Green steel production reduces carbon emissions by using renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power instead of fossil fuels. Hydrogen steel manufacturing replaces coal with green hydrogen in the reduction process, minimizing CO2 output and enabling cleaner production. Explore the differences and advantages of green steel versus hydrogen steel to understand their impact on sustainable manufacturing.
Why it is important
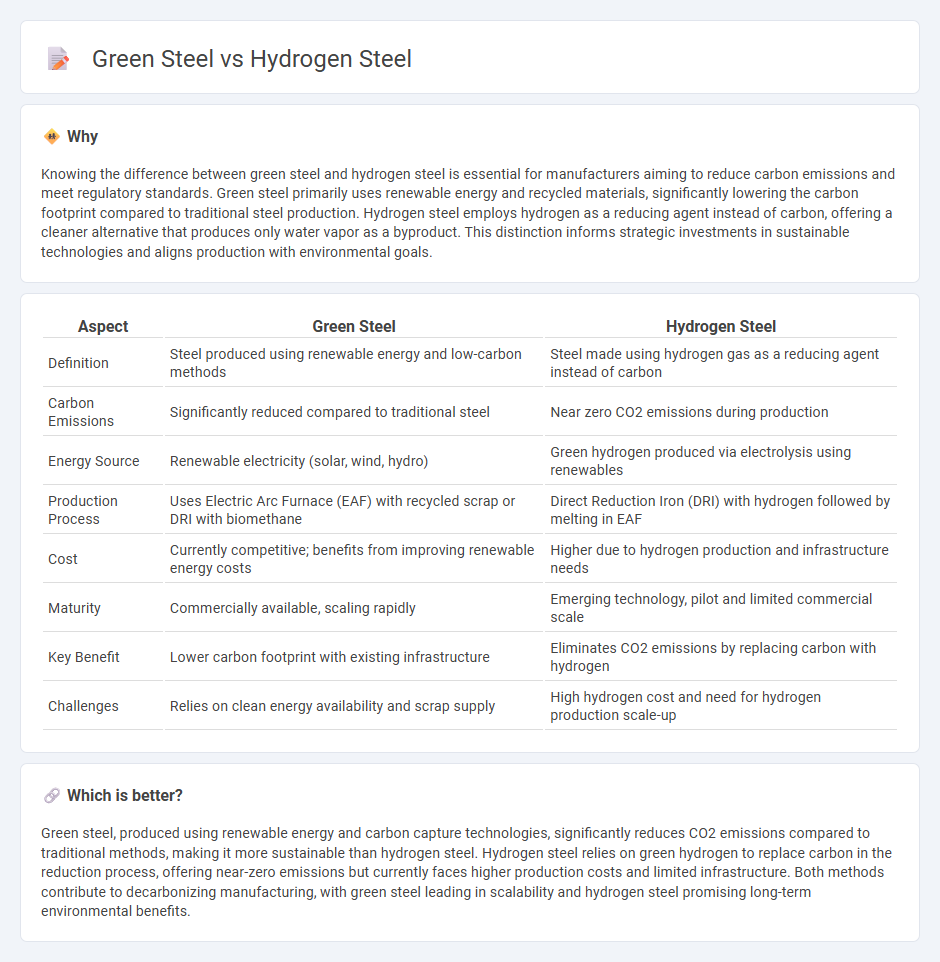
Knowing the difference between green steel and hydrogen steel is essential for manufacturers aiming to reduce carbon emissions and meet regulatory standards. Green steel primarily uses renewable energy and recycled materials, significantly lowering the carbon footprint compared to traditional steel production. Hydrogen steel employs hydrogen as a reducing agent instead of carbon, offering a cleaner alternative that produces only water vapor as a byproduct. This distinction informs strategic investments in sustainable technologies and aligns production with environmental goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Steel | Hydrogen Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Steel produced using renewable energy and low-carbon methods | Steel made using hydrogen gas as a reducing agent instead of carbon |
| Carbon Emissions | Significantly reduced compared to traditional steel | Near zero CO2 emissions during production |
| Energy Source | Renewable electricity (solar, wind, hydro) | Green hydrogen produced via electrolysis using renewables |
| Production Process | Uses Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) with recycled scrap or DRI with biomethane | Direct Reduction Iron (DRI) with hydrogen followed by melting in EAF |
| Cost | Currently competitive; benefits from improving renewable energy costs | Higher due to hydrogen production and infrastructure needs |
| Maturity | Commercially available, scaling rapidly | Emerging technology, pilot and limited commercial scale |
| Key Benefit | Lower carbon footprint with existing infrastructure | Eliminates CO2 emissions by replacing carbon with hydrogen |
| Challenges | Relies on clean energy availability and scrap supply | High hydrogen cost and need for hydrogen production scale-up |
Which is better?
