Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition through processes such as disassembly, cleaning, and component replacement, extending product life cycles and reducing waste. Circular manufacturing focuses on designing products and systems that enable continuous reuse of materials, emphasizing sustainability and resource efficiency throughout the production chain. Explore how these innovative manufacturing strategies drive environmental and economic benefits in today's industrial landscape.
Why it is important
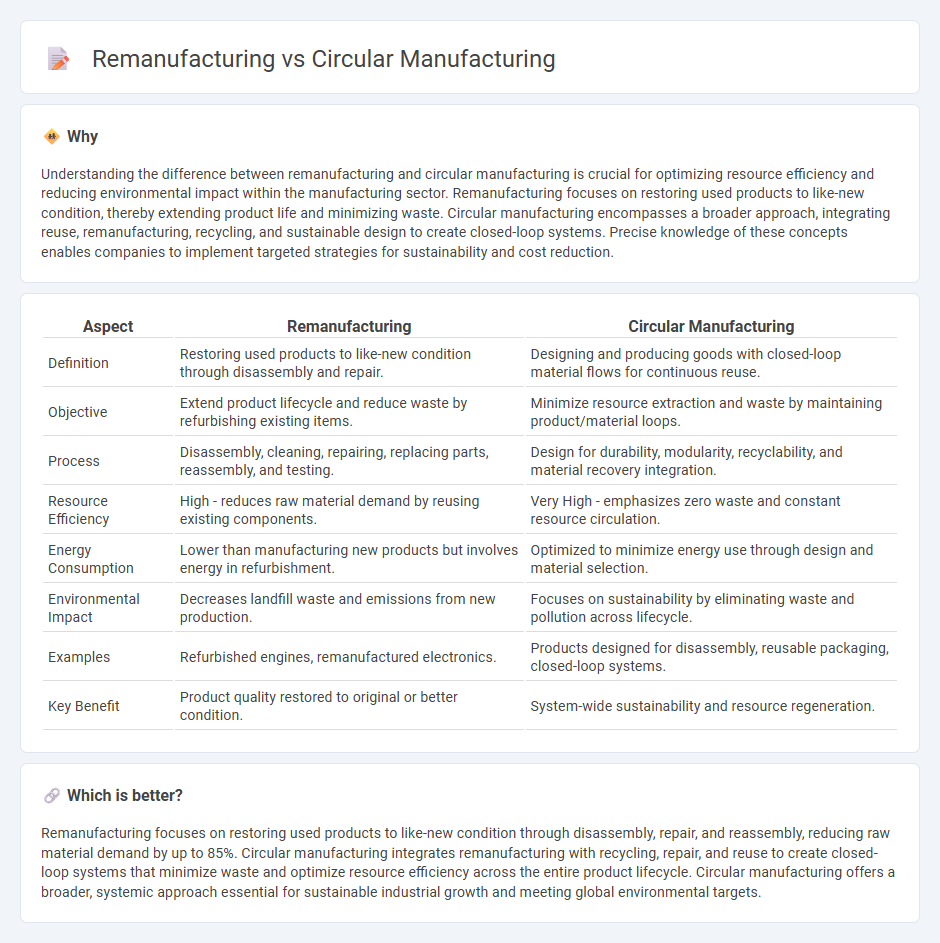
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and circular manufacturing is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and reducing environmental impact within the manufacturing sector. Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition, thereby extending product life and minimizing waste. Circular manufacturing encompasses a broader approach, integrating reuse, remanufacturing, recycling, and sustainable design to create closed-loop systems. Precise knowledge of these concepts enables companies to implement targeted strategies for sustainability and cost reduction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Circular Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restoring used products to like-new condition through disassembly and repair. | Designing and producing goods with closed-loop material flows for continuous reuse. |
| Objective | Extend product lifecycle and reduce waste by refurbishing existing items. | Minimize resource extraction and waste by maintaining product/material loops. |
| Process | Disassembly, cleaning, repairing, replacing parts, reassembly, and testing. | Design for durability, modularity, recyclability, and material recovery integration. |
| Resource Efficiency | High - reduces raw material demand by reusing existing components. | Very High - emphasizes zero waste and constant resource circulation. |
| Energy Consumption | Lower than manufacturing new products but involves energy in refurbishment. | Optimized to minimize energy use through design and material selection. |
| Environmental Impact | Decreases landfill waste and emissions from new production. | Focuses on sustainability by eliminating waste and pollution across lifecycle. |
| Examples | Refurbished engines, remanufactured electronics. | Products designed for disassembly, reusable packaging, closed-loop systems. |
| Key Benefit | Product quality restored to original or better condition. | System-wide sustainability and resource regeneration. |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition through disassembly, repair, and reassembly, reducing raw material demand by up to 85%. Circular manufacturing integrates remanufacturing with recycling, repair, and reuse to create closed-loop systems that minimize waste and optimize resource efficiency across the entire product lifecycle. Circular manufacturing offers a broader, systemic approach essential for sustainable industrial growth and meeting global environmental targets.
Connection
Remanufacturing is a core process within circular manufacturing, focusing on restoring used products to like-new condition to extend their lifecycle. Circular manufacturing prioritizes resource efficiency by integrating remanufacturing, recycling, and reuse to minimize waste and reduce raw material consumption. This interconnected approach supports sustainable production by closing the loop and promoting a circular economy in manufacturing industries.
Key Terms
Resource Loop Closure
Circular manufacturing emphasizes designing products for continuous reuse, repair, and recycling to achieve complete resource loop closure, minimizing waste and raw material extraction. Remanufacturing specifically targets the restoration of used products to like-new condition, extending product lifespans and conserving energy compared to new production. Explore more to understand how these strategies drive sustainable industrial transformation and efficient resource management.
Product Life Extension
Circular manufacturing emphasizes designing products with durable materials and modular components to maximize reuse opportunities and reduce waste throughout multiple life cycles. Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, extending product life by reclaiming value and minimizing resource consumption. Explore how integrating these strategies boosts sustainability and economic benefits in product life extension.
Component Reuse
Circular manufacturing emphasizes designing products for multiple life cycles, prioritizing component reuse to minimize waste and resource consumption. Remanufacturing specifically involves restoring used components to like-new condition, extending product lifespan while maintaining quality standards. Explore further to understand strategies enhancing sustainability through component reuse in both processes.
Source and External Links
What is Circular Manufacturing - Plataine - Circular manufacturing is a sustainable production approach focused on eliminating waste by maintaining and recapturing value from products using reduce, reuse, and recycle principles, shifting away from the traditional linear "take-make-dispose" economy to optimize resources and reduce environmental impact.
What is Circular Economy & Closed Loop Manufacturing? Katana - Circular manufacturing embodies the circular economy model which aims to eliminate waste by keeping materials in use as long as possible through repair, reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, thereby protecting ecosystems and reducing pollution.
How the circular economy secures manufacturing supply chains - World Economic Forum - Manufacturers adopting circular economy principles can build resilient, sustainable supply chains by reimagining product design and production, leveraging digital technologies, and viewing waste as opportunities for value creation and innovation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com