Dark factories leverage automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, significantly reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency. Just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing focuses on minimizing inventory and waste by producing goods based on demand, enhancing responsiveness and reducing storage expenses. Discover how these contrasting manufacturing strategies can optimize production processes for various industries.
Why it is important
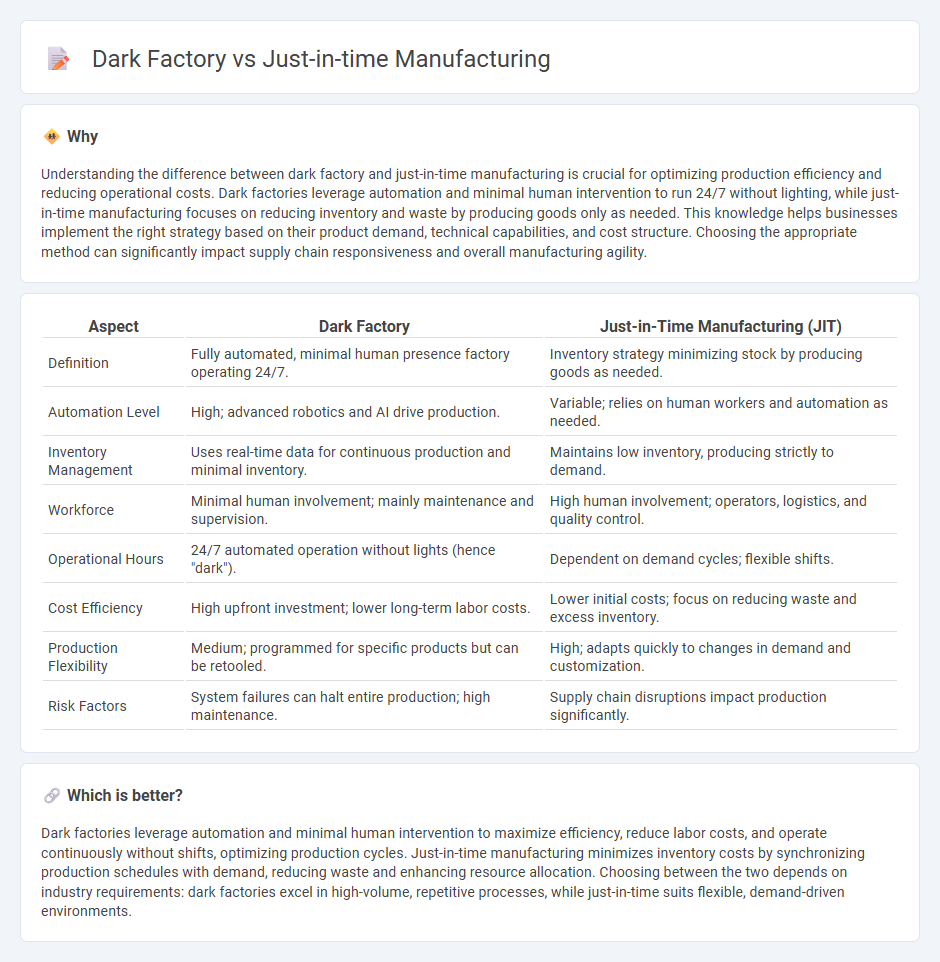
Understanding the difference between dark factory and just-in-time manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and reducing operational costs. Dark factories leverage automation and minimal human intervention to run 24/7 without lighting, while just-in-time manufacturing focuses on reducing inventory and waste by producing goods only as needed. This knowledge helps businesses implement the right strategy based on their product demand, technical capabilities, and cost structure. Choosing the appropriate method can significantly impact supply chain responsiveness and overall manufacturing agility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Factory | Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated, minimal human presence factory operating 24/7. | Inventory strategy minimizing stock by producing goods as needed. |
| Automation Level | High; advanced robotics and AI drive production. | Variable; relies on human workers and automation as needed. |
| Inventory Management | Uses real-time data for continuous production and minimal inventory. | Maintains low inventory, producing strictly to demand. |
| Workforce | Minimal human involvement; mainly maintenance and supervision. | High human involvement; operators, logistics, and quality control. |
| Operational Hours | 24/7 automated operation without lights (hence "dark"). | Dependent on demand cycles; flexible shifts. |
| Cost Efficiency | High upfront investment; lower long-term labor costs. | Lower initial costs; focus on reducing waste and excess inventory. |
| Production Flexibility | Medium; programmed for specific products but can be retooled. | High; adapts quickly to changes in demand and customization. |
| Risk Factors | System failures can halt entire production; high maintenance. | Supply chain disruptions impact production significantly. |
Which is better?
Dark factories leverage automation and minimal human intervention to maximize efficiency, reduce labor costs, and operate continuously without shifts, optimizing production cycles. Just-in-time manufacturing minimizes inventory costs by synchronizing production schedules with demand, reducing waste and enhancing resource allocation. Choosing between the two depends on industry requirements: dark factories excel in high-volume, repetitive processes, while just-in-time suits flexible, demand-driven environments.
Connection
Dark factories utilize automation and robotics to operate with minimal human intervention, aligning closely with just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing principles by reducing lead times and inventory costs. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in dark factories enhances real-time data monitoring, enabling precise JIT production schedules and minimizing waste. This synergy results in increased operational efficiency, lower overheads, and improved responsiveness to market demand.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Just-in-time manufacturing minimizes inventory by receiving materials only as needed, reducing carrying costs and waste through precise scheduling and supplier coordination. Dark factories optimize inventory management by leveraging automated systems and robotics to handle materials and production processes seamlessly 24/7, enhancing accuracy and reducing human error. Explore further to understand how these approaches transform inventory strategies in modern manufacturing.
Automation
Just-in-time manufacturing minimizes inventory by synchronizing production with demand, relying heavily on automated systems to streamline workflows and reduce waste. Dark factories operate entirely without human presence, utilizing advanced robotics and AI to maintain continuous, efficient production in a fully automated environment. Explore the cutting-edge automation technologies transforming modern manufacturing by learning more about these innovative approaches.
Human Labor
Just-in-time manufacturing relies heavily on human labor to coordinate inventory flow and assembly processes, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency through precise timing. In contrast, dark factories operate with minimal or no human presence, utilizing automation and robotics to maintain continuous production in controlled environments. Explore the impact of these differing labor approaches on productivity and operational costs.
Source and External Links
Just In Time Manufacturing: Definition, Benefits, and Origin - Just-in-time manufacturing (JIT) is a strategy that produces goods to meet customer orders exactly when needed, minimizing inventory, reducing waste, improving efficiency, and enhancing supplier relationships while allowing flexible adjustments to demand changes.
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - JIT manufacturing aligns production with demand using methodologies like setup reduction, balanced flow, cellular manufacturing, and pull systems to eliminate waste and ensure products are made just in time to meet customer needs.
What is just-in-time manufacturing (JIT manufacturing)? - TechTarget - JIT manufacturing is a production model focused on making products only as demand arises to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and speed delivery by eliminating overproduction, wait times, and excessive inventory.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com