Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems to continuously monitor and control production processes, ensuring higher precision and reduced defects. Additive manufacturing builds objects layer-by-layer directly from digital models, allowing complex geometries and customization without extensive tooling. Explore the differences and benefits of each approach to enhance your manufacturing strategy.
Why it is important
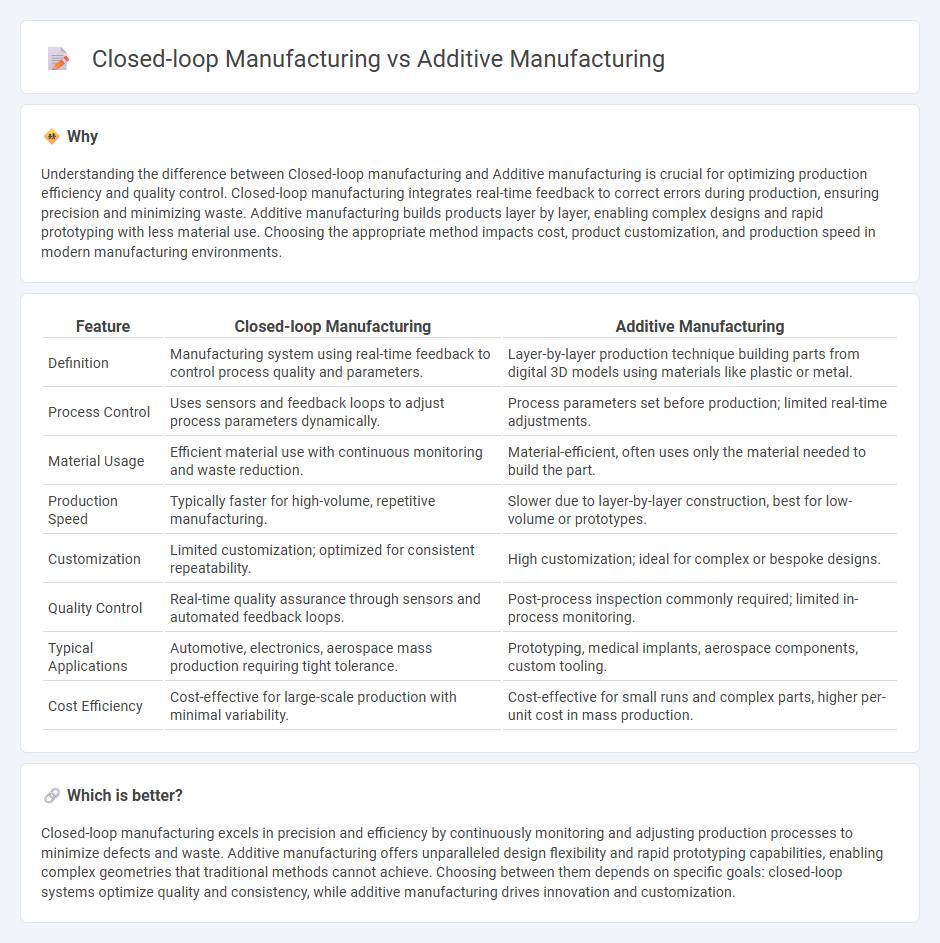
Understanding the difference between Closed-loop manufacturing and Additive manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and quality control. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback to correct errors during production, ensuring precision and minimizing waste. Additive manufacturing builds products layer by layer, enabling complex designs and rapid prototyping with less material use. Choosing the appropriate method impacts cost, product customization, and production speed in modern manufacturing environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Closed-loop Manufacturing | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturing system using real-time feedback to control process quality and parameters. | Layer-by-layer production technique building parts from digital 3D models using materials like plastic or metal. |
| Process Control | Uses sensors and feedback loops to adjust process parameters dynamically. | Process parameters set before production; limited real-time adjustments. |
| Material Usage | Efficient material use with continuous monitoring and waste reduction. | Material-efficient, often uses only the material needed to build the part. |
| Production Speed | Typically faster for high-volume, repetitive manufacturing. | Slower due to layer-by-layer construction, best for low-volume or prototypes. |
| Customization | Limited customization; optimized for consistent repeatability. | High customization; ideal for complex or bespoke designs. |
| Quality Control | Real-time quality assurance through sensors and automated feedback loops. | Post-process inspection commonly required; limited in-process monitoring. |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, electronics, aerospace mass production requiring tight tolerance. | Prototyping, medical implants, aerospace components, custom tooling. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large-scale production with minimal variability. | Cost-effective for small runs and complex parts, higher per-unit cost in mass production. |
Which is better?
Closed-loop manufacturing excels in precision and efficiency by continuously monitoring and adjusting production processes to minimize defects and waste. Additive manufacturing offers unparalleled design flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities, enabling complex geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve. Choosing between them depends on specific goals: closed-loop systems optimize quality and consistency, while additive manufacturing drives innovation and customization.
Connection
Closed-loop manufacturing integrates real-time feedback systems to continuously monitor and adjust production processes, enhancing precision and quality control. Additive manufacturing benefits from this approach by using data-driven adjustments to optimize layer deposition and material usage, reducing waste and improving structural integrity. The synergy between these methods drives efficiency and innovation in advanced manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Layer-by-layer fabrication (Additive manufacturing)
Additive manufacturing employs layer-by-layer fabrication to create complex geometries with high precision and minimal material waste by depositing successive layers of material, often using techniques like selective laser sintering or fused deposition modeling. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates continuous feedback control systems to optimize each layer's deposition in real time, enhancing accuracy and reducing defects during production. Discover how these advanced fabrication methods redefine manufacturing efficiency and quality.
Feedback control systems (Closed-loop manufacturing)
Feedback control systems in closed-loop manufacturing continuously monitor and adjust production parameters to enhance precision and reduce errors, unlike additive manufacturing which relies on predefined layering processes without real-time adjustment. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates sensors and real-time data analysis to optimize machine performance and product quality dynamically, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced material waste. Explore how feedback control systems revolutionize manufacturing processes and improve outcomes by visiting our detailed technical resource.
Process monitoring
Additive manufacturing relies heavily on in-situ sensors and real-time data acquisition to monitor layer deposition and ensure dimensional accuracy, reducing defects and material waste. Closed-loop manufacturing integrates advanced feedback control systems that continuously adjust process parameters such as temperature, laser power, or feed rate based on sensor data to maintain optimal production quality. Explore further to understand how state-of-the-art process monitoring technologies enhance precision and efficiency in both manufacturing methods.
Source and External Links
Additive manufacturing, explained | MIT Sloan - Additive manufacturing is the process of creating objects by building them up one layer at a time, typically using 3D printing technologies, and is the opposite of traditional subtractive manufacturing methods.
Additive manufacturing | NIST - Additive manufacturing uses digital design files to fabricate three-dimensional products layer by layer, enabling the production of complex parts with less waste compared to conventional manufacturing, and is increasingly used in industries like aerospace and biomedical engineering.
The 7 categories of Additive Manufacturing - Loughborough University - Additive manufacturing processes are classified into seven main categories, each with distinct methods and technologies, ranging from vat photopolymerization to binder jetting, and are standardized by ASTM F42.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com