Green steel production utilizes renewable energy and hydrogen to reduce iron ore, significantly lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional methods. Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) steel uses natural gas to remove oxygen from iron ore, offering improved efficiency but still relying on fossil fuels. Explore the environmental and economic impacts of both processes to understand their role in sustainable manufacturing.
Why it is important
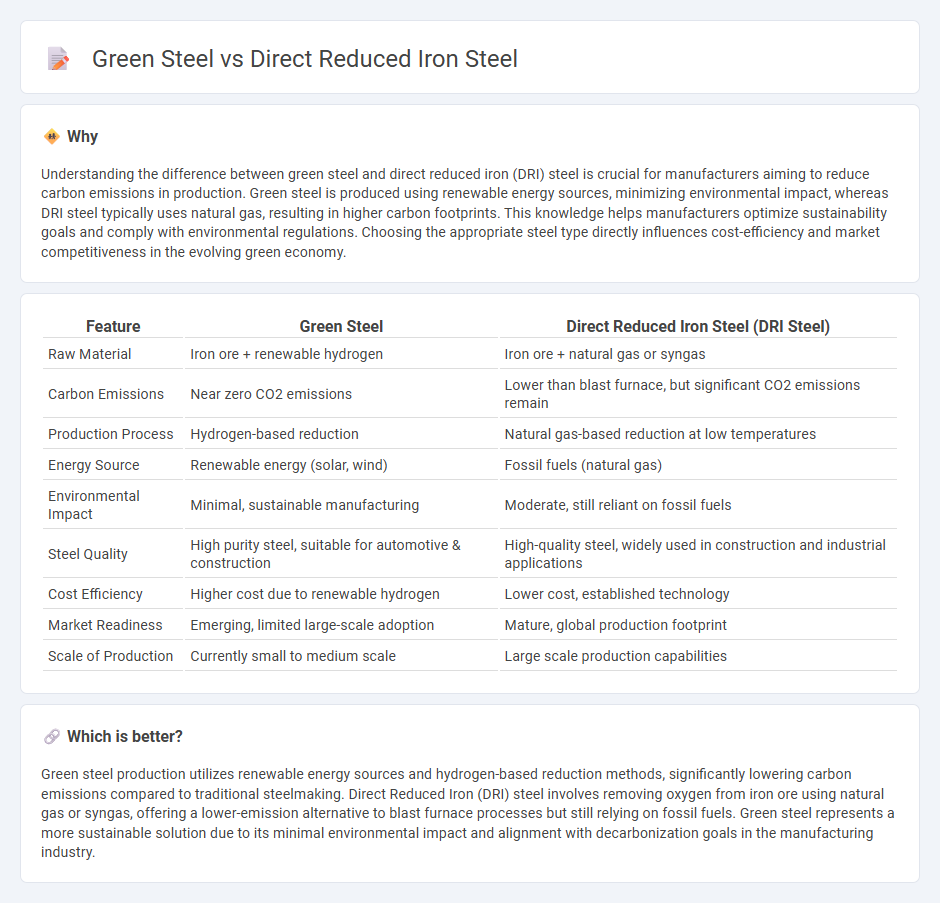
Understanding the difference between green steel and direct reduced iron (DRI) steel is crucial for manufacturers aiming to reduce carbon emissions in production. Green steel is produced using renewable energy sources, minimizing environmental impact, whereas DRI steel typically uses natural gas, resulting in higher carbon footprints. This knowledge helps manufacturers optimize sustainability goals and comply with environmental regulations. Choosing the appropriate steel type directly influences cost-efficiency and market competitiveness in the evolving green economy.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Green Steel | Direct Reduced Iron Steel (DRI Steel) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Iron ore + renewable hydrogen | Iron ore + natural gas or syngas |
| Carbon Emissions | Near zero CO2 emissions | Lower than blast furnace, but significant CO2 emissions remain |
| Production Process | Hydrogen-based reduction | Natural gas-based reduction at low temperatures |
| Energy Source | Renewable energy (solar, wind) | Fossil fuels (natural gas) |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal, sustainable manufacturing | Moderate, still reliant on fossil fuels |
| Steel Quality | High purity steel, suitable for automotive & construction | High-quality steel, widely used in construction and industrial applications |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost due to renewable hydrogen | Lower cost, established technology |
| Market Readiness | Emerging, limited large-scale adoption | Mature, global production footprint |
| Scale of Production | Currently small to medium scale | Large scale production capabilities |
Which is better?
Green steel production utilizes renewable energy sources and hydrogen-based reduction methods, significantly lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional steelmaking. Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) steel involves removing oxygen from iron ore using natural gas or syngas, offering a lower-emission alternative to blast furnace processes but still relying on fossil fuels. Green steel represents a more sustainable solution due to its minimal environmental impact and alignment with decarbonization goals in the manufacturing industry.
Connection
Green steel production relies heavily on direct reduced iron (DRI) as a low-carbon feedstock, utilizing hydrogen or natural gas instead of traditional coal-based methods to reduce iron ore. This process significantly lowers carbon dioxide emissions, aligning with sustainability goals in modern manufacturing. The integration of DRI technology in steelmaking represents a critical advancement towards achieving carbon-neutral steel production.
Key Terms
Hydrogen reduction
Direct reduced iron (DRI) steel produced via hydrogen reduction leverages hydrogen as a clean reducing agent, significantly lowering CO2 emissions compared to traditional fossil fuel methods. Green steel emphasizes this approach by utilizing renewable hydrogen derived from electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources, further decarbonizing the steel production process. Explore the advancements in hydrogen-based steelmaking to understand its potential for sustainable industrial transformation.
Carbon emissions
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) steel production emits significantly higher carbon emissions compared to green steel technologies that utilize renewable energy sources and hydrogen-based reduction. While DRI processes release approximately 2 tons of CO2 per ton of steel produced, green steel aims to reduce this footprint nearly to zero by replacing carbon-intensive methods with clean energy. Explore the latest advancements and environmental impacts of these steel production methods to understand their role in decarbonizing the industry.
Electric arc furnace
Direct reduced iron (DRI) steel offers high-quality scrap alternative feedstock for electric arc furnaces (EAF), improving yield and enhancing energy efficiency compared to traditional scrap inputs. Green steel produced via electric arc furnace technology integrates renewable energy sources, significantly lowering carbon emissions in steelmaking processes. Discover how these advancements in EAF utilization can transform sustainable steel production.
Source and External Links
Enhancing Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) for Use in Electric Steelmaking - Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) is the second most viable source of virgin iron for steelmaking after pig iron, produced by the direct reduction of iron ore using carbon monoxide and hydrogen, and is commonly used in electric arc furnace steelmaking especially in North America due to abundant natural gas.
Direct reduced iron - Wikipedia - DRI, also called sponge iron, is metallic iron produced by reducing iron ore in the solid state using reducing gases like carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures below iron's melting point, offering an energy-efficient alternative to blast furnace ironmaking and typically used in electric arc furnaces for steel production.
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) - Midrex Technologies, Inc. - DRI is a premium, high-iron-content metallic raw material made by removing oxygen from iron ore without melting, valued for low impurities and used in electric arc, blast, and basic oxygen furnaces; emerging green hydrogen-based DRI processes promise further decarbonization of steelmaking.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com