Servitization transforms traditional manufacturing by integrating services to enhance product value, shifting focus from mere production to comprehensive customer solutions. Additive Manufacturing employs layer-by-layer material deposition, enabling complex designs, customization, and reduced material waste, revolutionizing prototyping and production processes. Explore the evolving impact of servitization and additive manufacturing on modern industry dynamics.
Why it is important
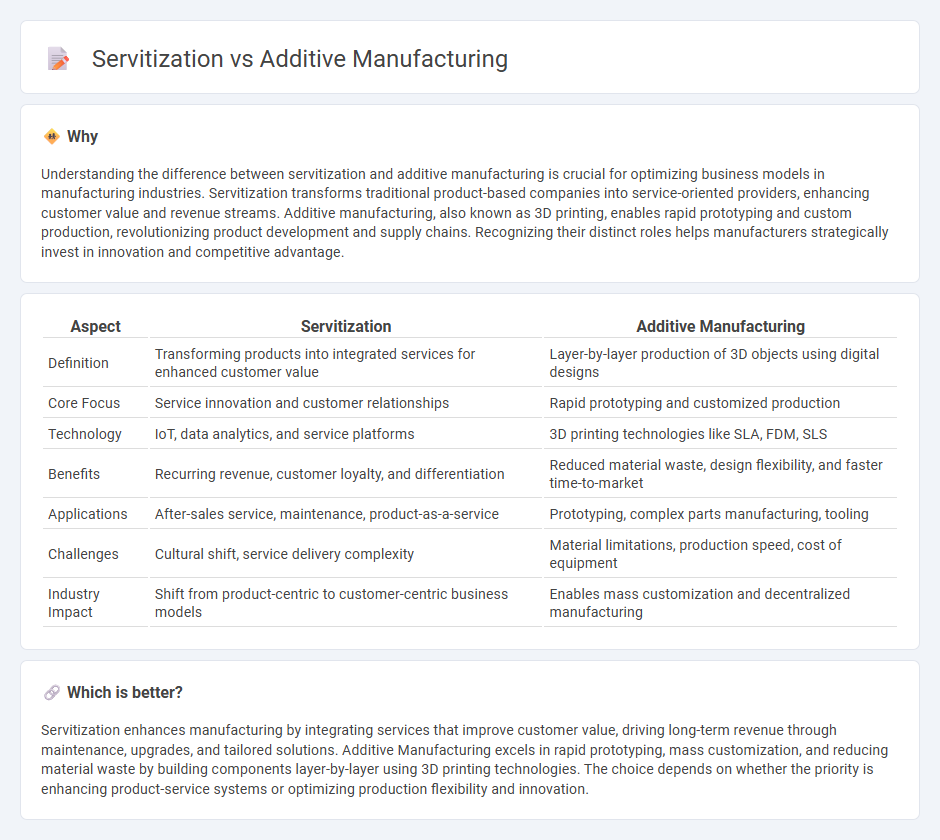
Understanding the difference between servitization and additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing business models in manufacturing industries. Servitization transforms traditional product-based companies into service-oriented providers, enhancing customer value and revenue streams. Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, enables rapid prototyping and custom production, revolutionizing product development and supply chains. Recognizing their distinct roles helps manufacturers strategically invest in innovation and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Servitization | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforming products into integrated services for enhanced customer value | Layer-by-layer production of 3D objects using digital designs |
| Core Focus | Service innovation and customer relationships | Rapid prototyping and customized production |
| Technology | IoT, data analytics, and service platforms | 3D printing technologies like SLA, FDM, SLS |
| Benefits | Recurring revenue, customer loyalty, and differentiation | Reduced material waste, design flexibility, and faster time-to-market |
| Applications | After-sales service, maintenance, product-as-a-service | Prototyping, complex parts manufacturing, tooling |
| Challenges | Cultural shift, service delivery complexity | Material limitations, production speed, cost of equipment |
| Industry Impact | Shift from product-centric to customer-centric business models | Enables mass customization and decentralized manufacturing |
Which is better?
Servitization enhances manufacturing by integrating services that improve customer value, driving long-term revenue through maintenance, upgrades, and tailored solutions. Additive Manufacturing excels in rapid prototyping, mass customization, and reducing material waste by building components layer-by-layer using 3D printing technologies. The choice depends on whether the priority is enhancing product-service systems or optimizing production flexibility and innovation.
Connection
Servitization enhances manufacturing by integrating services like maintenance and customization, which align with Additive Manufacturing's ability to produce complex, tailored parts on demand. Additive Manufacturing supports servitization by enabling rapid prototyping and scalable production of personalized products, increasing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Together, they drive innovation and create new revenue streams through combining product functionality with value-added services.
Key Terms
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, prominently exemplified by 3D printing, revolutionizes production by enabling layer-by-layer fabrication of complex geometries directly from digital models, significantly reducing material waste and lead times compared to traditional manufacturing. Servitization in the context of 3D printing transforms business models by integrating services such as design customization, on-demand production, and maintenance, enhancing value propositions beyond mere product delivery. Explore the evolving landscape of 3D printing technologies and servitization strategies to unlock innovative industrial solutions.
Digital Twin
Additive Manufacturing leverages digital twin technology to create precise virtual replicas of physical objects, enhancing production accuracy and customization in real-time. Servitization integrates digital twins to optimize product lifecycle management and enable predictive maintenance, transforming traditional manufacturing into service-oriented business models. Explore how digital twin innovations bridge additive manufacturing and servitization for smarter industrial solutions.
Product-Service Systems (PSS)
Additive Manufacturing enhances Product-Service Systems (PSS) by enabling customized, on-demand production that reduces inventory costs and accelerates product updates. Servitization transforms traditional manufacturing by integrating services such as maintenance and upgrades, creating continuous value beyond the initial sale. Explore how combining Additive Manufacturing with servitization strategies can optimize PSS for competitive advantage.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing is the process of creating objects by building them layer by layer, directly from digital designs, and encompasses a wide range of materials and applications from prototyping to industrial production.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing (AM), often called 3D printing, fabricates parts by adding material layer by layer, enabling complex designs with less waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
3D printing - Wikipedia - 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, constructs three-dimensional objects from digital models through various processes that deposit, join, or solidify material under computer control, typically layer by layer.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com