Microfactories leverage compact, flexible production units designed for localized manufacturing, enabling rapid customization and reduced lead times. Smart factories integrate advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to create highly efficient, data-driven manufacturing environments that optimize processes and resource use. Discover the key differences and benefits of microfactories versus smart factories to enhance your manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a microfactory and a smart factory is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and resource allocation. A microfactory is a small-scale, highly flexible production unit designed for localized manufacturing and rapid prototyping. A smart factory integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to enable large-scale, efficient, and data-driven production. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses choose the best approach for scalability, cost efficiency, and innovation.
Comparison Table
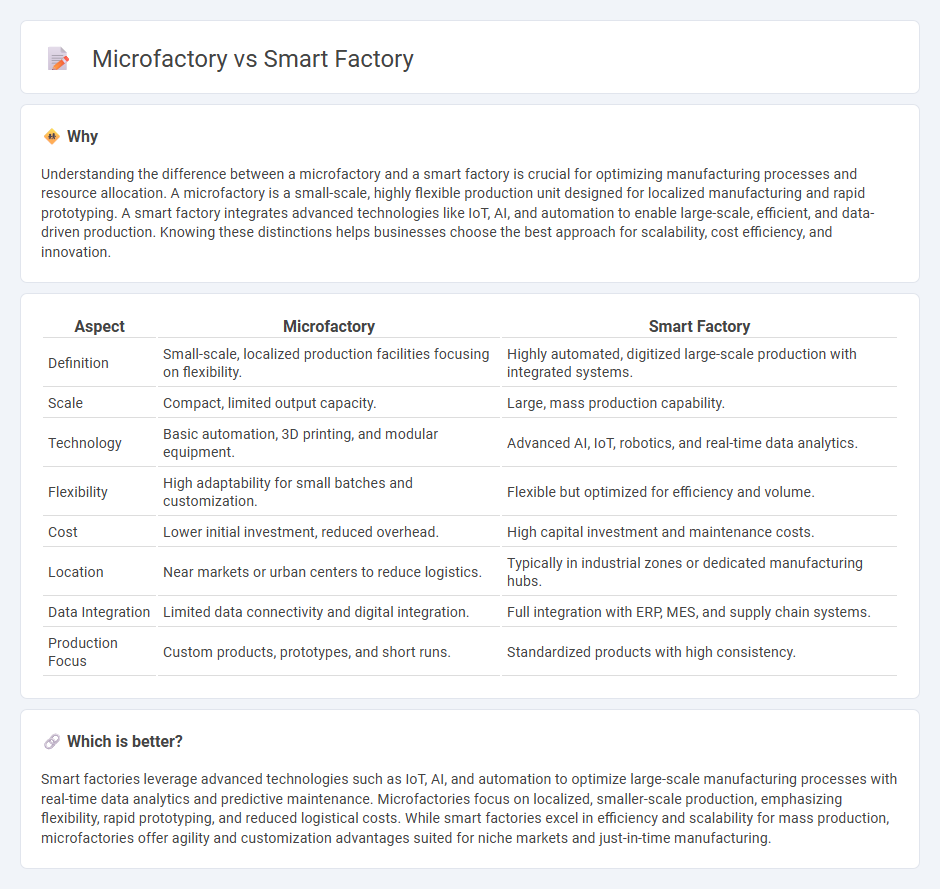
| Aspect | Microfactory | Smart Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small-scale, localized production facilities focusing on flexibility. | Highly automated, digitized large-scale production with integrated systems. |
| Scale | Compact, limited output capacity. | Large, mass production capability. |
| Technology | Basic automation, 3D printing, and modular equipment. | Advanced AI, IoT, robotics, and real-time data analytics. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability for small batches and customization. | Flexible but optimized for efficiency and volume. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, reduced overhead. | High capital investment and maintenance costs. |
| Location | Near markets or urban centers to reduce logistics. | Typically in industrial zones or dedicated manufacturing hubs. |
| Data Integration | Limited data connectivity and digital integration. | Full integration with ERP, MES, and supply chain systems. |
| Production Focus | Custom products, prototypes, and short runs. | Standardized products with high consistency. |
Which is better?
Smart factories leverage advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to optimize large-scale manufacturing processes with real-time data analytics and predictive maintenance. Microfactories focus on localized, smaller-scale production, emphasizing flexibility, rapid prototyping, and reduced logistical costs. While smart factories excel in efficiency and scalability for mass production, microfactories offer agility and customization advantages suited for niche markets and just-in-time manufacturing.
Connection
Microfactories and smart factories are connected through their reliance on advanced digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to enhance manufacturing efficiency and flexibility. Both leverage real-time data analytics and interconnected systems to optimize production processes, reduce waste, and enable rapid customization. Integration of microfactories within smart factory ecosystems supports decentralized manufacturing and agile response to market demands.
Key Terms
**Smart Factory:**
Smart factories employ advanced automation, IoT, and AI technologies to optimize manufacturing processes, enhance real-time data analysis, and increase production efficiency on a large scale. They integrate cyber-physical systems and machine learning to enable predictive maintenance and adaptive workflows, reducing downtime and operational costs. Explore deeper insights into how smart factories revolutionize industrial production with cutting-edge technology.
Automation
Smart factories leverage advanced automation technologies including IoT, AI, and robotics to optimize large-scale manufacturing processes and improve overall efficiency. Microfactories utilize compact, highly automated setups tailored for localized, flexible production, emphasizing rapid reconfiguration and reduced operational costs. Explore detailed insights on how automation differentiates smart factories from microfactories for modern manufacturing.
IoT Integration
Smart factories utilize comprehensive IoT integration to connect machinery, sensors, and data analytics platforms for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing overall operational efficiency. Microfactories, by contrast, incorporate IoT on a smaller scale, emphasizing rapid reconfiguration and local production flexibility, often tailored for niche markets and customized products. Explore the specific IoT technologies and benefits driving these manufacturing innovations to understand their distinct advantages.
Source and External Links
What is a smart factory? Understanding the future of manufacturing - A smart factory is a digitally integrated facility where sensors, cloud computing, AI, and machine learning enable real-time data analysis and autonomous process improvement across design, production, and supply chain as part of Industry 4.0.
What Is a Smart Factory? An Expert Guide - A smart factory is a highly automated, digitally connected manufacturing environment that uses robotics, machine learning, and advanced analytics to autonomously run and adapt production processes in real time for greater efficiency, quality, and flexibility.
Smart Factory Guide | L2L - A smart factory is a facility enabling smart manufacturing through the digital integration of machines, people, and processes, providing real-time data insights, improved asset efficiency, and reduced operational costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com