Machine vision integrates advanced imaging technologies to enhance precision in manufacturing processes, enabling real-time quality inspection and defect detection. Automation employs robotic systems and control software to streamline repetitive tasks, increase production speed, and reduce human error in factories. Explore the differences and synergies between machine vision and automation to optimize manufacturing efficiency and innovation.
Why it is important
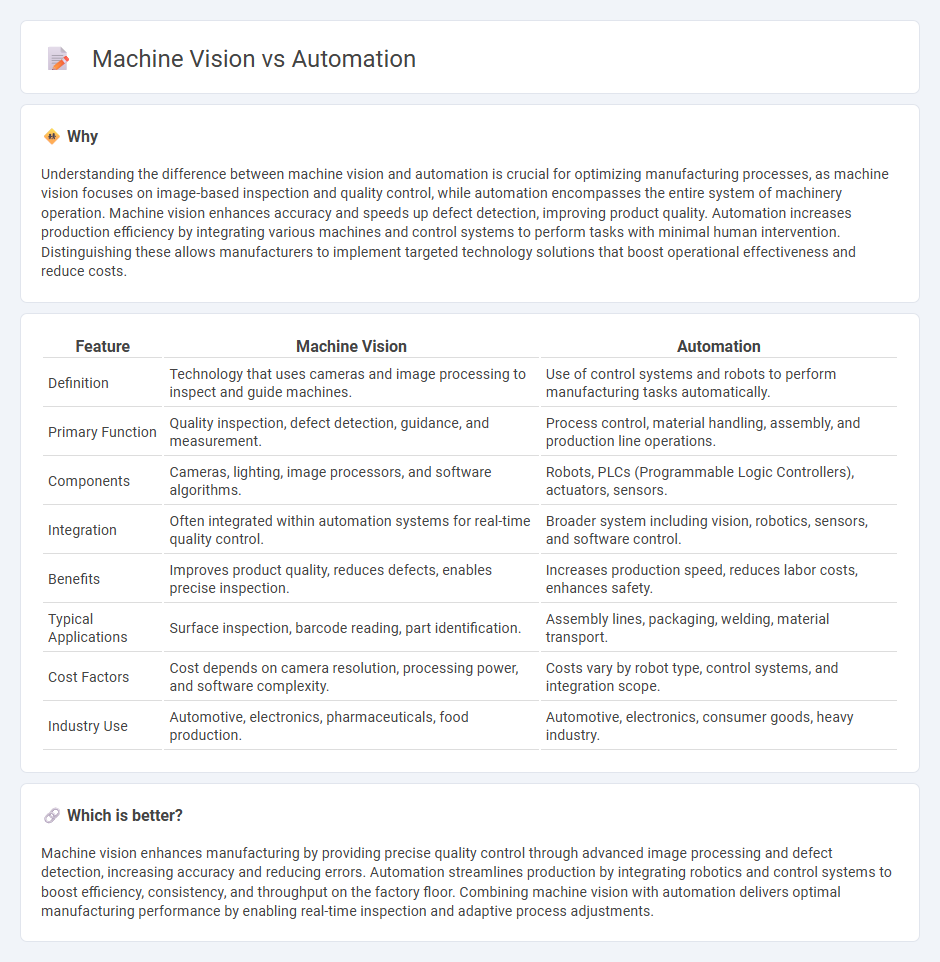
Understanding the difference between machine vision and automation is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, as machine vision focuses on image-based inspection and quality control, while automation encompasses the entire system of machinery operation. Machine vision enhances accuracy and speeds up defect detection, improving product quality. Automation increases production efficiency by integrating various machines and control systems to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. Distinguishing these allows manufacturers to implement targeted technology solutions that boost operational effectiveness and reduce costs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Machine Vision | Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology that uses cameras and image processing to inspect and guide machines. | Use of control systems and robots to perform manufacturing tasks automatically. |
| Primary Function | Quality inspection, defect detection, guidance, and measurement. | Process control, material handling, assembly, and production line operations. |
| Components | Cameras, lighting, image processors, and software algorithms. | Robots, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), actuators, sensors. |
| Integration | Often integrated within automation systems for real-time quality control. | Broader system including vision, robotics, sensors, and software control. |
| Benefits | Improves product quality, reduces defects, enables precise inspection. | Increases production speed, reduces labor costs, enhances safety. |
| Typical Applications | Surface inspection, barcode reading, part identification. | Assembly lines, packaging, welding, material transport. |
| Cost Factors | Cost depends on camera resolution, processing power, and software complexity. | Costs vary by robot type, control systems, and integration scope. |
| Industry Use | Automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, food production. | Automotive, electronics, consumer goods, heavy industry. |
Which is better?
Machine vision enhances manufacturing by providing precise quality control through advanced image processing and defect detection, increasing accuracy and reducing errors. Automation streamlines production by integrating robotics and control systems to boost efficiency, consistency, and throughput on the factory floor. Combining machine vision with automation delivers optimal manufacturing performance by enabling real-time inspection and adaptive process adjustments.
Connection
Machine vision integrates advanced imaging technologies with automation systems to enable real-time inspection, quality control, and precise guidance in manufacturing processes. Automated machinery equipped with machine vision can detect defects, measure dimensions, and ensure product consistency, significantly reducing human error and increasing production efficiency. This synergy drives the evolution of smart factories by enhancing accuracy, speed, and adaptability in manufacturing operations.
Key Terms
Robotics
Automation in robotics enhances efficiency by integrating programmable systems that perform repetitive tasks with minimal human input. Machine vision complements this by enabling robots to interpret visual data through cameras and sensors, improving precision in operations such as quality inspection and object recognition. Explore further to understand how these technologies synergize to revolutionize industrial robotics.
Image Processing
Automation in manufacturing increasingly relies on machine vision systems that utilize advanced image processing techniques to inspect, measure, and guide operations with high precision. Machine vision processes visual data through algorithms like pattern recognition, edge detection, and 3D imaging to enable real-time decision making and quality control. Explore how integrating cutting-edge image processing with automation boosts efficiency and accuracy in industrial applications.
Quality Control
Automation integrates programmable systems to manage repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency and consistency in industrial processes. Machine vision employs advanced imaging technologies and AI algorithms to inspect products, detect defects, and ensure precise quality control in manufacturing. Explore how combining automation and machine vision transforms quality assurance standards in your industry.
Source and External Links
Automation - Wikipedia - Automation involves technologies that reduce human intervention by predetermining decision criteria and actions, implemented via mechanical, hydraulic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, improving labor savings, quality, and efficiency across many industries.
What Is Automation? - IBM - Automation is applying technology, programs, robotics, or processes to achieve outcomes with minimal human input, widely used in business, healthcare, manufacturing, and home applications to increase productivity and reduce errors.
Understanding automation - Red Hat - Automation uses technology to perform tasks with reduced human assistance across industries like manufacturing and IT, including fields such as IT automation, business process automation, industrial automation, and artificial intelligence.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com