Human augmentation enhances manufacturing productivity by integrating advanced technologies such as exoskeletons and brain-computer interfaces to empower workers and reduce fatigue. Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and optimizing processes through techniques like just-in-time production and continuous improvement to increase efficiency. Explore how these approaches transform industrial operations and drive the future of manufacturing.
Why it is important
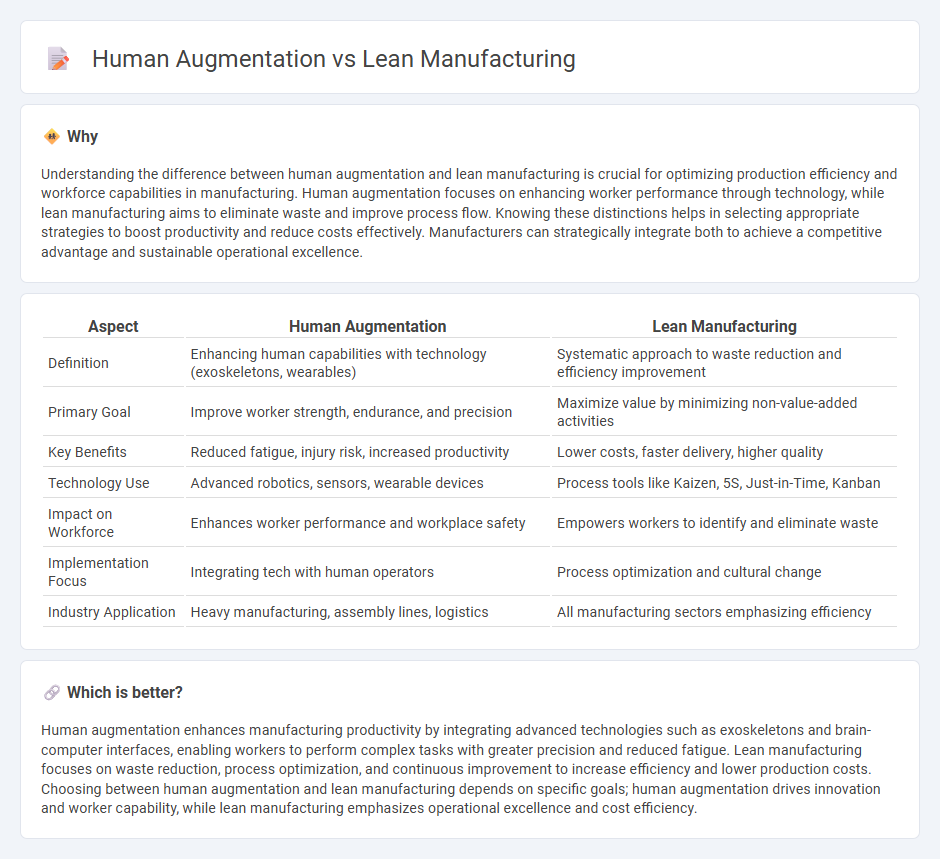
Understanding the difference between human augmentation and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and workforce capabilities in manufacturing. Human augmentation focuses on enhancing worker performance through technology, while lean manufacturing aims to eliminate waste and improve process flow. Knowing these distinctions helps in selecting appropriate strategies to boost productivity and reduce costs effectively. Manufacturers can strategically integrate both to achieve a competitive advantage and sustainable operational excellence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Human Augmentation | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancing human capabilities with technology (exoskeletons, wearables) | Systematic approach to waste reduction and efficiency improvement |
| Primary Goal | Improve worker strength, endurance, and precision | Maximize value by minimizing non-value-added activities |
| Key Benefits | Reduced fatigue, injury risk, increased productivity | Lower costs, faster delivery, higher quality |
| Technology Use | Advanced robotics, sensors, wearable devices | Process tools like Kaizen, 5S, Just-in-Time, Kanban |
| Impact on Workforce | Enhances worker performance and workplace safety | Empowers workers to identify and eliminate waste |
| Implementation Focus | Integrating tech with human operators | Process optimization and cultural change |
| Industry Application | Heavy manufacturing, assembly lines, logistics | All manufacturing sectors emphasizing efficiency |
Which is better?
Human augmentation enhances manufacturing productivity by integrating advanced technologies such as exoskeletons and brain-computer interfaces, enabling workers to perform complex tasks with greater precision and reduced fatigue. Lean manufacturing focuses on waste reduction, process optimization, and continuous improvement to increase efficiency and lower production costs. Choosing between human augmentation and lean manufacturing depends on specific goals; human augmentation drives innovation and worker capability, while lean manufacturing emphasizes operational excellence and cost efficiency.
Connection
Human augmentation enhances worker capabilities by integrating technologies such as exoskeletons and wearable sensors, which aligns with lean manufacturing principles focused on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. This synergy reduces physical strain, accelerates task completion, and improves precision, leading to streamlined production processes and higher quality output. Implementing human augmentation supports continuous improvement and just-in-time production, core tenets of lean manufacturing, by optimizing labor productivity and reducing downtime.
Key Terms
**Lean Manufacturing:**
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and maximizing value through efficient processes and employee involvement. Techniques like Just-In-Time production, Kaizen, and Value Stream Mapping optimize resource utilization and minimize defects. Explore how lean manufacturing transforms operational efficiency and drives business growth.
Just-in-Time (JIT)
Lean manufacturing optimizes production by minimizing waste and implementing Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory systems to ensure materials arrive precisely when needed, reducing storage costs and enhancing efficiency. Human augmentation complements JIT by enhancing worker precision, decision-making speed, and adaptability, enabling real-time adjustments in production flow and reducing downtime. Explore how integrating lean methodologies with human augmentation technologies transforms JIT processes for maximum operational excellence.
Value Stream Mapping
Lean manufacturing emphasizes Value Stream Mapping (VSM) to identify and eliminate waste, streamlining production processes for maximized efficiency and minimal delay. Human augmentation integrates advanced technologies such as wearable exoskeletons with VSM to enhance worker performance and reduce physical strain, improving overall productivity. Explore how combining lean principles with human augmentation transforms value stream optimization for next-level manufacturing efficiency.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on reducing production and supplier response times by eliminating waste and improving efficiency, originating from Toyota's production system emphasizing just-in-time inventory and quality control.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology aimed at minimizing waste and maximizing productivity by focusing only on processes that add value from the customer's viewpoint, with benefits like reduced lead times and operating costs.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing is based on five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection, all designed to maximize productivity and minimize waste throughout production processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com