Lattice structure design in manufacturing offers enhanced strength-to-weight ratios by utilizing intricate geometric frameworks, while composite structure design combines multiple materials to optimize mechanical properties and durability. Both approaches aim to improve performance in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries by reducing weight and increasing structural integrity. Explore the benefits and applications of lattice and composite structures to understand their impact on advanced manufacturing processes.
Why it is important
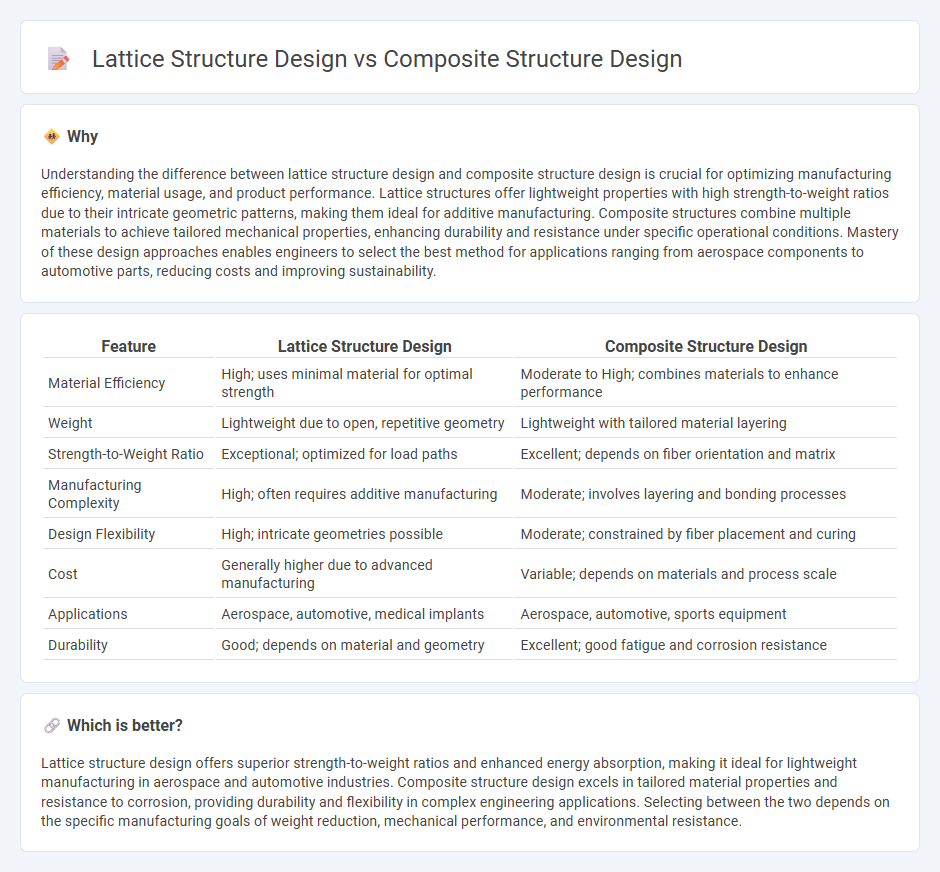
Understanding the difference between lattice structure design and composite structure design is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency, material usage, and product performance. Lattice structures offer lightweight properties with high strength-to-weight ratios due to their intricate geometric patterns, making them ideal for additive manufacturing. Composite structures combine multiple materials to achieve tailored mechanical properties, enhancing durability and resistance under specific operational conditions. Mastery of these design approaches enables engineers to select the best method for applications ranging from aerospace components to automotive parts, reducing costs and improving sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lattice Structure Design | Composite Structure Design |
|---|---|---|
| Material Efficiency | High; uses minimal material for optimal strength | Moderate to High; combines materials to enhance performance |
| Weight | Lightweight due to open, repetitive geometry | Lightweight with tailored material layering |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Exceptional; optimized for load paths | Excellent; depends on fiber orientation and matrix |
| Manufacturing Complexity | High; often requires additive manufacturing | Moderate; involves layering and bonding processes |
| Design Flexibility | High; intricate geometries possible | Moderate; constrained by fiber placement and curing |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced manufacturing | Variable; depends on materials and process scale |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, medical implants | Aerospace, automotive, sports equipment |
| Durability | Good; depends on material and geometry | Excellent; good fatigue and corrosion resistance |
Which is better?
Lattice structure design offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced energy absorption, making it ideal for lightweight manufacturing in aerospace and automotive industries. Composite structure design excels in tailored material properties and resistance to corrosion, providing durability and flexibility in complex engineering applications. Selecting between the two depends on the specific manufacturing goals of weight reduction, mechanical performance, and environmental resistance.
Connection
Lattice structure design and composite structure design are interconnected through their shared goal of enhancing material strength-to-weight ratios in manufacturing. Lattice structures provide a lightweight internal framework that complements how composite materials distribute stress across layered fibers. This synergy enables advanced manufacturing of aerospace and automotive components with improved mechanical performance and reduced weight.
Key Terms
Material Optimization
Composite structure design leverages heterogeneous materials to achieve superior strength-to-weight ratios, enabling tailored stiffness and enhanced load distribution within aerospace and automotive applications. Lattice structure design uses periodic, often three-dimensional geometric patterns to reduce material usage while maintaining structural integrity through optimized topology and internal voids. Explore detailed comparisons and advancements in material optimization techniques between these innovative design methodologies.
Weight Reduction
Composite structure design utilizes high-strength materials such as carbon fiber composites to achieve significant weight reduction while maintaining structural integrity, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. Lattice structure design leverages intricate, repetitive geometries to minimize material use and weight without compromising mechanical performance, often produced through advanced additive manufacturing techniques. Explore the benefits and applications of weight reduction strategies in composite and lattice structures to optimize your engineering projects.
Structural Integrity
Composite structure design leverages heterogeneous materials like carbon fiber reinforced polymers to maximize strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing structural integrity through tailored fiber orientation and layering. Lattice structure design employs interconnected geometric patterns to distribute loads efficiently, reduce weight, and increase stiffness, often used in additive manufacturing for optimized mechanical performance. Explore further to understand how these innovative design approaches impact durability and resilience in engineering applications.
Source and External Links
Fundamentals of Composite Structure Design - AIAA - This seminar offers an in-depth overview of structural design requirements, laminate configuration, strength analysis, joint detailing, and environmental considerations specifically tailored for engineers working with composite materials in structural applications.
Quick step-by-step guide for Composites design - Addcomposite - It provides a practical framework for composite design emphasizing material selection, construction form, structural integrity, environmental effects, and program objectives including weight savings and digital integration in manufacturing.
Design, modeling and drafting of composite structures - DiVA portal - This thesis addresses the complexities of modeling and drafting composite structures, offering recommended working methods using CAD tools to handle the detailed ply definitions and orientations inherent in composite materials.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com