling scalable, flexible, and collaborative production processes. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, builds objects layer by layer from digital models, allowing complex designs, rapid prototyping, and customization. Distinguishing these technologies helps businesses select appropriate strategies for innovation, cost reduction, and competitive advantage in Industry 4.0.
Comparison Table
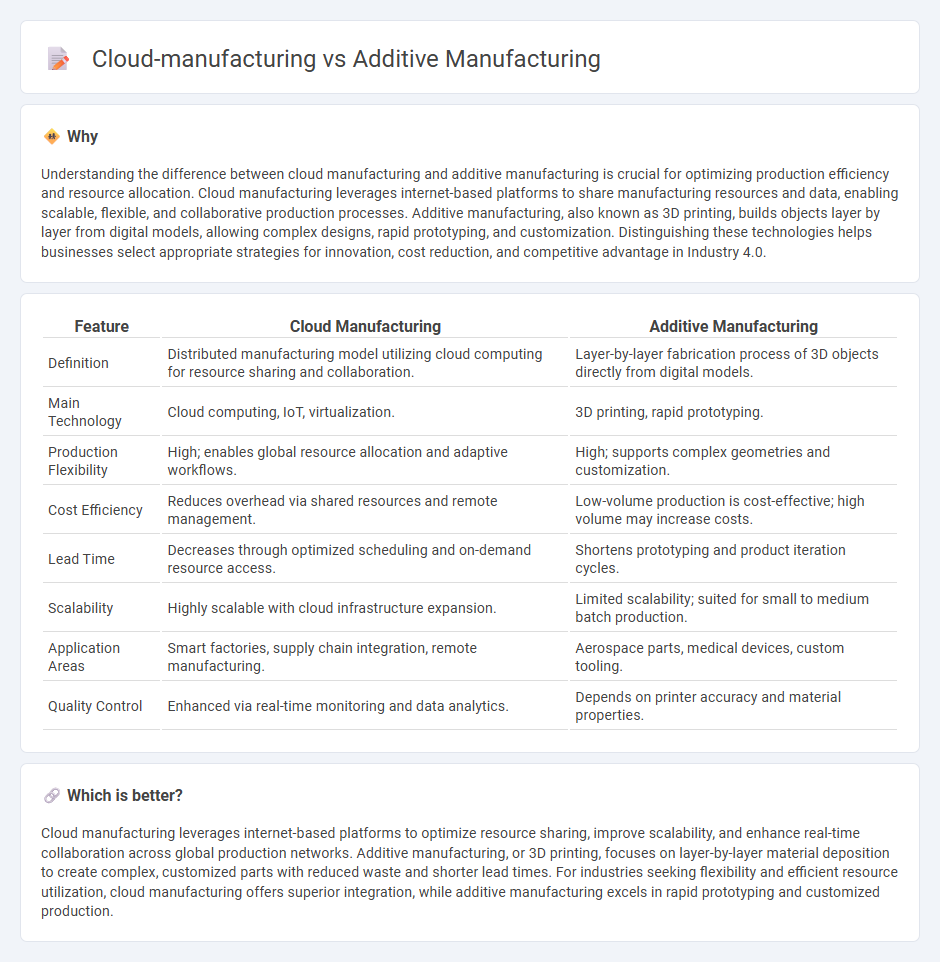
| Feature | Cloud Manufacturing | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed manufacturing model utilizing cloud computing for resource sharing and collaboration. | Layer-by-layer fabrication process of 3D objects directly from digital models. |
| Main Technology | Cloud computing, IoT, virtualization. | 3D printing, rapid prototyping. |
| Production Flexibility | High; enables global resource allocation and adaptive workflows. | High; supports complex geometries and customization. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces overhead via shared resources and remote management. | Low-volume production is cost-effective; high volume may increase costs. |
| Lead Time | Decreases through optimized scheduling and on-demand resource access. | Shortens prototyping and product iteration cycles. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with cloud infrastructure expansion. | Limited scalability; suited for small to medium batch production. |
| Application Areas | Smart factories, supply chain integration, remote manufacturing. | Aerospace parts, medical devices, custom tooling. |
| Quality Control | Enhanced via real-time monitoring and data analytics. | Depends on printer accuracy and material properties. |
Which is better?
Cloud manufacturing leverages internet-based platforms to optimize resource sharing, improve scalability, and enhance real-time collaboration across global production networks. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, focuses on layer-by-layer material deposition to create complex, customized parts with reduced waste and shorter lead times. For industries seeking flexibility and efficient resource utilization, cloud manufacturing offers superior integration, while additive manufacturing excels in rapid prototyping and customized production.
Connection
Cloud manufacturing integrates additive manufacturing by enabling on-demand access to 3D printing resources and real-time collaboration across distributed production facilities. This synergy enhances scalability, reduces lead times, and optimizes resource allocation by leveraging cloud computing for process control and data analytics. The combination accelerates innovation cycles and supports customized manufacturing at reduced costs.
Key Terms
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, fabricates objects layer by layer from digital models, enabling complex designs and rapid prototyping with materials such as polymers, metals, and ceramics. Cloud manufacturing integrates IoT, big data, and cloud computing to coordinate distributed production resources and services remotely, enhancing flexibility and collaboration across global supply chains. Explore how combining additive manufacturing with cloud manufacturing transforms production efficiency and customization opportunities.
Digital Fabrication Platforms (Cloud-manufacturing)
Additive manufacturing leverages layer-by-layer production techniques for creating complex parts directly from digital models, while cloud manufacturing integrates digital fabrication platforms to provide on-demand access to manufacturing resources, including additive processes, via the internet. Digital fabrication platforms in cloud manufacturing enable real-time collaboration, scalable resource sharing, and streamlined project management across distributed locations, enhancing flexibility and reducing production lead times. Explore how cloud manufacturing transforms traditional additive manufacturing by connecting multiple production sites and optimizing workflow efficiency.
Distributed Production
Additive manufacturing enables localized production through layer-by-layer fabrication, reducing material waste and lead times, while cloud manufacturing integrates distributed production resources via the internet to optimize real-time collaboration and scalability. Distributed production benefits from cloud manufacturing platforms by connecting decentralized additive manufacturing units, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness across global supply chains. Discover how combining these technologies transforms manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained - Additive manufacturing is the process of creating an object layer by layer, typically through 3D printing, starting from a digital design and using materials like polymers, metals, ceramics, and more to build functional products.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing uses digital designs to fabricate complex three-dimensional products layer by layer with less material waste than traditional manufacturing methods, and is applied in areas such as aerospace and biomedical implants.
What Is Additive Manufacturing? | 3D Printing Simulation - Additive manufacturing builds physical models from digital CAD designs by layering materials using diverse printing technologies like powder bed fusion, material extrusion, binder jetting, photopolymerization, and direct energy deposition for industrial applications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com