Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition through disassembly, cleaning, and part replacement, preserving original specifications and quality standards. Upcycling transforms discarded materials or products into new, often higher-value items without breaking them down to raw components, focusing on creativity and sustainability. Explore the distinct benefits and processes of remanufacturing versus upcycling to enhance your manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
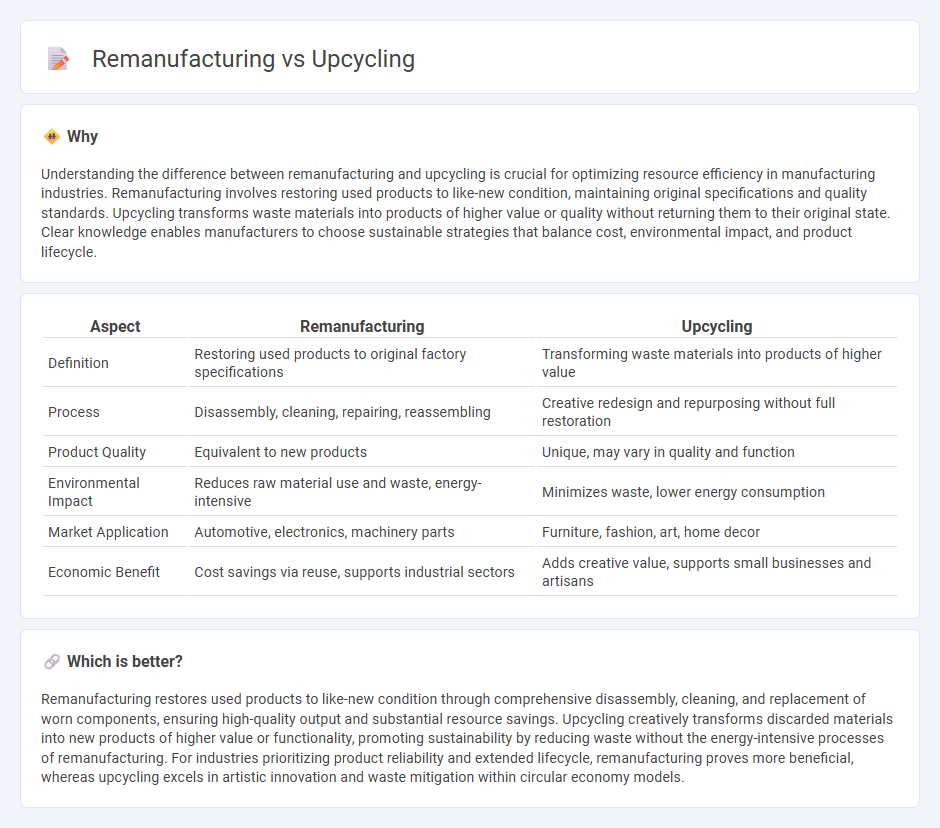
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and upcycling is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency in manufacturing industries. Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, maintaining original specifications and quality standards. Upcycling transforms waste materials into products of higher value or quality without returning them to their original state. Clear knowledge enables manufacturers to choose sustainable strategies that balance cost, environmental impact, and product lifecycle.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Upcycling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restoring used products to original factory specifications | Transforming waste materials into products of higher value |
| Process | Disassembly, cleaning, repairing, reassembling | Creative redesign and repurposing without full restoration |
| Product Quality | Equivalent to new products | Unique, may vary in quality and function |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces raw material use and waste, energy-intensive | Minimizes waste, lower energy consumption |
| Market Application | Automotive, electronics, machinery parts | Furniture, fashion, art, home decor |
| Economic Benefit | Cost savings via reuse, supports industrial sectors | Adds creative value, supports small businesses and artisans |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing restores used products to like-new condition through comprehensive disassembly, cleaning, and replacement of worn components, ensuring high-quality output and substantial resource savings. Upcycling creatively transforms discarded materials into new products of higher value or functionality, promoting sustainability by reducing waste without the energy-intensive processes of remanufacturing. For industries prioritizing product reliability and extended lifecycle, remanufacturing proves more beneficial, whereas upcycling excels in artistic innovation and waste mitigation within circular economy models.
Connection
Remanufacturing and upcycling both extend product life cycles by transforming used materials into valuable goods, reducing waste and resource consumption. Remanufacturing involves restoring products to original specifications using existing components, while upcycling creatively enhances materials to produce higher-value items. These sustainable practices contribute significantly to circular manufacturing by minimizing environmental impact and promoting resource efficiency.
Key Terms
Value Retention
Upcycling enhances value retention by transforming waste materials into new products with higher worth, fostering creativity and sustainability. Remanufacturing restores used products to original or better performance standards, preserving functional value and reducing resource consumption. Explore the detailed benefits and applications of upcycling and remanufacturing to maximize value retention in your projects.
Process Complexity
Upcycling involves creatively transforming waste materials into new products with higher value or quality, often requiring less intricate processing steps compared to remanufacturing. Remanufacturing entails systematically disassembling, restoring, and testing used products to meet original specifications, involving complex workflows including precise quality control and specialized machinery. Explore the detailed process nuances and environmental impacts to understand how each approach optimizes resource efficiency.
End-Use Quality
Upcycling transforms waste materials into new products with added value but may compromise consistent end-use quality due to varied input sources, while remanufacturing restores used products to meet original factory specifications, ensuring reliable performance and durability. Remanufactured goods typically undergo rigorous quality control, making them preferable for applications demanding high precision and safety. Explore the detailed differences in end-use quality to determine the best sustainable strategy for your needs.
Source and External Links
About Upcycling - Upcycling is the creative process of transforming waste materials into new objects that have higher value or functionality, giving them a second life without breaking them down as in recycling.
Upcycling - Wikipedia - Upcycling, also called creative reuse, means turning unwanted products into items of greater quality or value through rethinking, reforming, and rebirthing them, unlike recycling which breaks down materials to reuse.
65 Useful Upcycling Ideas for Beginners 2023 - Good Housekeeping - Upcycling reduces waste and pollution by creatively repurposing old items like furniture, jars, or t-shirts into functional or decorative objects, providing practical ways to embrace sustainability at home.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com