Microfactories leverage compact, flexible production environments to customize products quickly and reduce inventory costs, contrasting with mass production's emphasis on high-volume, standardized output to maximize efficiency and lower unit costs. Microfactories excel in agility and innovation, enabling manufacturers to respond promptly to market changes, while mass production benefits from economies of scale and streamlined assembly lines. Explore the evolving dynamics between microfactory setups and traditional mass production to understand their impact on manufacturing efficiency and product diversity.
Why it is important
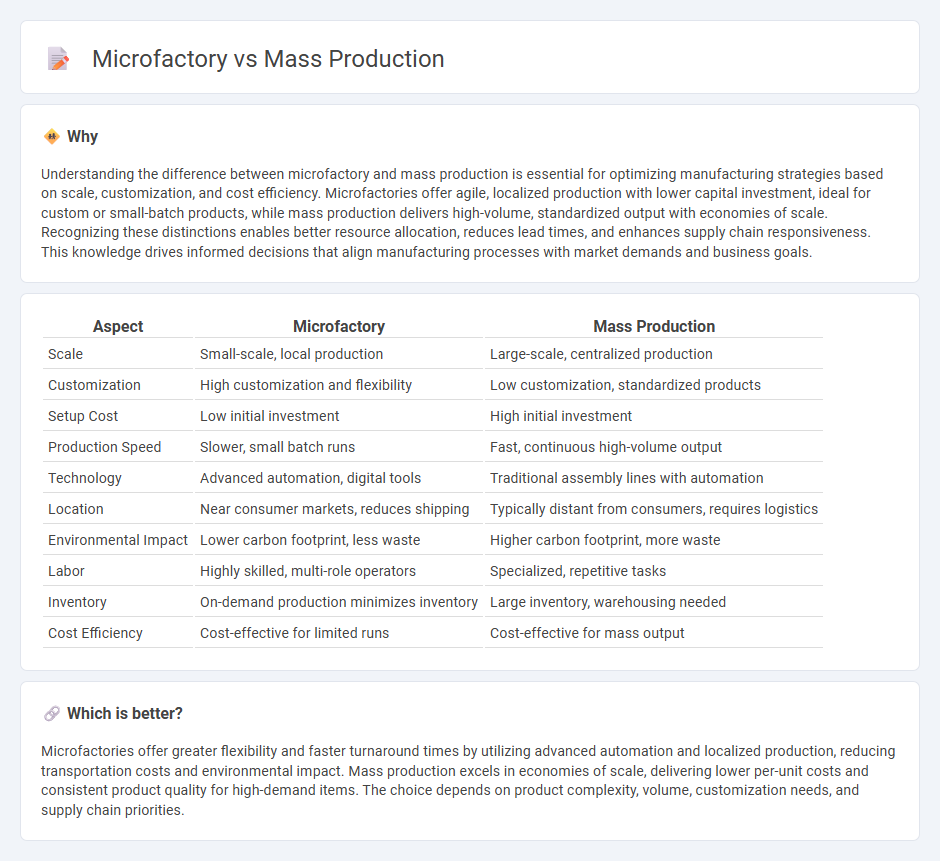
Understanding the difference between microfactory and mass production is essential for optimizing manufacturing strategies based on scale, customization, and cost efficiency. Microfactories offer agile, localized production with lower capital investment, ideal for custom or small-batch products, while mass production delivers high-volume, standardized output with economies of scale. Recognizing these distinctions enables better resource allocation, reduces lead times, and enhances supply chain responsiveness. This knowledge drives informed decisions that align manufacturing processes with market demands and business goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfactory | Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Small-scale, local production | Large-scale, centralized production |
| Customization | High customization and flexibility | Low customization, standardized products |
| Setup Cost | Low initial investment | High initial investment |
| Production Speed | Slower, small batch runs | Fast, continuous high-volume output |
| Technology | Advanced automation, digital tools | Traditional assembly lines with automation |
| Location | Near consumer markets, reduces shipping | Typically distant from consumers, requires logistics |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, less waste | Higher carbon footprint, more waste |
| Labor | Highly skilled, multi-role operators | Specialized, repetitive tasks |
| Inventory | On-demand production minimizes inventory | Large inventory, warehousing needed |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for limited runs | Cost-effective for mass output |
Which is better?
Microfactories offer greater flexibility and faster turnaround times by utilizing advanced automation and localized production, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact. Mass production excels in economies of scale, delivering lower per-unit costs and consistent product quality for high-demand items. The choice depends on product complexity, volume, customization needs, and supply chain priorities.
Connection
Microfactories and mass production are connected through their complementary roles in manufacturing efficiency and scalability. Microfactories focus on localized, flexible, and small-batch production, enabling rapid prototyping and customization, while mass production emphasizes high-volume output with standardized processes to minimize unit costs. Integrating microfactory capabilities into mass production systems enhances responsiveness to market demand and supports lean manufacturing principles.
Key Terms
Scale
Mass production leverages large-scale facilities to produce goods in high volumes, achieving economies of scale that reduce per-unit costs significantly. Microfactories operate on a smaller scale, emphasizing flexibility, customization, and rapid response to market changes while minimizing inventory and transportation expenses. Explore the benefits and trade-offs between mass production and microfactories to optimize your manufacturing strategy.
Automation
Mass production relies heavily on large-scale automation systems designed to maximize output efficiency in manufacturing processes through standardized tasks. Microfactories integrate advanced automation technologies with flexible, modular setups that enable quick adaptability and customization for small-batch production. Explore how automation transforms manufacturing efficiency and scalability by learning more about the distinct advantages of mass production and microfactories.
Flexibility
Mass production offers high output but limited flexibility, as it relies on standardized processes and equipment designed for large-scale manufacturing. Microfactories emphasize adaptability by using modular systems and advanced technologies like automation and 3D printing, enabling rapid product changes and customization. Explore how these approaches redefine manufacturing efficiency and responsiveness in various industries.
Source and External Links
What Is Mass Production? A Comprehensive Guide - MRPeasy - Mass production is a manufacturing method designed for large-scale, high-volume production of standardized products using specialization, mechanization, and economies of scale to maximize efficiency and consistency.
Mass production - Wikipedia - Mass production involves fast production of many identical products using assembly lines where workers perform specific steps, emphasizing automation and capital-intensive processes to reduce unit costs.
Mass Production - Overview, How It Works, Advantages - Mass production uses automation and assembly lines to manufacture standardized product lines continuously, relying on labor division, mechanization, and specialized equipment to keep costs low while maintaining quality.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com