Lights out factories operate fully automated systems with minimal to no human intervention, maximizing efficiency and reducing labor costs through continuous, round-the-clock production. Smart factories integrate advanced IoT sensors, data analytics, and AI-driven automation to enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive manufacturing processes. Discover how these innovative approaches transform industrial production for enhanced productivity and cost savings.
Why it is important
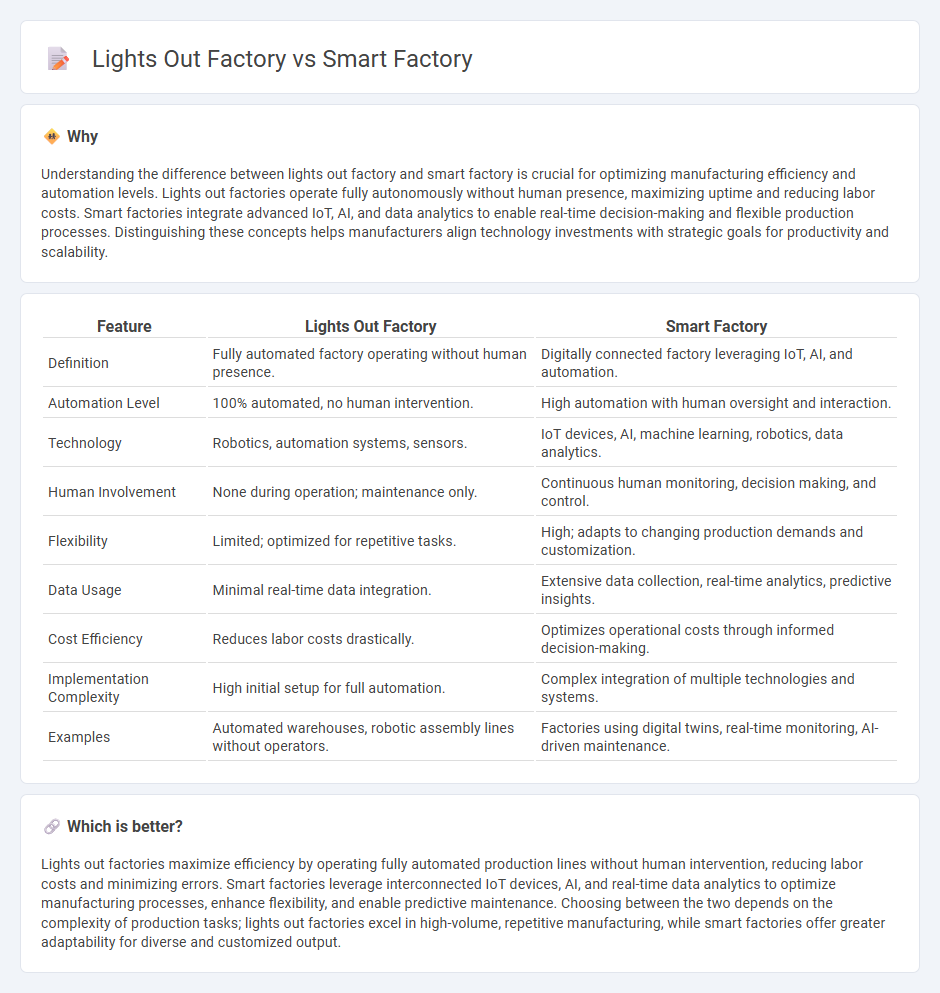
Understanding the difference between lights out factory and smart factory is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and automation levels. Lights out factories operate fully autonomously without human presence, maximizing uptime and reducing labor costs. Smart factories integrate advanced IoT, AI, and data analytics to enable real-time decision-making and flexible production processes. Distinguishing these concepts helps manufacturers align technology investments with strategic goals for productivity and scalability.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lights Out Factory | Smart Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fully automated factory operating without human presence. | Digitally connected factory leveraging IoT, AI, and automation. |
| Automation Level | 100% automated, no human intervention. | High automation with human oversight and interaction. |
| Technology | Robotics, automation systems, sensors. | IoT devices, AI, machine learning, robotics, data analytics. |
| Human Involvement | None during operation; maintenance only. | Continuous human monitoring, decision making, and control. |
| Flexibility | Limited; optimized for repetitive tasks. | High; adapts to changing production demands and customization. |
| Data Usage | Minimal real-time data integration. | Extensive data collection, real-time analytics, predictive insights. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces labor costs drastically. | Optimizes operational costs through informed decision-making. |
| Implementation Complexity | High initial setup for full automation. | Complex integration of multiple technologies and systems. |
| Examples | Automated warehouses, robotic assembly lines without operators. | Factories using digital twins, real-time monitoring, AI-driven maintenance. |
Which is better?
Lights out factories maximize efficiency by operating fully automated production lines without human intervention, reducing labor costs and minimizing errors. Smart factories leverage interconnected IoT devices, AI, and real-time data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes, enhance flexibility, and enable predictive maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on the complexity of production tasks; lights out factories excel in high-volume, repetitive manufacturing, while smart factories offer greater adaptability for diverse and customized output.
Connection
Lights out factories utilize fully automated systems allowing continuous production without human intervention, aligning closely with smart factory principles that integrate IoT, AI, and advanced robotics for optimized manufacturing efficiency. Smart factories provide real-time data analytics and predictive maintenance, enabling lights out operations to maintain high precision and reduce downtime. The synergy between lights out and smart factories drives enhanced productivity, cost reduction, and scalability in modern manufacturing processes.
Key Terms
Automation
Smart factories integrate advanced automation technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and robotics to optimize real-time production processes and enhance decision-making efficiency. Lights out factories operate under full automation with zero human intervention, relying on autonomous robots, machine learning algorithms, and automated monitoring systems to maintain continuous, 24/7 production. Explore the differences between these automation approaches to discover how they transform manufacturing productivity and innovation.
Data Integration
Smart factories leverage advanced data integration techniques to connect machines, systems, and processes, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance to enhance operational efficiency. Lights-out factories operate fully autonomously without human intervention, relying heavily on seamless data integration across IoT devices, AI algorithms, and cloud platforms to ensure uninterrupted production. Explore the latest innovations in data integration to optimize both smart and lights-out factory performance.
Human Intervention
Smart factories integrate advanced automation and IoT technologies to enhance production efficiency while still allowing for targeted human intervention to handle complex decision-making and maintenance tasks. Lights-out factories operate with minimal to no human presence, relying entirely on robotic systems and AI for continuous, autonomous manufacturing processes. Explore the key differences in human intervention between these factory models to optimize your industrial automation strategy.
Source and External Links
What is a smart factory? How to build ... - A smart factory is a digitalized manufacturing facility using sensors, cloud computing, AI, and machine learning to continuously improve production through real-time data analysis and intelligent automation as part of Industry 4.0.
What Is a Smart Factory? An Expert Guide - A smart factory is a highly automated, digitally connected environment integrating robotics, AI, and sensors to autonomously monitor and optimize manufacturing processes for increased efficiency, flexibility, and quality.
Smart Factory Guide | L2L - A smart factory connects machines, people, and processes with digital technologies, enabling data-driven improvements in efficiency, asset utilization, and cost reduction within the Industry 4.0 framework.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com