Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in manufacturing streamlines repetitive tasks by using software robots to enhance operational efficiency, while Advanced Process Control (APC) optimizes complex process variables through real-time data analytics and feedback loops to improve product quality and reduce waste. Both technologies drive digital transformation in production environments, with RPA focusing on administrative automation and APC targeting process optimization. Explore how integrating RPA and APC can revolutionize your manufacturing operations.
Why it is important
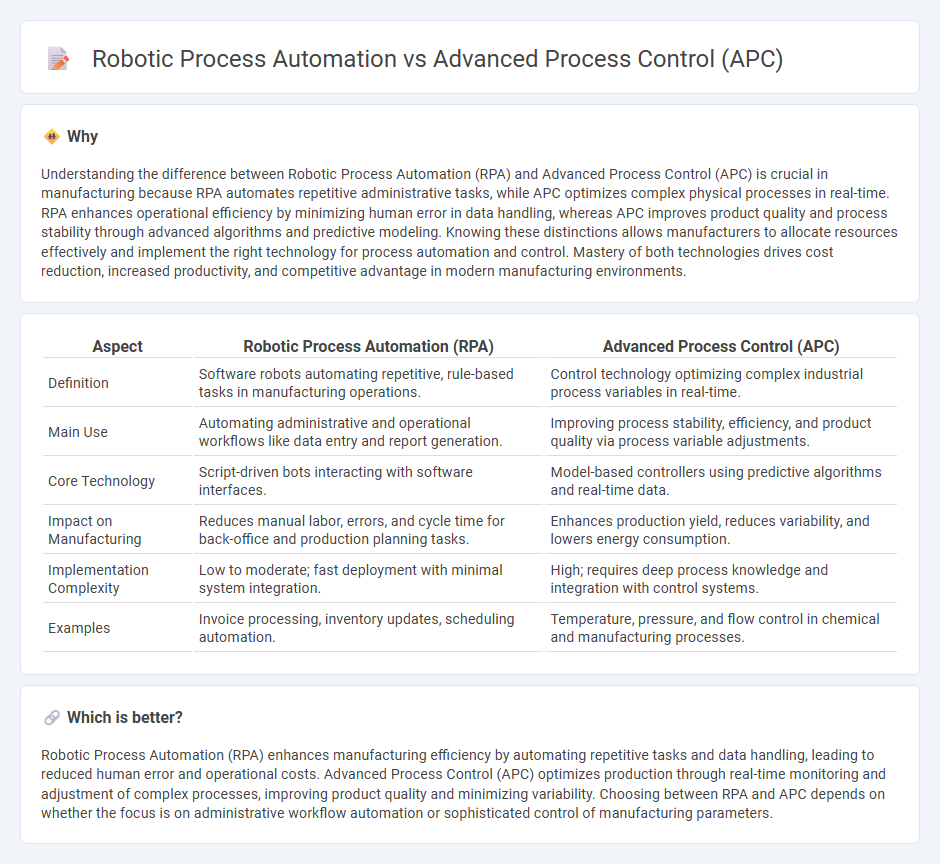
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Advanced Process Control (APC) is crucial in manufacturing because RPA automates repetitive administrative tasks, while APC optimizes complex physical processes in real-time. RPA enhances operational efficiency by minimizing human error in data handling, whereas APC improves product quality and process stability through advanced algorithms and predictive modeling. Knowing these distinctions allows manufacturers to allocate resources effectively and implement the right technology for process automation and control. Mastery of both technologies drives cost reduction, increased productivity, and competitive advantage in modern manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Advanced Process Control (APC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automating repetitive, rule-based tasks in manufacturing operations. | Control technology optimizing complex industrial process variables in real-time. |
| Main Use | Automating administrative and operational workflows like data entry and report generation. | Improving process stability, efficiency, and product quality via process variable adjustments. |
| Core Technology | Script-driven bots interacting with software interfaces. | Model-based controllers using predictive algorithms and real-time data. |
| Impact on Manufacturing | Reduces manual labor, errors, and cycle time for back-office and production planning tasks. | Enhances production yield, reduces variability, and lowers energy consumption. |
| Implementation Complexity | Low to moderate; fast deployment with minimal system integration. | High; requires deep process knowledge and integration with control systems. |
| Examples | Invoice processing, inventory updates, scheduling automation. | Temperature, pressure, and flow control in chemical and manufacturing processes. |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances manufacturing efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and data handling, leading to reduced human error and operational costs. Advanced Process Control (APC) optimizes production through real-time monitoring and adjustment of complex processes, improving product quality and minimizing variability. Choosing between RPA and APC depends on whether the focus is on administrative workflow automation or sophisticated control of manufacturing parameters.
Connection
Robotic process automation (RPA) and Advanced Process Control (APC) are interconnected in manufacturing through their ability to enhance operational efficiency and precision. RPA streamlines repetitive tasks such as data collection and reporting, while APC optimizes control of manufacturing processes by using real-time data analytics and predictive algorithms. Integrating RPA with APC enables manufacturers to achieve higher productivity, reduce downtime, and maintain consistent product quality through automated decision-making and process adjustments.
Key Terms
Real-time optimization
Advanced Process Control (APC) employs real-time optimization techniques to enhance manufacturing process efficiency and product quality by continuously adjusting control variables based on dynamic data. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive digital tasks without real-time data integration or process optimization capabilities. Explore how APC's real-time optimization transforms industrial operations beyond RPA's automation scope.
Feedback control systems
Advanced Process Control (APC) leverages feedback control systems to optimize industrial processes by continuously adjusting variables based on real-time data, enhancing stability and efficiency in dynamic environments. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based digital tasks but lacks the adaptive feedback mechanisms inherent in APC's control loops. Explore the critical distinctions between APC's feedback-driven optimization and RPA's task automation to improve process management strategies.
Automated task execution
Advanced process control (APC) optimizes industrial processes by using real-time data and predictive algorithms to enhance production efficiency, quality, and stability. Robotic process automation (RPA) automates repetitive administrative tasks by mimicking human actions in software systems to improve accuracy and reduce manual workload. Explore the detailed comparison between APC and RPA to understand which automation suits your operational goals.
Source and External Links
Advanced process control - Wikipedia - Advanced process control (APC) refers to a broad range of techniques and technologies implemented beyond basic process controls to improve industrial process performance in industries like chemicals, refining, food processing, and power generation, often using distributed control systems and supervisory computers.
Advanced Process Control: Definition, Benefits, and Applications - APC integrates advanced techniques such as model predictive control, multivariable control, process models, optimization algorithms, and real-time data analytics to enhance control over complex industrial processes by predicting future behavior, managing multiple variables, and optimizing operations safely and efficiently.
Advanced Process Control Software, Solutions & Systems - ABB - APC is a software solution interfacing with distributed control systems to improve plant profitability by enhancing production, yield, and efficiency through technologies like fuzzy logic, MPC, soft sensors, and machine learning, with typical savings ranging from hundreds of thousands to millions annually.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com