Green steel, produced using renewable energy and carbon capture technologies, significantly reduces CO2 emissions compared to traditional methods, making it more sustainable than hydrogen steel. Hydrogen steel relies on green hydrogen to replace carbon in the reduction process, offering near-zero emissions but currently faces higher production costs and limited infrastructure. Both methods contribute to decarbonizing manufacturing, with green steel leading in scalability and hydrogen steel promising long-term environmental benefits.
Connection
Green steel and hydrogen steel are interconnected through the use of hydrogen as a clean reducing agent in the steel manufacturing process, replacing carbon-intensive coke typically used in traditional methods. This shift reduces CO2 emissions significantly by utilizing green hydrogen produced via renewable energy sources, aligning with the industry's goals for sustainable and low-carbon steel production. Both technologies contribute to decarbonizing manufacturing, enhancing energy efficiency, and meeting global climate targets within the steel sector.
Key Terms
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI)
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) is a critical component in both hydrogen steel and green steel production, serving as the iron source with significantly lower carbon emissions compared to traditional blast furnace methods. Hydrogen-based DRI uses hydrogen gas as the reducing agent, effectively eliminating CO2 emissions by producing water vapor, whereas green steel production integrates DRI with renewable energy sources and carbon capture technologies to enhance sustainability. Explore in-depth how DRI innovations drive the future of low-carbon steel manufacturing.
Electrolysis
Hydrogen steel production uses electrolysis to generate green hydrogen by splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, minimizing carbon emissions compared to traditional steelmaking. Green steel, often produced through direct use of this green hydrogen in reduction processes, significantly reduces reliance on coal and fossil fuels, driving a cleaner industry. Explore how electrolysis technology is transforming steel manufacturing towards sustainability with lower environmental impact.
Carbon Emissions
Hydrogen steel production utilizes green hydrogen to reduce carbon emissions by replacing coal in the steelmaking process, significantly lowering CO2 output compared to traditional methods. Green steel, often produced through electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy, achieves near-zero carbon emissions by recycling scrap steel or using direct reduction of iron with hydrogen. Explore the technological advancements and environmental impacts of hydrogen steel versus green steel to understand their roles in sustainable industry transformation.
Source and External Links
Hydrogen sparks change for the future of green steel production - Hydrogen, especially when produced as "blue" or "green" hydrogen, is emerging as a key technology to decarbonize steel production, offering reduced carbon emissions and improved local environmental quality, though it remains more expensive and is still at the pilot stage globally.
Cutting the Carbon Intensity of Steel Using Hydrogen and Renewables - Hydrogen-based direct reduction of iron ore is a promising low-carbon steelmaking process, releasing only water vapor instead of CO2, with major steel companies now planning large-scale hydrogen-powered plants worldwide.
Green H2-DRI Steelmaking: 15 Challenges and solutions - The transition to green hydrogen in direct reduced iron (H2-DRI) steelmaking offers significant climate benefits, but faces technological and economic challenges in scaling up to replace conventional coal-based production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com