Industrial Internet integrates advanced sensors, data analytics, and machine-to-machine communication to optimize manufacturing processes with real-time insights and predictive maintenance. Smart Factory employs automation, IoT technologies, and adaptive manufacturing systems to create flexible, efficient production environments that enhance productivity and reduce downtime. Discover how these innovations are transforming the future of manufacturing.
Why it is important
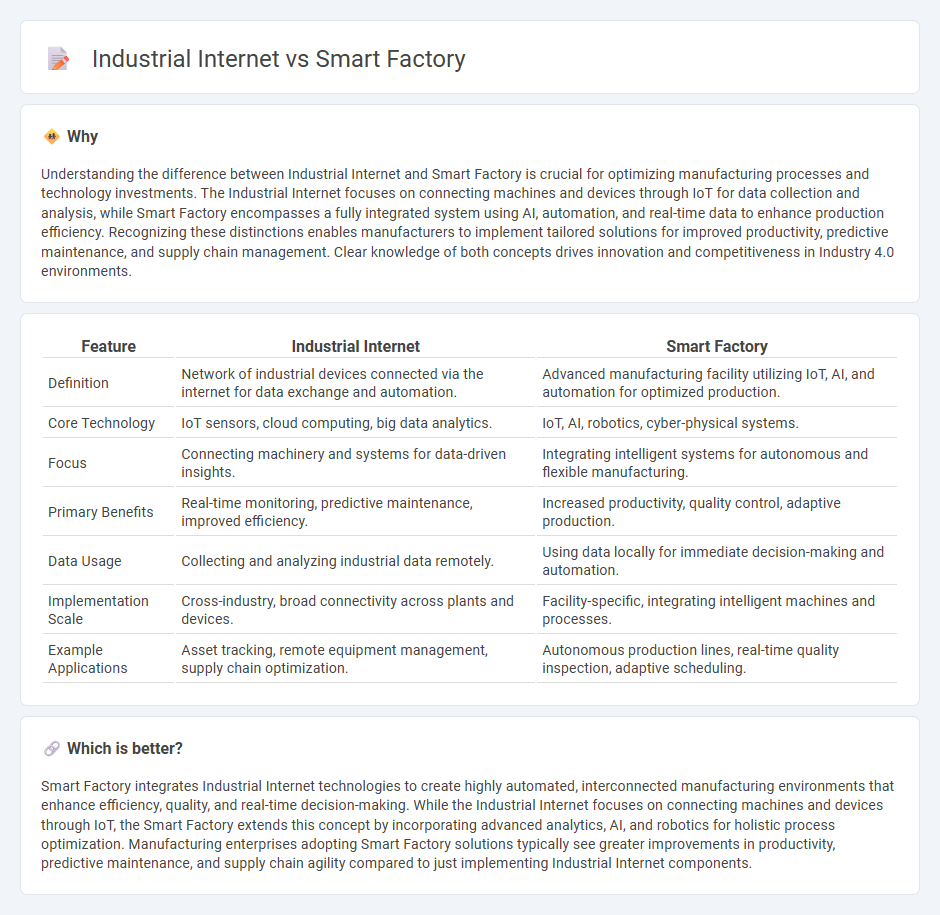
Understanding the difference between Industrial Internet and Smart Factory is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes and technology investments. The Industrial Internet focuses on connecting machines and devices through IoT for data collection and analysis, while Smart Factory encompasses a fully integrated system using AI, automation, and real-time data to enhance production efficiency. Recognizing these distinctions enables manufacturers to implement tailored solutions for improved productivity, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management. Clear knowledge of both concepts drives innovation and competitiveness in Industry 4.0 environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Industrial Internet | Smart Factory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network of industrial devices connected via the internet for data exchange and automation. | Advanced manufacturing facility utilizing IoT, AI, and automation for optimized production. |
| Core Technology | IoT sensors, cloud computing, big data analytics. | IoT, AI, robotics, cyber-physical systems. |
| Focus | Connecting machinery and systems for data-driven insights. | Integrating intelligent systems for autonomous and flexible manufacturing. |
| Primary Benefits | Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, improved efficiency. | Increased productivity, quality control, adaptive production. |
| Data Usage | Collecting and analyzing industrial data remotely. | Using data locally for immediate decision-making and automation. |
| Implementation Scale | Cross-industry, broad connectivity across plants and devices. | Facility-specific, integrating intelligent machines and processes. |
| Example Applications | Asset tracking, remote equipment management, supply chain optimization. | Autonomous production lines, real-time quality inspection, adaptive scheduling. |
Which is better?
Smart Factory integrates Industrial Internet technologies to create highly automated, interconnected manufacturing environments that enhance efficiency, quality, and real-time decision-making. While the Industrial Internet focuses on connecting machines and devices through IoT, the Smart Factory extends this concept by incorporating advanced analytics, AI, and robotics for holistic process optimization. Manufacturing enterprises adopting Smart Factory solutions typically see greater improvements in productivity, predictive maintenance, and supply chain agility compared to just implementing Industrial Internet components.
Connection
The Industrial Internet integrates advanced sensors, data analytics, and machine-to-machine communication to enable real-time monitoring and automation within Smart Factories. Smart Factories utilize this connectivity to optimize production processes, enhance efficiency, and reduce downtime through predictive maintenance and intelligent supply chain management. The synergy between the Industrial Internet and Smart Factory frameworks drives digital transformation in manufacturing, promoting higher productivity and adaptive manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Automation
Smart Factory integrates advanced automation technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-driven robotics, and real-time data analytics to optimize manufacturing processes, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality. The Industrial Internet emphasizes connectivity of industrial devices and systems to enable predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and improved operational efficiency across complex supply chains. Explore the differences and applications of these automation-driven solutions to unlock the full potential of modern manufacturing.
IoT (Internet of Things)
The Smart Factory integrates IoT technologies to enable real-time data exchange, automation, and enhanced operational efficiency, transforming traditional manufacturing processes into interconnected systems. The Industrial Internet, a broader concept, connects heavy machinery and industrial equipment through IoT to optimize asset performance, predictive maintenance, and scalability across sectors. Explore the key distinctions and synergies between Smart Factories and the Industrial Internet to maximize IoT benefits in your operations.
Data Analytics
Smart factories leverage advanced data analytics to optimize production processes, enhance real-time decision-making, and improve operational efficiency by integrating IoT sensors, AI, and machine learning algorithms. The industrial internet emphasizes connecting industrial devices and systems to collect vast amounts of data, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime through intelligent analytics platforms. Explore how data analytics transforms manufacturing by unlocking comprehensive insights into both smart factory environments and industrial internet ecosystems.
Source and External Links
What Is a Smart Factory? An Expert Guide - A smart factory is a highly automated, digitally connected manufacturing environment that uses advanced technologies like AI, robotics, and machine learning to continuously improve operations and enable autonomous production processes with benefits including increased revenue, reduced costs, and better product quality.
What is a smart factory? How to build ... - A smart factory is the production component of smart manufacturing, leveraging digitalization, sensors, AI, and cloud computing to enable continuous process improvement, serving as a key part of Industry 4.0's intelligent automation.
What is Smart Factory and Smart Manufacturing? - A smart factory integrates interconnected systems and sensors to generate real-time data that enhances production efficiency, machine maintenance, and product quality by predicting needs and preventing defects through digital-physical convergence.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com